

A new security vulnerability targeting Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) has emerged, exposing organizations and users to potential exploitation.
Dubbed the “whoAMI name confusion attack,” this flaw allows attackers to publish malicious virtual machine images under misleading names, tricking unsuspecting users into deploying them within their Amazon Web Services (AWS) infrastructure.
Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) are pre-configured virtual machine templates used to launch EC2 instances in AWS.


While AMIs can be private, public, or purchased through the AWS Marketplace, users often rely on AWS’s search functionality via the ec2:DescribeImages API to find the most recent AMIs for specific operating systems or configurations.
However, if users or organizations fail to apply specific security measures, such as specifying trusted “owners” during the AMI search process, they may inadvertently use an unverified or malicious image.

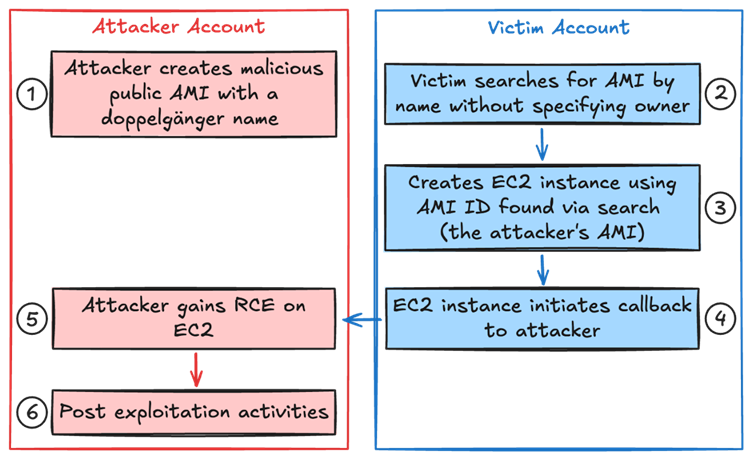
This vulnerability, classified as a name confusion attack, exploits situations where organizations rely on AMI names or patterns without verifying the image’s source or owner, as per a report by Data Dog Security Labs.
By publishing a malicious AMI with a name resembling legitimate ones (e.g., matching patterns such as “ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-*”), attackers can ensure their AMI appears as the “latest” in search results.
Once deployed, these malicious AMIs can act as backdoors, exfiltrating sensitive data or enabling unauthorized access to systems.
In one reported instance, researchers demonstrated the attack by creating a malicious AMI named “ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-whoAMI” that mimicked legitimate resources.
This malicious AMI was successfully retrieved and used by vulnerable configurations.
The vulnerability arises due to a misconfiguration in how AMI searches are performed.
For example, using the following Terraform code for AMI retrieval can result in vulnerabilities if the “owners” attribute is omitted:
data "aws_ami" "ubuntu" {
most_recent = true
filter {
name = "name"
values = ["ubuntu/images/hvm-ssd/ubuntu-focal-20.04-amd64-server-*"]
}
}This configuration results in Terraform querying the ec2:DescribeImages API, returning a list of all AMIs matching the search criteria—including those from untrusted or malicious sources.
If the most_recent=true attribute is applied, Terraform automatically selects the newest AMI, which could be an attacker’s malicious resource.
Attackers can exploit this by publishing public AMIs with names that include keywords like “amzn”, “ubuntu”, or other well-known patterns, ensuring that their AMI is selected by automated or human-driven searches.
Once selected, the malicious AMI can include backdoors, malware, or other harmful elements, making it a serious threat to cloud security.
Mitigation and Prevention
aws ec2 describe-images \
--filters "Name=name,Values=amzn2-ami-hvm-*-x86_64-gp2" \
--owners "137112412989"rules:
- id: missing-owners-in-aws-ami
languages:
- terraform
patterns:
- pattern: |
data "aws_ami" $NAME {
...
most_recent = true
}
- pattern-not: |
owners = $OWNERSAWS has acknowledged the potential impact of this vulnerability and has worked with researchers to address it.
According to their statement, the affected systems within AWS environments were non-production and had no customer data exposure.
In addition, AWS introduced the Allowed AMIs feature to mitigate such risks and encouraged customers to implement this guardrail.
The “whoAMI” vulnerability underscores the critical need for secure configurations and due diligence when operating in cloud environments.
Organizations must adopt secure practices, such as validating AMI ownership during searches and leveraging AWS’s new security features.
With thousands of accounts potentially affected, maintaining vigilance is essential to protecting sensitive workloads and data on AWS.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links & Phishing Attacks With Threat Intelligence Lookup - Try for Free
A new project has exposed a critical attack vector that exploits protocol vulnerabilities to disrupt…
A threat actor known as #LongNight has reportedly put up for sale remote code execution…
Ivanti disclosed two critical vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428, affecting Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile…
Hackers are increasingly targeting macOS users with malicious clones of Ledger Live, the popular application…
The European Union has escalated its response to Russia’s ongoing campaign of hybrid threats, announcing…
Venice.ai has rapidly emerged as a disruptive force in the AI landscape, positioning itself as…