The build and shared components on the CPUs are exploited by a method called Collide+Power. This attack vector does not target specific programs but the hardware itself.
Advanced software-based power side channels echoed the discovery of Meltdown and Spectre vulnerability, which leaked actual data values through underlying hardware.
The core causes of this vulnerability are the shared CPU components like internal memory systems.
Combining the data from the attacker and other application data results in combined leakage signals in the power consumption.
There have been two attack scenarios that belonged to the Collide+Power category.
The first attack breaks the isolation of CPU hyperthreads, and the second attack which breaks the isolation between user programs and the operating system.
In addition, this attack technique can boost any power-related side channel signal like RAPL (PLATYPUS) or frequency throttling (Hertzbleed).
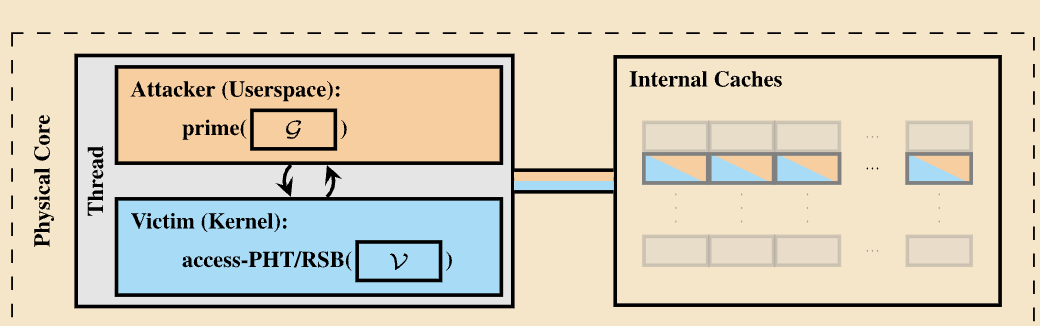
Working of Collide+Power
For instance, the attacker fills the targeted CPU component, like the CPU cache, with attacker-controlled data. Then, the attacker forces the victim’s data to overwrite the attacker-controlled data, which results in the collision of data with the victim’s secret.
Since CPUs are designed to consume power as per the data usage, the collision results in a large number of iterations in the overwriting process. Finally, the attacker can get the exact secret value of the victim.
There were two variants in the Collide+Power variants,
Variant 1: The victim program constantly accesses important secret data like decryption keys to encrypt or decrypt a large chunk of data. This attack variant requires hyperthreading to be enabled.

Variant 2: In this attack variant, the attacker used a prefetch gadget in the operating system to bring arbitrary data into the shared CPU component, which can be extracted using the data collisions. This attack variant has reduced leakage rates but does not require hyperthreading.
Several CVEs were discovered in the past, which include CVE-2020-8694, CVE-2020-8695, CVE-2022-23823, and CVE-2022-24436. However, a recent vulnerability was discovered on AMD CPUs which was reported and fixed.
CVE-2023-20583: Software-based Power Side Channel on AMD CPUs
An attacker can exploit this vulnerability in AMD processors to monitor CPU power consumption since the data in the cache line changes over time which can result in the leakage of sensitive data. The CVSS score for this vulnerability is yet to be confirmed.
AMD has released a security advisory for addressing this vulnerability.
A complete report has been published regarding this new discovery which provides detailed information regarding the threat vectors, mitigations, and others.
Keep yourself informed about the latest Cyber Security News by following us on GoogleNews, Linkedin, Twitter, and Facebook.



.png
)
