Security researchers have uncovered a new attack campaign by the North Korean state-sponsored APT group Kimsuky, also known as “Black Banshee.”
The group, active since at least 2012, has been observed employing advanced tactics and malicious scripts in their latest cyber espionage efforts targeting countries such as South Korea, Japan, and the United States.
The attack begins with a ZIP file containing four components: a VBScript, a PowerShell script, and two encoded text files.
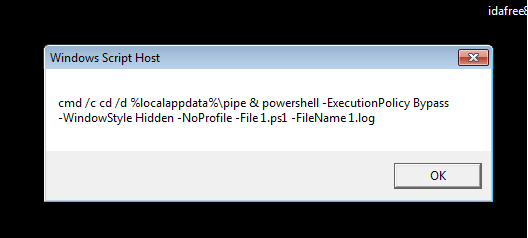
The VBScript utilizes obfuscation techniques, leveraging chr() and CLng() functions to dynamically generate characters and execute commands, effectively bypassing signature-based detection methods.
Multi-Stage Payload Analysis
Upon execution, the initial script triggers a PowerShell component that decodes base64-encoded data from one of the text files.
According to the Report, this decoded script performs several critical functions, including system reconnaissance, data exfiltration, and command-and-control (C2) communication.
The malware exhibits VM-aware behavior, terminating its execution if it detects a virtual machine environment.
For non-VM targets, it proceeds to collect sensitive information, including the BIOS serial number, which is used to create a unique directory for storing attack-related files.

Advanced Data Theft and Persistence Mechanisms
The Kimsuky malware demonstrates sophisticated capabilities for data exfiltration.
It targets multiple browsers, including Edge, Firefox, Chrome, and Naver Whale, to extract user profiles, cookies, login information, and web data.
The malware also searches for cryptocurrency wallet extensions and harvests their associated files.
Furthermore, the malware creates a comprehensive system profile, gathering hardware information, network adapter status, and a list of installed programs.
It implements persistence through scheduled tasks and continuously monitors the system for new data to exfiltrate.
In the final stage of the attack, the malware deploys a keylogger component.
This module imports Windows API functions to detect key presses, monitor clipboard activity, and log window titles.

The collected data is periodically uploaded to the attacker’s C2 server, providing real-time surveillance of the victim’s activities.
The Kimsuky group’s evolving tactics and multi-component approach highlight the increasing sophistication of state-sponsored cyber threats.

As these attacks become more evasive and complex, organizations must remain vigilant and employ robust security measures to protect against such advanced persistent threats.
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams? – Analyse Malware, Phishing Incidents & get live Access with ANY.RUN -> Start Now for Free.
.webp?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)


.png
)
