

The Microsoft Threat Intelligence Center (MSTIC) has uncovered an ongoing and sophisticated phishing campaign leveraging Microsoft Teams invites to gain unauthorized access to user accounts and sensitive data.
The campaign, attributed to a threat actor known as Storm-2372, has been active since August 2024 and has targeted a wide range of industries, including government, defense, healthcare, technology, and energy in Europe, North America, Africa, and the Middle East.
Storm-2372’s method involves device code phishing, a technique wherein the threat actor uses fake meeting invitations to trick users into providing authentication tokens.

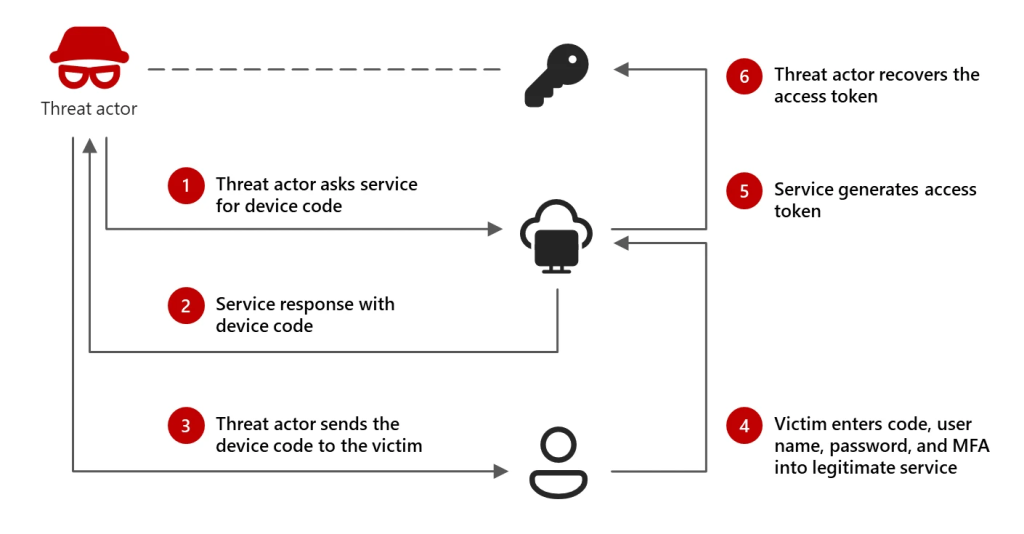
Upon receiving an invite, unsuspecting users are redirected to a legitimate authentication page and prompted to enter a device code generated by the attacker.
The stolen tokens allow the attacker to access the victim’s accounts without requiring a password, granting access to sensitive emails, cloud storage, and other services.

Once the initial breach occurs, Storm-2372 is observed moving laterally within compromised networks by sending further phishing emails from victim accounts.
The attacker has also exploited Microsoft’s Graph API to search for sensitive information, exfiltrating data using keywords such as “password,” “admin,” and “credentials.”
Recent updates to the group’s tactics include the use of the Microsoft Authentication Broker client ID to register actor-controlled devices, enabling persistent access and further escalation.
Microsoft has linked Storm-2372 to Russian state interests due to its targeting patterns and tradecraft.
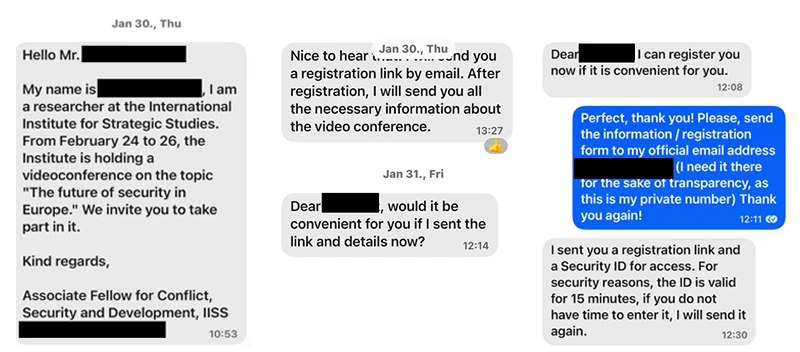
The campaign shows the actor leveraging popular third-party messaging apps, including WhatsApp and Signal, to pose as notable individuals and build trust with targets before delivering phishing invites.
To mitigate risks, Microsoft advises organizations to implement strict security measures, such as restricting device enrollment permissions, monitoring anomalous token activity, and reinforcing employee awareness about phishing techniques.
Microsoft is also actively notifying affected customers to secure their environments.
This incident underscores the evolving sophistication of phishing campaigns and the critical need for businesses to harden their defenses against such exploits.
With attacks such as these, vigilance and proactive security measures remain paramount in safeguarding sensitive data and infrastructure.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links & Phishing Attacks With Threat Intelligence Lookup - Try for Free
Brinker, an innovative narrative intelligence platform dedicated to combating disinformation and influence campaigns, has been…
A recent investigation by cybersecurity researchers has uncovered a large-scale malware campaign leveraging the DeepSeek…
A recent malware campaign has been observed targeting the First Ukrainian International Bank (PUMB), utilizing…
A newly discovered malware, dubbed Trojan.Arcanum, is targeting enthusiasts of tarot, astrology, and other esoteric…
A sophisticated phishing campaign orchestrated by a Russian-speaking threat actor has been uncovered, revealing the…
A sophisticated malware campaign has compromised over 1,500 PostgreSQL servers, leveraging fileless techniques to deploy…