Researchers discovered a new evasion technique used by attackers in client-side web skimmer to bypass their conceal their fraudulent activity.
Recently, a security researcher revealed a steganography-based credit card skimmer in which they found that the attackers uploads or modifies an existing image and appends the JS code.
With this Steganography technique, attackers hiding malicious code inside of the picture files, and it is a great way to go undetected the malformed files, and it has mainly used to target the eCommerce sites.
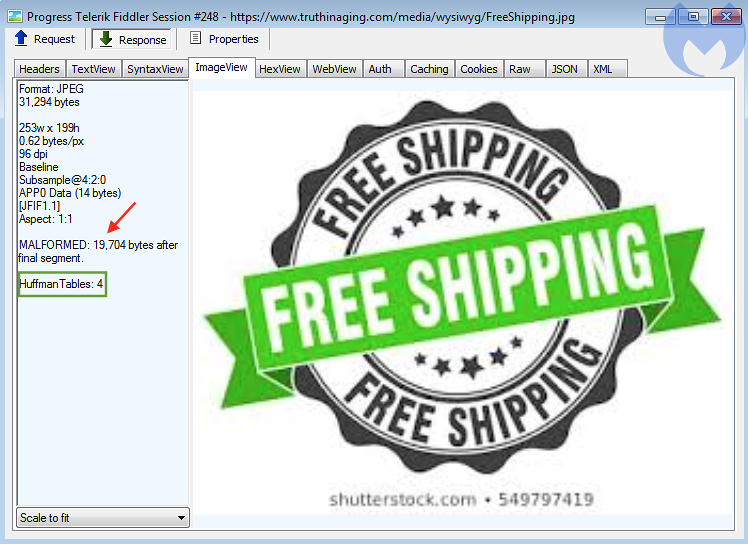
There is one chance to figure out the file whether it is malformed are not is by analysing the additional data found at the end of the normal file.
Skimmers Found in Steganographic Images
Researchers from Malwarebytes analyzed the sample malformed steganographic image in a hex editor, and find the extra data was added after the final segment.
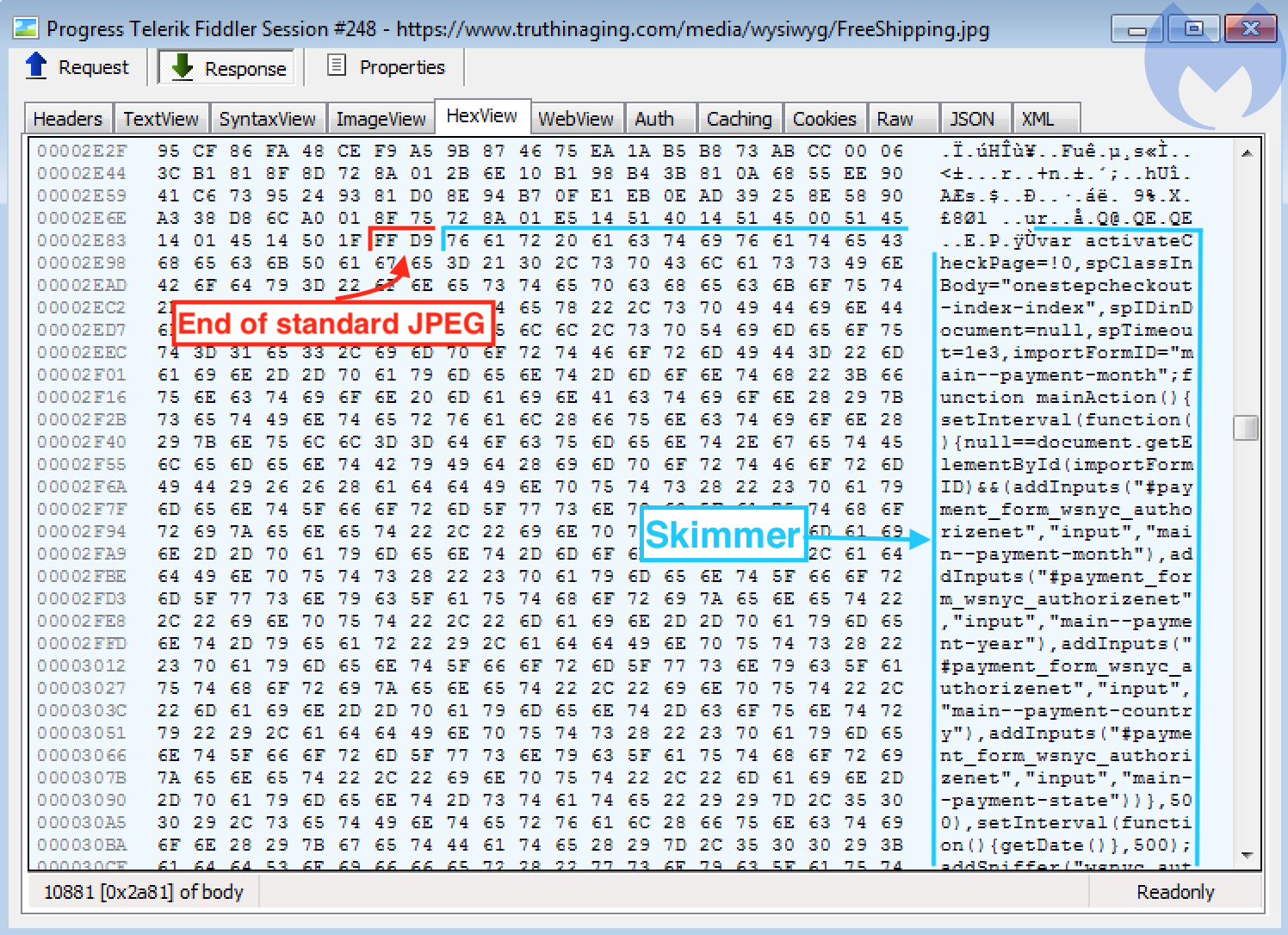
By analyzing the strings such as onestepcheckout or authorizenet, research confirmed that this is the credit-card skimming code.
According to Malwarebyte’s research, All compromised sites we found using a steganographic skimmer were injected with similar code snippets (typically after the footer element or Google Tag Manager) to load the fake image and parse its JavaScript content via the slice() method.
There are several following artifacts researchers observed from the web skimmer.
- Skimmer code injected directly into a compromised site (JavaScript in the DOM)
- Skimmer code loaded from an external resource (script tag with src attribute)
- Exfiltration of the stolen data (HTTP GET or HTTP POST requests with encoded data)
Attackers cleverly using a WebSocket, a communication protocol to conceal a connection to a server controlled by the criminals over a WebSocket.
Once the malicious Javascript code runs in the browser, it triggers the client handshake request and a series of bidirectional messages will be exchanged between the client (victim’s browser) and server (malicious host).
Later a Javascript code turns into the credit card skimming code and it performs exfiltration attempts with the help of WebSockets from the form fields present on the checkout page.

“The techniques give headaches for defenders and give some threat actors additional time to carry on their activities without being disturbed. But as mentioned before, this kind of cat-and-mouse game was to be expected in the light of regular new publications on Magecart and web skimmer.” Malwarebytes said.



