

Cybersecurity researchers from SafeBreach Labs have revealed new vulnerabilities in Google’s Quick Share file-transfer utility for Windows, including a critical flaw that allows attackers to execute code on targeted devices.
The findings, disclosed this week, highlight risks in the widely used tool—even after Google patched earlier issues reported in 2024.
Initially presented at DEF CON 32 (2024), the “QuickShell” research exposed 10 vulnerabilities in Quick Share, a cross-platform tool for transferring files between Android, Windows, and ChromeOS devices.
The utility employs Bluetooth, Wi-Fi Direct, and other protocols to enable peer-to-peer sharing.

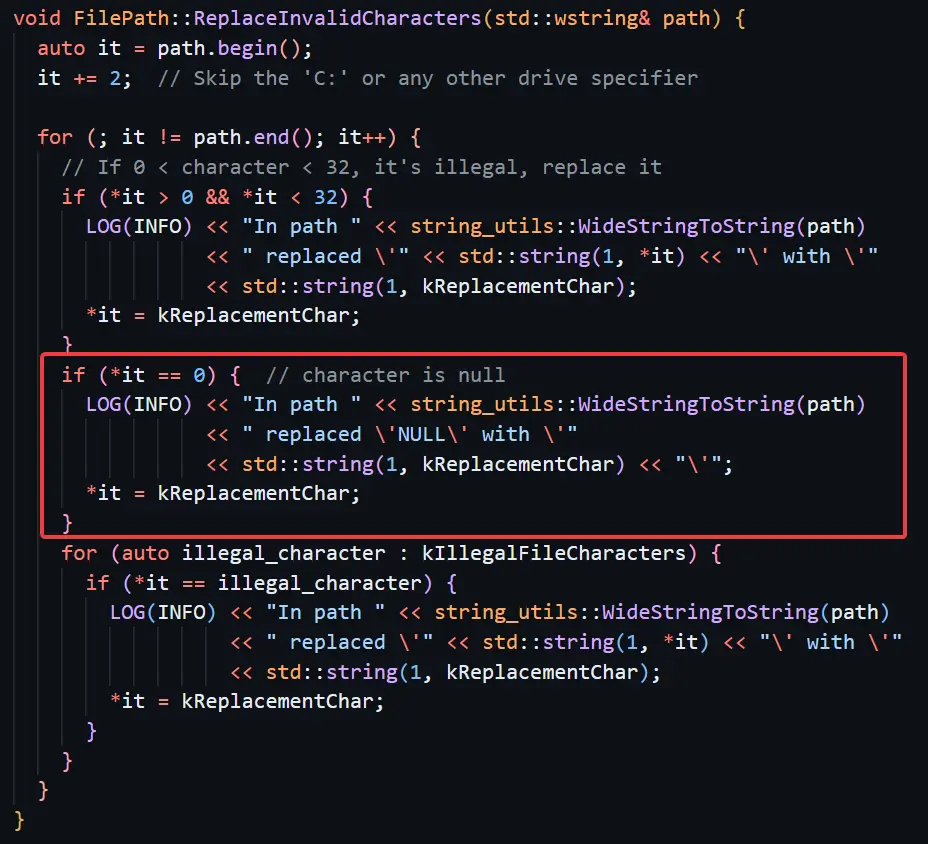
Researchers Shir Tamari and Shmuel Cohen discovered that attackers could chain these flaws to achieve remote code execution (RCE) on Windows systems, enabling full device takeover.
Key weaknesses included:
Google addressed these flaws in early 2024, but follow-up tests revealed gaps in the fixes.
In August 2024, SafeBreach researchers revisited the patched vulnerabilities and identified two critical oversights:
Google addressed the new flaws in late 2024, assigning CVE-2024-10668 to the file-write bypass. Patches have been rolled out via automatic updates.
“This case underscores the challenges of securing complex, protocol-diverse applications,” said Tamari. “While Google responded swiftly, layered defenses and rigorous patch verification are essential.”
Quick Ship pre-installs on newer Windows PCs amplify risks. Users are urged to:
The findings highlight broader lessons for multi-protocol software—particularly tools bridging mobile and desktop ecosystems. As Tamari noted, “Attackers will always seek gaps in logic. Defenders must think like them.”
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, & X to Get Instant Updates!
Verizon Business's 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR), released on April 24, 2025, paints a…
A recent cyber espionage campaign by the notorious Lazarus Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group, tracked…
In a alarming cybersecurity breach uncovered by Cisco Talos in 2023, a critical infrastructure enterprise…
In a startling revelation from Microsoft Threat Intelligence, threat actors are increasingly targeting unsecured Kubernetes…
A recently uncovered cyberattack campaign has brought steganography back into the spotlight, showcasing the creative…
Threat actors exploited a zero-day vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure, identified as CVE-2025-0282, to deploy…