Security researchers at Cado Security Labs have uncovered a new variant of the Cerber ransomware targeting Linux systems.
This strain of the notorious malware has been observed exploiting a recent vulnerability in the Atlassian Confluence application to gain a foothold on targeted servers.
CVE-2023-22518: The Vulnerability Exploited
The primary attack vector for this Cerber variant is the exploitation of CVE-2023-22518, a vulnerability in the Atlassian Confluence application that allows an attacker to reset the application and create a new administrative account, as reported by Cado Security Labs.
This flaw, disclosed and patched earlier this year, has become a prime target for threat actors seeking to compromise Confluence servers.
Technical Details
The Cerber Linux ransomware is a highly obfuscated C++ payload, compiled as a 64-bit Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) binary and packed with the UPX packer.
This technique is employed to prevent traditional malware scanning and analysis.
Once the attacker gains access to the Confluence server through the CVE-2023-22518 exploit, they use the newly created administrative account to upload and install a malicious web shell plugin, Effluence.
Free Live Webinar for DIFR/SOC Teams: Securing the Top 3 SME Cyber Attack Vectors - Register Here.
This web shell provides a user interface for executing arbitrary commands on the compromised host.

The primary Cerber payload is then downloaded and executed through the web shell.
This payload is a stager responsible for setting up the environment and fetching additional components, including a log checker and the final encryptor payload.
The log checker payload, known as “agttydck,” is a simple C++ program that attempts to write a “success” message to a file.
This is likely a check for the appropriate permissions and sandbox detection.
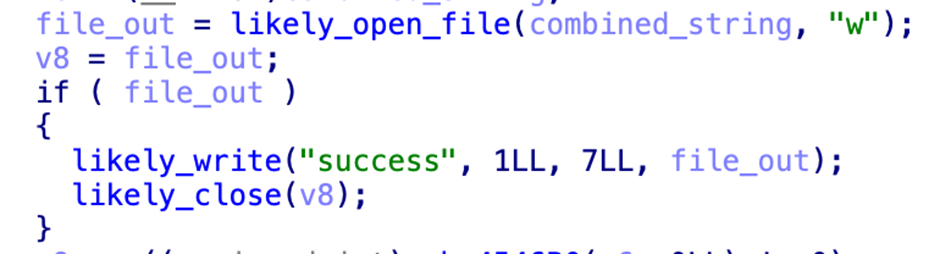
The final encryptor payload, “agttydcb,” is the core of the ransomware.
It systematically encrypts files across the file system, overwriting the original content with the encrypted data and appending the “.L0CK3D” extension.
A ransom note is also left in each directory, demanding payment for the decryption of the files.
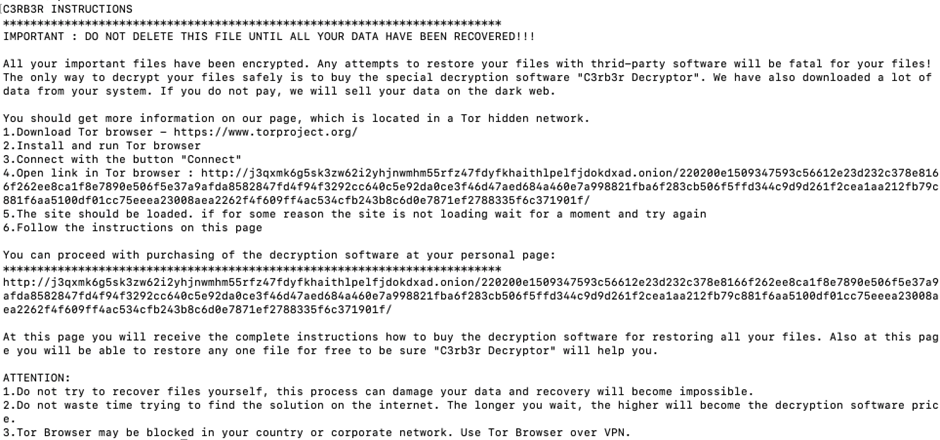
The Cerber Linux ransomware exploited the Atlassian Confluence vulnerability, highlighting the importance of timely patching and vigilance in securing critical enterprise applications.
As threat actors continue to target vulnerabilities in popular software, organizations must remain proactive in their security measures to protect against such sophisticated attacks.
Looking to Safeguard Your Company from Advanced Cyber Threats? Deploy TrustNet to Your Radar ASAP
.webp?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)


.png
)
