

Cybersecurity researchers have unveiled an advanced technique to uncover hackers’ operational infrastructure using passive DNS data.
This groundbreaking method sheds light on how attackers establish and maintain their networks to perpetrate malicious activities while remaining resilient to detection.
By leveraging passive DNS analysis, experts have made significant strides in identifying threats before they wreak havoc, thus fortifying defenses against evolving cyber threats.
The backbone of any cyberattack lies in its infrastructure, which consists of servers, domains, and compromised devices. Attackers employ various tactics to maintain their operations while evading detection.
A popular method is infrastructure churn, where hackers frequently change domains and IPs when one server is detected and blocked. This differs from DNS fast flux, which involves rapid, automated IP rotation for a single domain.
Leveraging 2024 MITRE ATT&CK Results for SME & MSP Cybersecurity Leaders – Attend Free Webinar
For example, the CatDDoS botnet, an evolution of the infamous Mirai malware, exemplifies infrastructure churn.

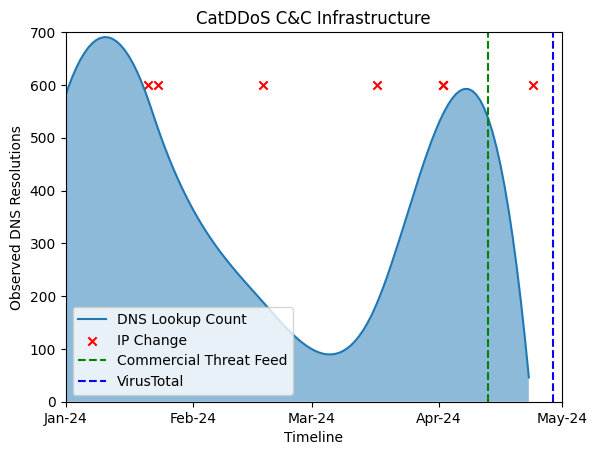
It uses alternative domain systems, such as OpenNIC domains, alongside sophisticated payload encryption techniques like ChaCha20.
Over six months, researchers observed frequent changes in the botnet’s command-and-control (C&C) server infrastructure, making traditional detection strategies ineffective.
How Passive DNS Works
Passive DNS is a core tool for uncovering malicious networks. It involves collecting and analyzing DNS logs from network transit paths, without actively querying domains.
This historical data includes records of domain-IP relationships, timestamps, and query counts, allowing researchers to map out how attackers operate.
For instance, passive DNS sensors can be deployed across diverse network paths like enterprise, government, or residential environments.
Even a single DNS query from a malicious domain can reveal connections to other suspicious domains or servers. Researchers meticulously clean this data to remove noise (e.g., queries from legitimate websites or content delivery networks).
Juniper Threat Labs has effectively used passive DNS data to identify malicious infrastructure before attacks unfold. One standout case involved the discovery of threat actors abusing Cloudflare’s tunneling service to deliver remote access trojans (RATs).
Cybercriminals used phishing emails to infect victims with trojans like XWorm, AsyncRAT, and VenomRAT, which then exfiltrated sensitive data.
Key Discoveries
For example, a campaign active between July and August 2024 revealed that attackers created up to three new domains every 10 days to bypass detection.
Passive DNS sensors were instrumental in uncovering these domains, highlighting their growing query counts and suspicious domain-IP associations.
The proactive use of passive DNS gives cybersecurity teams a distinct advantage. By identifying zero-day infrastructure earlier, researchers can include these domains in blocklists before attackers deploy them at full scale.
This forces hackers to continuously invest in new resources, increasing their operational costs and reducing profitability.
Additionally, passive DNS data enables security providers to strengthen their threat intelligence feeds, benefiting organizations subscribed to advanced defense solutions.
For instance, Juniper’s customers received updated SecIntel feeds that blocked newly identified malicious domains and IPs.
Cybersecurity experts caution that while passive DNS is powerful, its efficacy depends on the quality of data and sensor placement. However, its benefits in increasing attacker costs and reducing the success of cyber campaigns are undeniable.
This technique not only provides visibility into emerging threats but also equips organizations with the tools to stay one step ahead in the ever-changing landscape of cyber warfare.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links,Malware & Phishing Attacks With ANY.RUN - Try for Free
A startling discovery by BeyondTrust researchers has unveiled a critical vulnerability in Microsoft Entra ID…
The Cofense Phishing Defense Center has uncovered a highly strategic phishing campaign that leverages Google…
Cybersecurity researchers from Trustwave’s Threat Intelligence Team have uncovered a large-scale phishing campaign orchestrated by…
Cisco Talos has uncovered a series of malicious threats masquerading as legitimate AI tool installers,…
Pure Crypter, a well-known malware-as-a-service (MaaS) loader, has been recognized as a crucial tool for…
A recent discovery by security researchers at BeyondTrust has revealed a critical, yet by-design, security…