

Threat actors are increasingly targeting Node.js—a staple tool for modern web developers—to launch sophisticated malware campaigns aimed at data theft and system compromise.
Microsoft Defender Experts (DEX) have reported a spike in such attacks since October 2024, especially focusing on malvertising and deceptive software installers.
Node.js is an open-source JavaScript runtime, trusted for its flexibility building both front- and back-end applications.
Unfortunately, the very characteristics that make Node.js a favorite among developers—cross-platform compatibility, command-line script execution, and seamless integration—are also appealing to cybercriminals.

Attackers are blending malicious Node.js scripts with legitimate applications, sidestepping conventional security measures.
While Python, PHP, and other scripting languages remain widely abused, the uptake of Node.js in malware delivery marks a significant shift in attacker tactics.
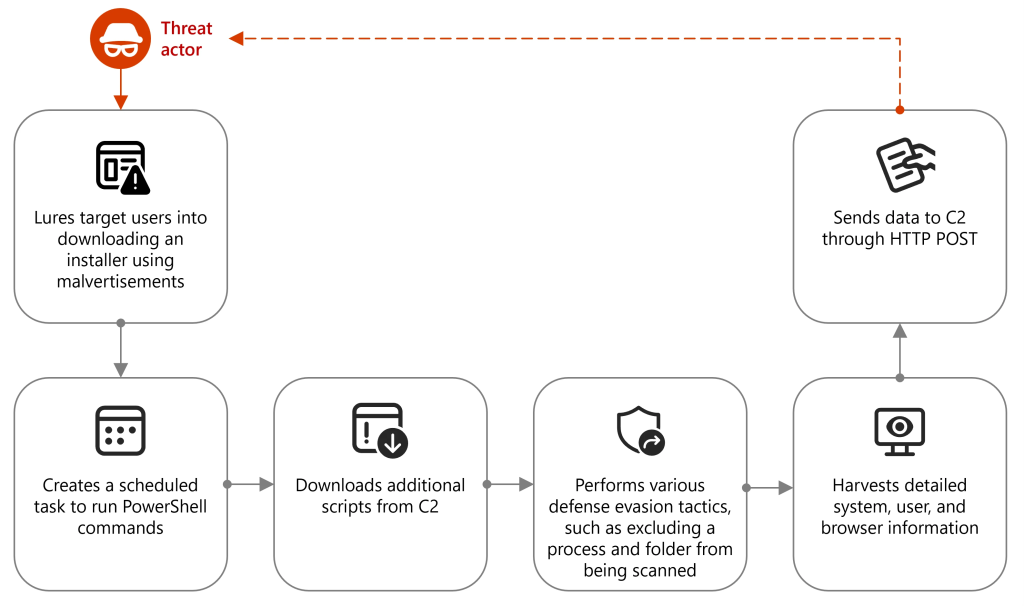
A notable ongoing threat involves a malvertising campaign targeting cryptocurrency enthusiasts. It entices users to visit fraudulent sites via seemingly legitimate ads, then lures them into downloading a fake installer.
This installer, typically disguised as cryptocurrency trading software, contains a malicious DLL that sets up persistence on the victim’s machine via scheduled tasks and PowerShell commands.
Once active, the malware excludes itself from Windows Defender scans, collects detailed system and user data—including BIOS, OS version, network adapters, and even browser credentials—and transmits this information to a command-and-control (C2) server controlled by the attackers.
After gathering and exfiltrating data, the attackers deliver a secondary payload: an archive containing Node.js (node.exe), a compiled JavaScript file (JSC), and supporting modules.
The malicious JavaScript is executed, launching routines that may steal further credentials, install additional malware, or set up persistent remote access.
Beyond packaged executables, attackers are also leveraging Node.js for inline JavaScript execution. In some cases, attackers trick users into running PowerShell commands that download Node.js and immediately execute JavaScript code.
This code maps corporate networks, identifies high-value assets, and disguises outbound traffic as legitimate, making detection even harder.
Security experts urge organizations to:
With Node.js malware techniques growing in sophistication and frequency, vigilance and proactive defense are essential for safeguarding sensitive information in today’s evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, & X to Get Instant Updates!
A new project has exposed a critical attack vector that exploits protocol vulnerabilities to disrupt…
A threat actor known as #LongNight has reportedly put up for sale remote code execution…
Ivanti disclosed two critical vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428, affecting Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile…
Hackers are increasingly targeting macOS users with malicious clones of Ledger Live, the popular application…
The European Union has escalated its response to Russia’s ongoing campaign of hybrid threats, announcing…
Venice.ai has rapidly emerged as a disruptive force in the AI landscape, positioning itself as…