Security researchers have uncovered a new strain of Android malware that masquerades as the popular Google Chrome browser to steal sensitive banking information from unsuspecting users.
The malware, dubbed “Mamont Spy Banker,” has been found to target Android devices highly sophisticatedly.
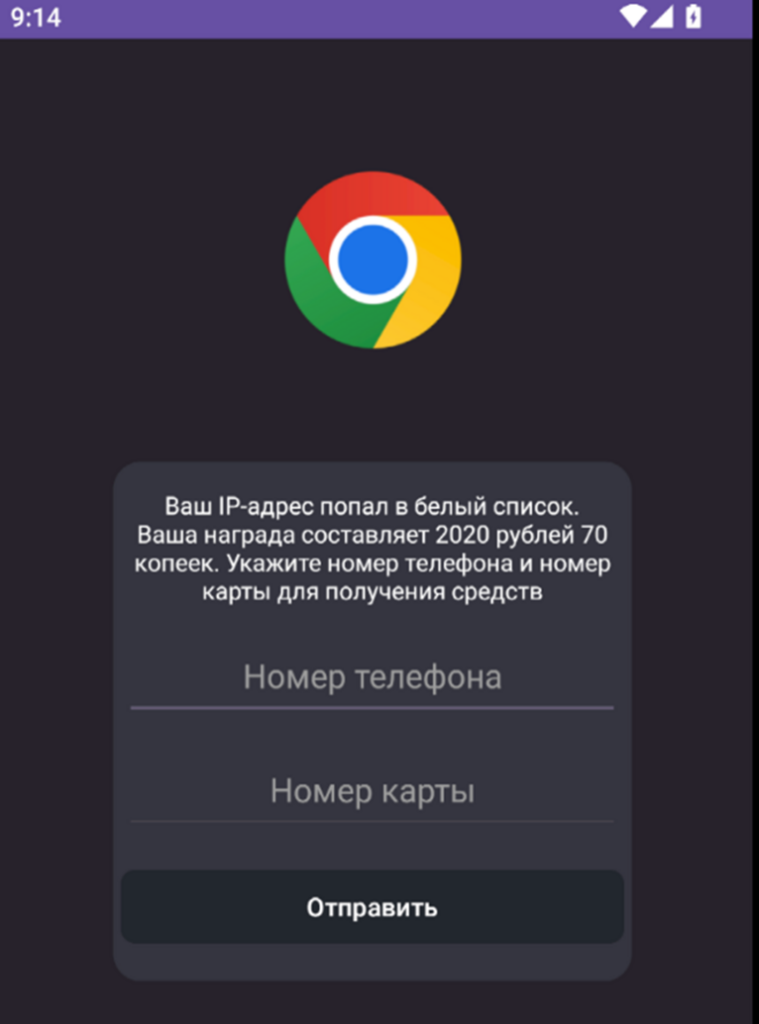
Mimicking Google Chrome
The malware’s primary tactic is impersonating the Google Chrome app, tricking users into believing they are interacting with a legitimate and trusted application.
This deception is achieved through a nearly identical user interface and branding, making it challenging for even intelligent users to distinguish the malicious app from the real Chrome browser.
According to a recent blog post by GData, a new strain of Android malware has been discovered that impersonates Google Chrome to steal banking credentials.
Free Live Webinarfor DIFR/SOC Teams: Securing the Top 3 SME Cyber Attack Vectors - Register Here.
Stealing Banking Details
Once installed, the Mamont Spy Banker malware is designed to intercept and steal sensitive banking information, including login credentials, account numbers, and other financial data.
This information is then siphoned off to the malware’s command-and-control servers, putting victims at risk of financial fraud and identity theft.
The researchers at G DATA have noted that the Mamont Spy Banker malware employs sophisticated evasion tactics to avoid detection by traditional security measures.
These include using advanced obfuscation techniques, dynamic code loading, and adapting its behavior based on the device’s environment.
To safeguard against this threat, security experts recommend that Android users exercise caution when downloading and installing apps, even from trusted sources.
Users should also be wary of any apps that closely resemble well-known applications and always verify an app’s legitimacy before granting it access to sensitive information.
Additionally, keeping Android devices up-to-date with the latest security patches and using a reputable antivirus solution can help mitigate the risk of falling victim to this and other emerging Android malware threats.
Looking to Safeguard Your Company from Advanced Cyber Threats? Deploy TrustNet to Your Radar ASAP
.webp?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)


.png
)
