

Concerning a development for organizations leveraging Apache’s big-data solutions, a new variant of the Lucifer DDoS botnet malware targeting Apache Hadoop and Apache Druid servers has been identified.
This sophisticated malware campaign exploits existing vulnerabilities and misconfigurations within these systems to execute malicious activities, including cryptojacking and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
Live attack simulation Webinar demonstrates various ways in which account takeover can happen and practices to protect your websites and APIs against ATO attacks .
The Lucifer malware targets misconfigurations and known vulnerabilities within Apache Hadoop and Apache Druid environments, according to the Aquasec report.
One of the critical vulnerabilities exploited is CVE-2021-25646, a command injection vulnerability in Apache Druid that allows authenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code.

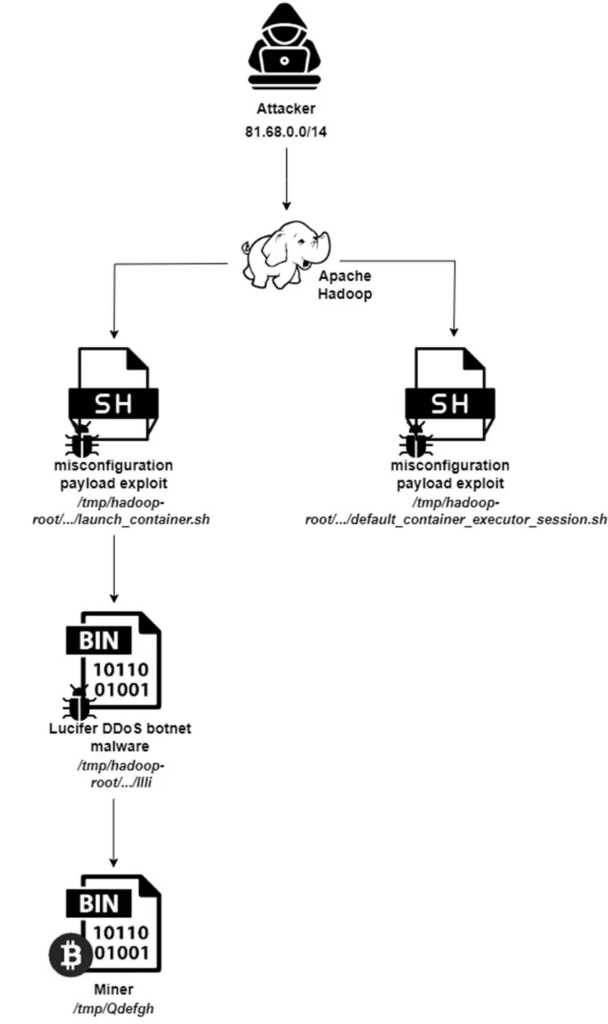
By exploiting these weaknesses, attackers gain unauthorized access to the systems, enabling them to carry out their nefarious activities.
Combining cryptojacking and DDoS capabilities, its hybrid nature sets the Lucifer malware apart.
Once the malware gains a foothold, it transforms vulnerable Linux servers into Monero cryptomining bots.
Additionally, the malware can initiate DDoS attacks, further compromising the integrity and availability of the targeted servers.
The emergence of the Lucifer malware targeting Apache’s big-data stack serves as a stark reminder of the ever-present cyber threats facing organizations.
With over 3,000 unique attacks detected in just the past month, the urgency for heightened security measures cannot be overstated.
Organizations must proactively scan their environments for vulnerabilities, apply necessary patches, and employ runtime detection to identify and thwart unknown threats.
As the cyber threat landscape evolves, staying informed and vigilant is paramount.
The Lucifer DDoS botnet malware campaign targeting Apache Hadoop and Apache Druid servers exemplifies attackers’ sophisticated tactics to exploit vulnerabilities and misconfigurations for malicious gain.
Organizations can safeguard their critical infrastructure against such insidious threats by adopting comprehensive security strategies.
You can block malware, including Trojans, ransomware, spyware, rootkits, worms, and zero-day exploits, with Perimeter81 malware protection. All are extremely harmful, can wreak havoc, and damage your network.
Stay updated on Cybersecurity news, Whitepapers, and Infographics. Follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter.
SonicWall has issued an urgent advisory (SNWLID-2025-0009) warning of a high-severity vulnerability in its SSLVPN…
A sweeping wave of suspicious online activity is putting organizations on alert as hackers ramp…
Blue Shield of California has disclosed a significant data privacy incident affecting up to 4.7…
Microsoft has launched a new bounty program that offers up to $30,000 to security researchers…
Despite billions spent annually on cybersecurity technology, organizations continue to experience breaches with alarming frequency.…
WhatsApp, the world’s leading messaging platform, has unveiled a major privacy upgrade called "Advanced Chat…