Cybersecurity experts have successfully decrypted Zoom Team Chat data, revealing a wealth of information about user activities.
This achievement underscores the importance of digital forensics in uncovering hidden digital evidence.
The focus on Zoom Team Chat artifacts has shown that, despite encryption, crucial communications and shared files can be exposed through meticulous analysis.
The decryption was part of a CTF (Capture The Flag) challenge where participants were given a disk image to analyze.
The system had been hit by ransomware, encrypting many files and damaging registry data, complicating the search for artifacts.
However, using Windows jumplists and other execution artifacts, the team found clues pointing to a suspicious HTA file, hinting at obfuscated JavaScript requiring deobfuscation.
Tracing User Activity
The investigation by InfoSec Writeups, involved analyzing Chrome browsing history and Discord chat logs, which led to a pair of Discord chats referencing Zoom communications.
This trail sparked interest in Zoom’s data storage practices, particularly the encrypted databases containing Zoom Team Chat information.
Zoom Data Storage
Zoom stores its application data in two encrypted databases:
- Main Database (zoomus.enc.db): General Zoom account and session information.
- User-Specific Database (zoomus.async.enksdb): Stores Zoom Team Chat data encrypted using SQLCipher with custom parameters.
Decryption Process
- Finding the Main Key:
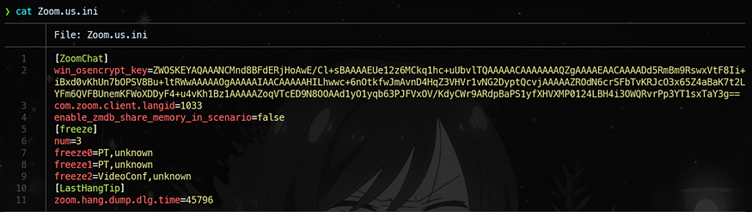
- The key to decrypt the main database is stored as a DPAPI-encrypted string in zoom.us.ini.
- Due to a weak Windows password hint, the team cracked the local password using John the Ripper, enabling decryption of the DPAPI-protected key.

- Decrypting Main Database:
- Though not necessary for the challenge, the main database contains useful information, such as the Zoom account email.
- Other encrypted fields can be decrypted using a provided Python script.
# Example decryption script for encrypted fields in the main database
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Hash import SHA256
from base64 import b64decode
main_key = "Main Key Here"
key = SHA256.new(main_key).digest() # Derive AES key from main_key
raw = b64decode("encrypted_field_value")
iv, tag, data = raw[1:13], raw[-16:], raw[19:-16] # Extract IV, authentication tag, and ciphertext
plaintext = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_GCM, iv).decrypt_and_verify(data, tag) # Decrypt and verify
print(plaintext.decode('utf-8'))- Decrypting User-Specific Database:
- Requires the Key Wrapping Key (KWK) stored on Zoom’s servers.
- Capturing KWK involves monitoring Zoom’s API calls during login or session refresh using tools like RhobitoB API monitoring.
- Deriving User Key:
- Once both main key and KWK are obtained, apply steps to derive the user key.
# Python script to derive the user_key for decrypting user-specific database
import hashlib
import base64
main_key = b'L4jYqZnRF/ZrwJuMcVvPOFqklFzqtMPj554VF82B9g' # First 42 bytes of main_key
kwk = b'nB9oO3Kg8XA+gzd6O+k8YMq+iGCpDmHAe9m0iqtJY3w='
h1 = hashlib.sha256(main_key).hexdigest()
h2 = hashlib.sha256(kwk).hexdigest()
final = hashlib.sha256(bytes.fromhex(h1 + h2)).digest()
print(base64.b64encode(final).decode())The decryption of Zoom Team Chat data highlights the complexities and possibilities in digital forensic analysis.
While Zoom’s encryption measures are robust, combining forensic techniques with API monitoring can uncover crucial user activity data.
This breakthrough serves as a reminder of the potential vulnerabilities even in seemingly secure communication platforms and underscores the need for continued innovation in digital forensics.
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams? – Analyse Malware Incidents & get live Access with ANY.RUN -> Start Now for Free.



.png
)
