The new variant of Linux botnet WatchBog adds BlueKeep Vulnerability Scanner module to prepare a list of vulnerable windows RDP servers. The hackers behind WatchBog is familiar with exploiting know vulnerabilities.
Bluekeep is windows-based vulnerability which allows an attacker to access the vulnerable machine without authentication. The vulnerability can be tracked as CVE-2019-0708, till now no attack has been spotted exploiting this vulnerability.
Intezer observed the new campaign active before June 5, incorporates various recently published exploits and went undetected by security vendors.
New Exploits and BlueKeep Vulnerability Scanner
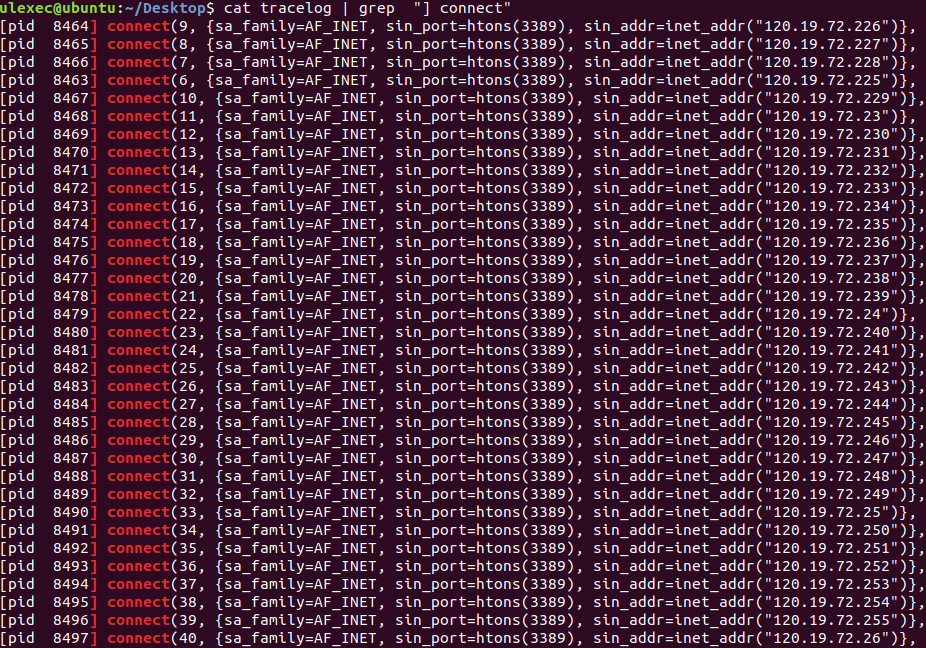
The new variant includes newly published exploits that include Jira’s, Exim’s, Solr’s and BlueKeep Vulnerability Scanner. The BlueKeep Vulnerability Scanner attached with WatchBog scans the attempts to find out the vulnerable RDP servers.
Once the scanning process completed it returns a list of RC4 encrypted vulnerable IP addresses encoded as a hexadecimal string.
Researchers believe that “the threat actors behind WatchBog may be gathering a list of vulnerable BlueKeep Windows endpoints for future use, or perhaps to sell to a third party to make a profit.”
Scanner Modules
- Jira module
- Solr module
- BlueKeep module
Exploits
- CVE-2019-11581 (Jira)
- CVE-2019-10149 (Exim)
- CVE-2019-0192 (Solr)
- CVE-2018-1000861 (Jenkins)
- CVE-2019-7238 (Nexus Repository Manager 3)
Bruteforce Modules
- CouchDB
- Redis
All the exploit modules allow an attacker to achieve RCE, WatchBog scans for the vulnerable machine, once vulnerable service is spotted, it invokes the right exploit modules and installs the malicious Monero miner modules from Pastebin.
To maintain persistence it utilizes crontab and downloads another spreader module – a cython combined binary(ELF executable), the binary retrieves the C2 servers from Pastebin.
Intezer believes that “around 4,500 endpoints were infected with the use of these specific Pastebin links. As WatchBog is known to have been active before June 5—which is the upload date of these Pastebins—we believe additional machines may have been infected with the use of older Pastebin links.”
Server administrators are recommended to update the software to the latest versions and to verify the open ports exists outside of the trusted network.
Linux users could check for the existence of “/tmp/.tmplassstgggzzzqpppppp12233333” file or the “/tmp/.gooobb” file, if you suspect that the system is infected.
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity updates also you can take the Best Cybersecurity course online to keep yourself updated.



.png
)
