

Google has announced the launch of OSV-Scanner V2, an open-source tool designed to enhance vulnerability scanning and remediation across various software ecosystems.
This update follows the recent release of OSV-SCALIBR, another powerful tool in the OSV suite, which together form a comprehensive platform for managing vulnerability metadata and streamlining vulnerability detection and management.

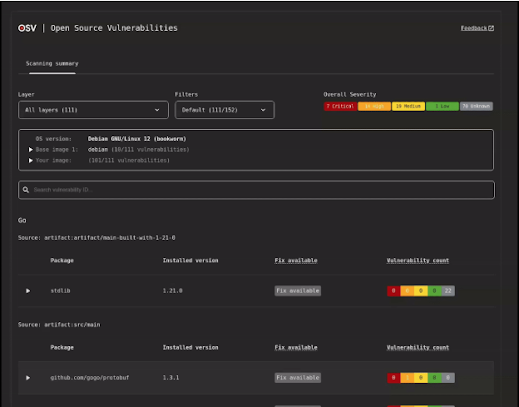
Google has outlined several plans for future developments:
Users can engage with OSV-Scanner V2 by visiting the OSV-Scanner or OSV-SCALIBR repositories.
Google encourages contributions via these repositories and invites feedback through the OSV discussion list at osv-discuss@google.com.
This initiative marks a significant step towards open collaboration in cybersecurity, making it easier for developers and security teams to identify and manage vulnerabilities efficiently.
As the technology landscape continues to evolve, tools like OSV-Scanner V2 are crucial for maintaining the integrity of software systems and fostering a more secure digital environment.
With its robust features and collaborative development approach, OSV-Scanner is poised to become an essential tool in the fight against cyber threats.
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams? – Analyse Malware Incidents & get live Access with ANY.RUN -> Start Now for Free.
Enterprises and managed service providers globally are now facing urgent security concerns following the disclosure…
Security researcher Alessandro Sgreccia (aka "rainpwn") has revealed a set of critical vulnerabilities in Zyxel’s…
A high-severity denial-of-service (DoS) vulnerability in Redis, tracked as CVE-2025-21605, allows unauthenticated attackers to crash servers…
Google’s Mandiant team has released its M-Trends 2025 report, highlighting the increasing sophistication of threat…
A critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, identified as CVE-2025-3248 with a CVSS score of…
GitLab, a leading DevOps platform, has released a critical security patch impacting both its Community…