Security researchers have uncovered a massive campaign of repository confusion attacks on GitHub, affecting over 100,000 repositories and potentially millions more.
This sophisticated cyberattack targets developers by tricking them into downloading and using malicious repositories disguised as legitimate ones.
Apiiro has developed a malicious code detection system that monitors codebases and uses advanced techniques like deep code analysis and deobfuscation to identify and prevent such attacks.

You can analyze a malware file, network, module, and registry activity with the ANY.RUN malware sandbox and the Threat Intelligence Lookup that will let you interact with the OS directly from the browser.
How Repo Confusion Attacks Work
Repo confusion attacks are similar to dependency confusion attacks but exploit human error rather than package manager systems.
Attackers clone popular repositories, inject them with malware, and then upload them back to GitHub with identical names.
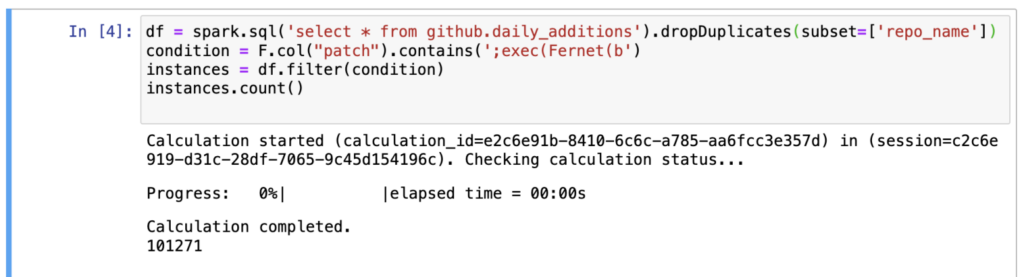
These repositories are automatically forked thousands of times and promoted across various online platforms to increase their visibility and likelihood of being mistakenly used by developers.
Apiiro’s deep application security posture management (ASPM) technology uncovers next-generation software supply chain and application threats beyond vulnerability detection and ingestion.
Malicious Payload
When developers use these malicious repositories, the malware executes a complex unpacking process involving seven layers of obfuscation.
It ultimately deploys a modified version of BlackCap-Grabber, a malicious code designed to steal sensitive information such as login credentials, browser passwords, and cookies. This data is transmitted to the attackers’ command-and-control servers for further malicious activities.

While GitHub’s automated systems have been able to remove many of the forked repositories, the sheer scale of the attack means that a significant number remain.
The platform’s security teams are actively working to detect and remove these malicious repositories, but the campaign’s scope and the subtlety of the attack make it a challenging task.
Evolution of Malware Campaigns
This campaign marks a shift in strategy for cyber attackers, moving from package managers to source code management (SCM) platforms like GitHub.
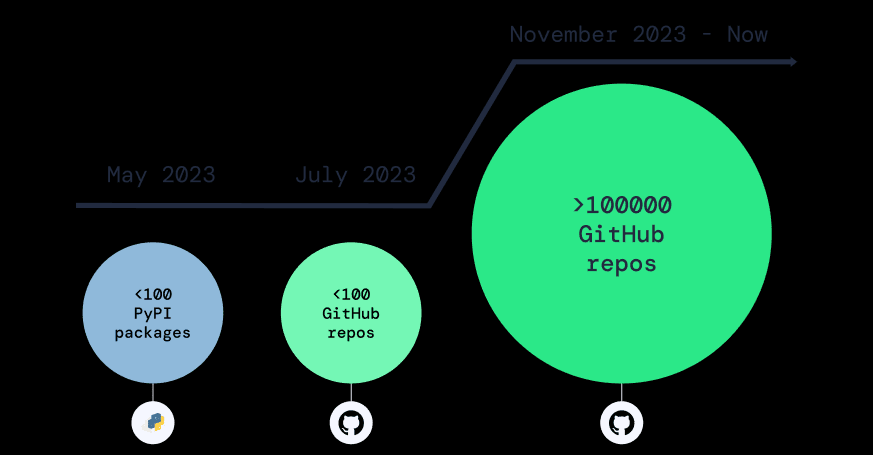
The ease of creating accounts and repositories on GitHub, combined with its vast size, makes it an attractive target for those looking to covertly infiltrate the software supply chain.
Protecting Against Repo Confusion
To combat these attacks, GitHub has been notified, and most malicious repositories have been deleted. However, the campaign persists, and the threat to the software supply chain remains significant.
Apiiro has developed a malicious code detection system that monitors codebases and uses advanced techniques like deep code analysis and deobfuscation to identify and prevent such attacks.
The discovery of this large-scale repo confusion campaign highlights the ongoing vulnerabilities within the software supply chain.
Developers and organizations must remain vigilant and employ advanced security measures to protect against these sophisticated attacks.
The security community continues to adapt and develop new strategies to safeguard against these ever-evolving threats
You can block malware, including Trojans, ransomware, spyware, rootkits, worms, and zero-day exploits, with Perimeter81 malware protection. All are incredibly harmful, can wreak havoc, and damage your network.
Stay updated on Cybersecurity news, Whitepapers, and Infographics. Follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter.



.png
)
