Researchers uncovered a new covert channel to steal sensitive information from Air-gapped systems over the air from a distance of 2m.
The ‘air-gap’ computers are physically isolated from a network or device from external networks such as the Internet.

The air-gapped computers are maintained in banking, stock exchange networks, critical infrastructure, life-critical systems, and medical equipment.
COVID-bit Secret Channel to Exfiltrate Data
Researchers from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel, uncovered a new unique covert channel that let attackers leak data from air-gapped systems.
The attack method leverages the malware already planted on the isolated computer with the help of an insider or through other mediums.
In this attack model, the attacker must compromise the targeted system and infect or maintain electronic devices such as radio receivers, microphones, and optical cameras.
The malware on the air-gapped computer generates radio waves by executing crafted code on the target system and exploiting the power consumption of computers the malware is able to generate low-frequency electromagnetic radiation.
Notably, the attack is highly evasive since it executes from an ordinary user-level process, does not require root privileges, and is effective even within a Virtual Machine(VM).
By using the Radio signals sensitive information such as files, encryption keys, biometric data, and keylogging can be modulated and leaked.
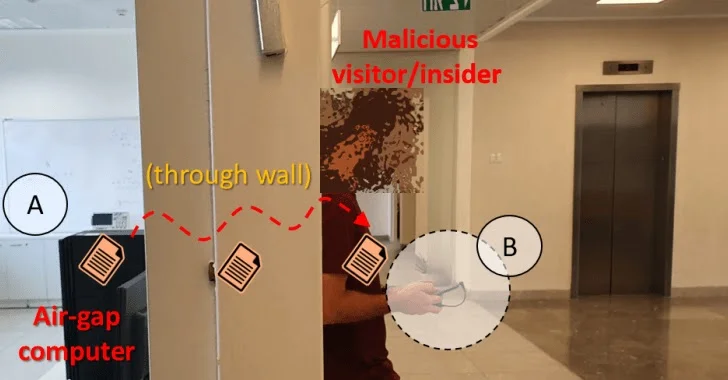
“Attack scenario (‘insider’): malware within the infected air-gapped computer (A) transmits the sensitive file via electromagnetic radiation. The file is received by a smartphone of a malicious insider/visitor standing behind the wall in a less secure area (B).”
The signals are observed using a smartphone or laptop with a small loop antenna from a distance of about 2m. Observed signals are decoded and delivered to the attacker via the Internet.
“It is important to note that the attack model compound of transmitters and receivers has been broadly discussed in the domain of covert channels for the last twenty years.”
“We showed that malware on air-gapped computers could generate electromagnetic radiation in specific low-frequency bands. The malicious code exploits modern computers’ dynamic power and voltage regulation and manipulates the loads on CPU cores.”
Secure Web Gateway – Web Filter Rules, Activity Tracking & Malware Protection – Download Free E-Book



.png
)
