Netskope Threat Labs uncovered a sprawling phishing operation involving 260 domains hosting approximately 5,000 malicious PDF files.
These documents, disguised as legitimate resources, employ fake CAPTCHA prompts to redirect victims to phishing sites designed to harvest credit card details and personal information.
The campaign, active since the second half of 2024, has impacted over 1,150 organizations and 7,000 users globally, with a focus on technology, financial services, and manufacturing sectors in North America, Asia, and Southern Europe.
Campaign Overview: SEO Poisoning and Fake CAPTCHA Threats
Attackers leveraged search engine optimization (SEO) poisoning to ensure malicious PDFs appear prominently in search results for common queries.
By embedding fake CAPTCHA images—hosted on platforms like Webflow’s content delivery network (CDN)—into PDFs, victims are lured into interacting with what appears to be a verification step.
Clicking the CAPTCHA redirects users to phishing pages mimicking trusted brands, where they are prompted to enter payment details or login credentials.
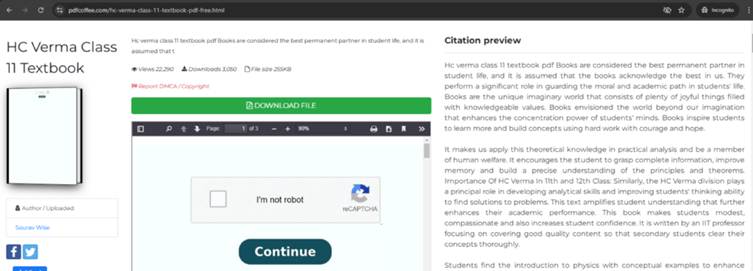
Netskope’s analysis revealed that 40% of the malicious PDFs target users seeking user manuals or technical guides, while 35% pose as templates for invoices, tax forms, or legal agreements.
Keywords such as “free,” “downloadable,” and “printable” were systematically embedded to exploit victims searching for time-sensitive resources.
Notably, attackers expanded their reach by uploading PDFs to repositories like PDFCoffee, PDF4Pro, and the Internet Archive, capitalizing on these platforms’ inherent trustworthiness.
Infrastructure and Domain Exploitation
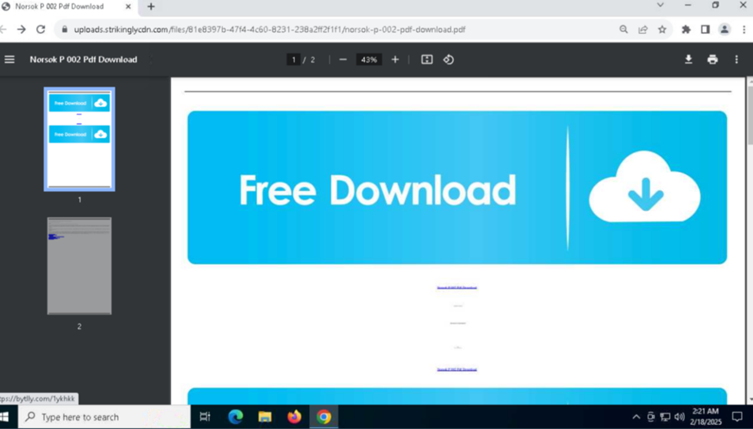
Webflow’s CDN emerged as the most abused platform, hosting 22% of the malicious PDFs.
However, the campaign diversified across multiple content delivery networks, including GoDaddy-associated domains (wsimg.com, s123-cdn-static.com), Strikingly, Wix, and Fastly.

This multi-platform approach complicates detection, as fraudulent content blends with legitimate traffic on widely used services.
Researchers identified three distinct phishing strategies:
- Direct Financial Theft: PDFs prompting immediate credit card entry under pretenses like “document access fees” or “membership verification.”
- Credential Harvesting: Fake login portals for cloud services (e.g., Microsoft 365, Google Workspace) linked directly from PDF buttons.
- Malware Delivery: A subset of PDFs used fake CAPTCHAs to trigger PowerShell-based malware downloads, notably the Lumma Stealer.
Lumma Stealer’s Role in the Attack Chain
While most PDFs focused on financial scams, 8% served as entry points for Lumma Stealer, an infostealer capable of extracting browser passwords, cryptocurrency wallets, and session cookies.

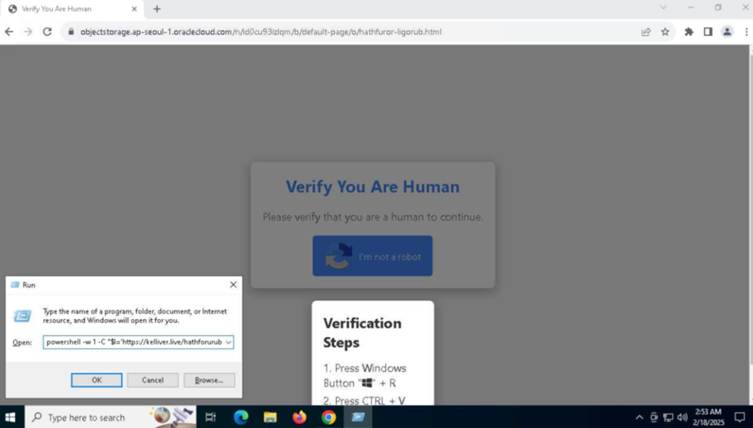
The infection chain begins when a victim clicks a “Download” button embedded in the PDF, redirecting them to a page instructing them to paste a PowerShell command into the Run dialog.
The command utilizes MSHTA (Microsoft HTML Application Host) to fetch a script from a compromised WordPress site, which then downloads and executes Lumma Stealer.
Attackers deliberately used PowerShell v1.0—a legacy version often exempt from modern security monitoring—to evade detection.
This technique mirrors tactics observed in Q4 2024 campaigns, suggesting the involvement of experienced threat actors familiar with endpoint security gaps.
Sector-Specific Targeting and Global Impact
The technology sector accounted for 34% of attacks, with threat actors exploiting the frequent need for technical documentation among IT professionals.
Financial services (27%) and manufacturing (19%) followed, likely due to their reliance on template-driven processes like procurement and compliance.
Geographically, the U.S. (42%), India (18%), and Italy (12%) saw the highest concentration of incidents, aligning with regions where the targeted industries dominate economic activity.
Mitigation Challenges and Recommendations
Netskope emphasized the difficulty in combating SEO-powered phishing, as takedowns of one domain often lead to rapid re-emergence on others.
The use of reputable CDNs further complicates blacklisting, as security teams risk blocking legitimate services. To counter these threats, organizations are advised to:
- Deploy advanced URL filtering that analyzes page content in real-time, rather than relying solely on domain reputation.
- Restrict PowerShell execution to signed scripts and monitor for legacy version usage.
- Educate employees on identifying “too good to be true” PDF resources, particularly those requiring CAPTCHAs for access.
This campaign underscores the evolving sophistication of phishing operations, where attackers blend traditional social engineering with infrastructure agility.
As Netskope Threat Labs continues to monitor the threat landscape, the discovery highlights the critical need for layered defenses combining AI-driven threat detection, strict endpoint policies, and cross-sector threat intelligence sharing.
With attackers increasingly abusing trusted platforms, proactive security measures must extend beyond the network perimeter to include user education and behavioral analytics.
Collect Threat Intelligence on the Latest Malware and Phishing Attacks with ANY.RUN TI Lookup -> Try for free



