

Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a sophisticated exploitation campaign involving a zero-day (0-day) vulnerability in Cleo file transfer software platforms.
This campaign has been used to deliver a newly identified malware family, now dubbed “Malichus.”
The threat, recently analyzed by Huntress and corroborated by other industry vendors, demonstrates significant technical complexity, raising alarms across the cybersecurity community due to its potential implications for organizations relying on Cleo technologies for secure file exchange.

Cleo, often used for enterprise data transfer and integration, was targeted by attackers who leveraged a previously unknown vulnerability to compromise systems.
The exploitation of this 0-day allows attackers to deploy Malichus, a modular malware framework with advanced capabilities aimed at exfiltration, reconnaissance, and post-exploitation operations.
2024 MITRE ATT&CK Evaluation Results for SMEs & MSPs -> Download Free Guide
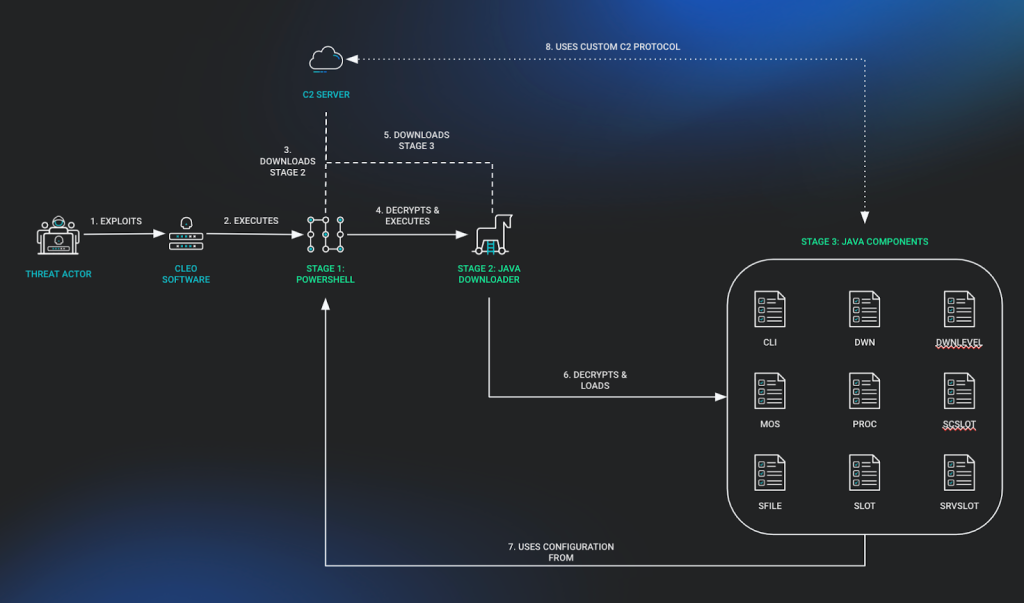
The name “Malichus” references Malichus I, a historical adversary of Cleopatra known for his calculated acts of revenge, fitting the malware’s destructive and strategic nature. The attack follows a multi-stage process:
Each stage utilizes bespoke techniques to avoid detection, evade analysis, and maximize system control.
The Malichus malware family is characterized by a three-stage deployment process, each carefully designed to establish reliable command-and-control (C2) communication, maintain persistence, and enable a wide range of malicious activities.
The initial stage uses a small PowerShell script that acts as a loader. This script is obfuscated using Base64 encoding and functions to:
This stage ensures the swift setup of the host for further exploitation while staying lightweight to evade endpoint detection systems.
The second stage involves a Java-based downloader that is responsible for retrieving the final payload. This downloader:
The implementation of custom routines, such as environment variable parsing and encrypted C2 communication, displays the malware authors’ attention to stealth and adaptability.
The final stage is a Java-based framework comprising nine distinct class files, delivering comprehensive functionality for the attacker’s objectives. Key components of this framework include:
The modular design and expansive feature set of Malichus indicate a tailored approach to targeting organizations using Cleo software, particularly those in industries where secure file transfer and business integration are critical.
By leveraging its understanding of Cleo’s configuration structure, the malware can:
Of particular concern is the adaptability of Malichus. Its multi-platform support (Windows and Linux), dynamic C2 handling, and encrypted packet protocols make detection and mitigation challenging for standard cybersecurity defenses.
The Cleo 0-day vulnerability exploited to deploy Malichus malware highlights the ever-evolving tactics of cybercriminals in targeting critical business systems.
Malichus represents a sophisticated and focused attack that warrants immediate attention from organizations relying on Cleo software.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links, Malware & Phishing Attacks With ANY.RUN – Try for Free
A startling discovery by BeyondTrust researchers has unveiled a critical vulnerability in Microsoft Entra ID…
The Cofense Phishing Defense Center has uncovered a highly strategic phishing campaign that leverages Google…
Cybersecurity researchers from Trustwave’s Threat Intelligence Team have uncovered a large-scale phishing campaign orchestrated by…
Cisco Talos has uncovered a series of malicious threats masquerading as legitimate AI tool installers,…
Pure Crypter, a well-known malware-as-a-service (MaaS) loader, has been recognized as a crucial tool for…
A recent discovery by security researchers at BeyondTrust has revealed a critical, yet by-design, security…