A newly developed remote administration tool (RAT) named “Sakura RAT” has been released on GitHub, raising alarms for its powerful capabilities and ability to bypass modern detection systems like antivirus (AV) software and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools.
Tagged as a tool for malware analysts and security researchers, its release has sparked debate over its potential misuse by cybercriminals.
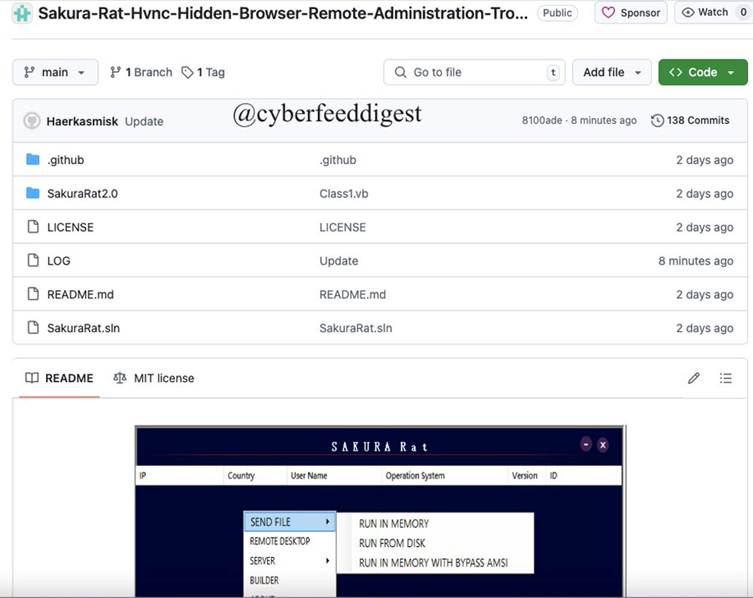
What is Sakura RAT?
Sakura RAT is an advanced remote administration tool bundled with several potent features that make it exceptionally stealthy and effective.
According to its GitHub description, the tool provides full system control, hidden browsing capabilities, and hidden virtual network computing (HVNC) functionality, allowing attackers to remotely access a victim’s machine without generating alerts.
Here are some key features of Sakura RAT:
- Hidden Browser: Enables attackers to browse the web through a victim’s machine, leaving no traceable signs of activity.
- HVNC: Offers stealthy, hidden desktop access that operates without triggering security alarms.
- Fileless Execution: Executes payloads directly in memory, sidestepping traditional file-based detection by antivirus programs.
- Multi-Session Control: Allows attackers to manage multiple infected systems simultaneously, making it suitable for larger campaigns.
- Anti-Detection Mechanisms: Designed to bypass antivirus and EDR tools, utilizing obfuscation and other stealth tactics.
- Broad Compatibility: Offers native support across various Windows platforms, ensuring widespread usability.
A Tool for Research or a Cybercrime Weapon
Sakura RAT is marketed as a tool for malware analysts and cybersecurity professionals to study modern attacks.
However, critics argue that its open availability on GitHub makes it a double-edged sword, easily exploitable by malicious actors for nefarious activities.
Cybercrime groups seeking stealthy tools for data exfiltration, ransomware attacks, or covert surveillance could potentially weaponize this release.
The availability of such advanced tools to bypass detection systems poses significant challenges for defenders.
With its fileless execution feature and anti-detection capabilities, even advanced AV and EDR products may struggle to identify and neutralize it.
Cybersecurity experts are urging GitHub to remove the repository to prevent potential misuse, though the code has likely already been cloned or redistributed by interested parties.
Professionals are also calling for enhanced heuristics and behavioral detection systems to mitigate the risks posed by such sophisticated RATs.
Meanwhile, organizations are encouraged to strengthen endpoint monitoring, implement robust access controls, and educate employees about phishing schemes to reduce the likelihood of initial infection.
The Sakura RAT release highlights the ongoing tension between ethical research and the risk of abuse in cybersecurity.
While tools like this can advance defensive research, they also underscore the importance of continued vigilance against evolving threats.
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, & X to Get Instant Updates!



.png
)
