

Apple, one of the most trusted technology brands in the world, recently faced a critical security exposure in its service ticket portal.
The vulnerability, discovered by a tech enthusiast while submitting a repair request uncovered severe flaws in Apple’s system that could have resulted in a massive breach of customer data.

This security issue originated from an Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) vulnerability. IDOR allows unauthorized users to gain access to sensitive information by simply manipulating parameters in service requests.
In this case, by altering certain inputs (like mobile numbers or user IDs) while interacting with the Apple service portal, the researcher was able to bypass authentication controls, exposing data that should have been off-limits.

What Was Exposed?
The scope of the vulnerability was alarming. Exploiting the flaw granted access to a wide range of sensitive information across the platform, including:
To make matters worse, the platform did not implement rate-limiting mechanisms, which meant attackers could automate requests to gather an extensive amount of customer data through brute-force attacks.
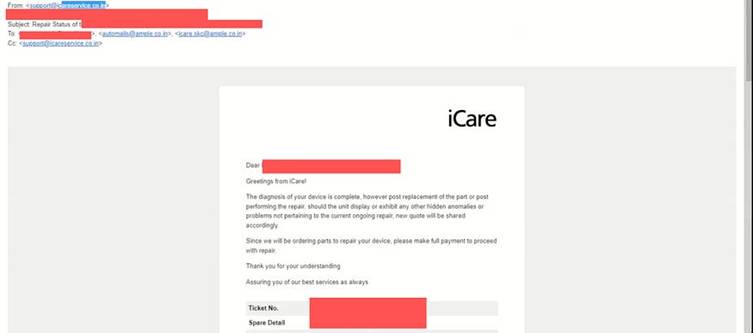
The vulnerability was discovered during a routine visit to an Apple service center.
The researcher scanned a QR code to submit a repair request for their MacBook. Out of curiosity, they decided to examine the portal’s security.
While analyzing the service request URL, the researcher noticed a modifiable parameter—their mobile number.
Simply changing the value in this field allowed them to access the details of other users, exposing a significant flaw in the portal’s authentication mechanism.
Potential Risks and Impact
Had malicious actors exploited this vulnerability, the consequences could have been devastating:
After responsibly disclosing the issue to Apple, the company quickly patched the vulnerability. This swift response prevented potential abuse of the flaw, safeguarding millions of customer records in their system.
This incident highlights the importance of robust security protocols, even for trusted companies like Apple.
While the vulnerability has been addressed, it serves as a reminder that no system is infallible. Companies must invest in stronger protections, including rate-limiting, user request validation, and regular vulnerability assessments.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links & Phishing Attacks With Threat Intelligence Lookup - Try for Free
A new project has exposed a critical attack vector that exploits protocol vulnerabilities to disrupt…
A threat actor known as #LongNight has reportedly put up for sale remote code execution…
Ivanti disclosed two critical vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428, affecting Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile…
Hackers are increasingly targeting macOS users with malicious clones of Ledger Live, the popular application…
The European Union has escalated its response to Russia’s ongoing campaign of hybrid threats, announcing…
Venice.ai has rapidly emerged as a disruptive force in the AI landscape, positioning itself as…