ProjectSend, an open-source file-sharing web application, has become a target of active exploitation following the recent assignment of CVE-2024-11680 on November 25, 2024.
Despite the availability of a patch for more than a year, adoption rates remain alarmingly low, leaving many instances vulnerable to attack.
ProjectSend Authentication Vulnerability
ProjectSend is moderately popular, with nearly 1,500 GitHub stars and over 4,000 instances indexed by Censys.
A vulnerability in its authentication mechanism, disclosed by Synactiv in January 2023, enables attackers to modify core configuration settings and potentially escalate privileges post-authentication.
Analyze cyber threats with ANYRUN's powerful sandbox. Black Friday Deals : Get up to 3 Free Licenses.
This flaw allows for activities such as embedding malicious JavaScript or even uploading webshells to compromised instances.
Although a fix for this issue was released on May 16, 2023, the CVE assignment was delayed until November 2024, contributing to a lack of widespread awareness.
Multiple exploitation tools, including those by Synactiv, Project Discovery (Nuclei), and Rapid7 (Metasploit), have also made the vulnerability easier to exploit.
Exploitation Timeline
- January 19, 2023: Vulnerability disclosed by Synactiv to ProjectSend.
- May 16, 2023: ProjectSend releases an initial patch.
- July 19, 2024: Synactiv publishes a security advisory.
- August 30, 2024: Metasploit pull request demonstrating exploitation is submitted.
- November 25, 2024: CVE-2024-11680 is officially assigned.
Signs of exploitation began appearing in September 2024, coinciding with the release of Metasploit and Nuclei vulnerability checks.
Researchers observed public-facing ProjectSend instances altering their landing page titles to random strings—characteristic of these exploit tools’ testing methods.
More concerning is the trend of attackers enabling non-default user registration settings post-authentication, granting them elevated privileges.
In many cases, attackers appear to go beyond reconnaissance, uploading webshells, or executing malicious scripts.
Web shells were discovered in predictable file paths (upload/files/), often identifiable through server logs for direct file access.
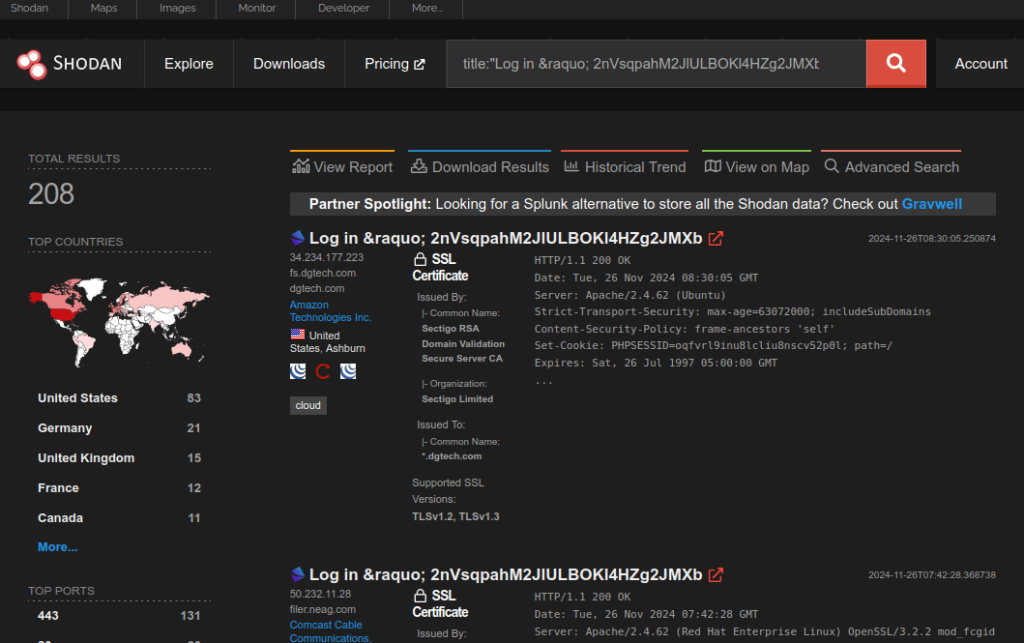
Despite the patch being available for over a year, patching rates are dismal. A VulnCheck analysis using Shodan data revealed:
- 1% of instances are running the latest patched version (r1750).
- 99% of instances remain outdated, with 55% running a version released in October 2022.
This lag in patch adoption has left many systems exposed to exploitation campaigns, which may grow in scale as awareness spreads.
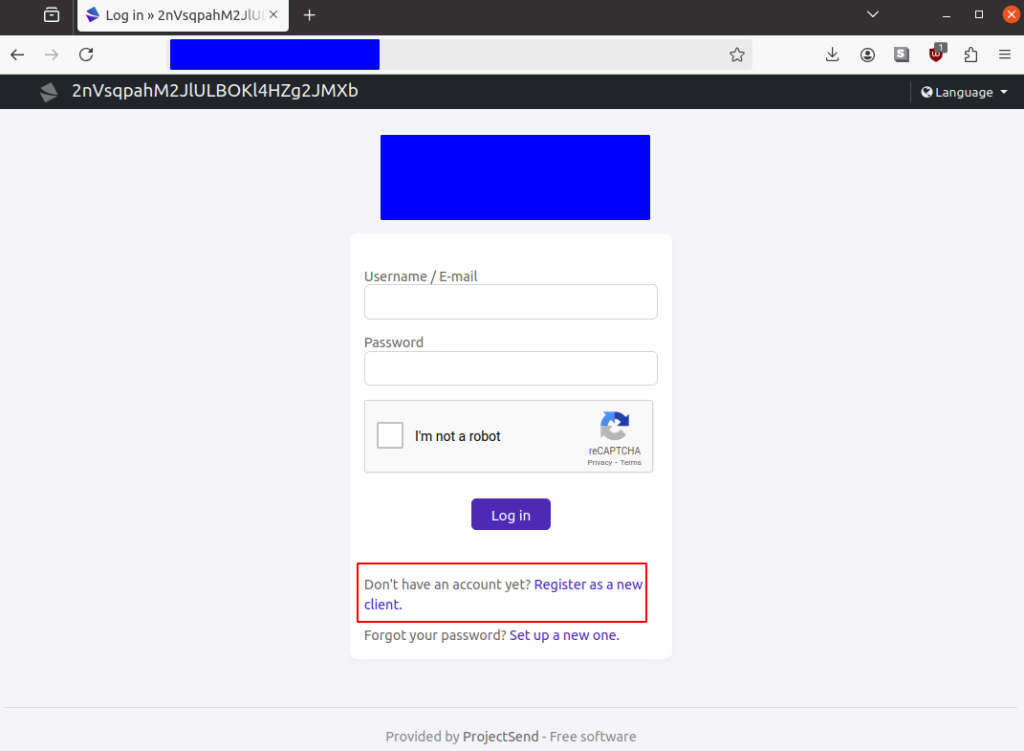
According to the VulnCheck report, the widespread exploitation of CVE-2024-11680 highlights the critical importance of timely patch management, centralized vulnerability documentation, and robust incident response measures.
Organizations using ProjectSend should immediately assess their systems for exposure, upgrade to the latest version (r1750), and monitor logs for signs of compromise. As exploitation expands, proactive measures are essential to mitigate this escalating security risk.
Leveraging 2024 MITRE ATT&CK Results for SME & MSP Cybersecurity Leaders – Attend Free Webinar



.png
)
