A recent campaign dubbed FLUX#CONSOLE has come to light, leveraging Microsoft Common Console Document (.MSC) files to infiltrate systems with backdoor malware.
The campaign showcases the growing sophistication of phishing techniques and the exploitation of lesser-known Windows features.
The FLUX#CONSOLE Campaign
The FLUX#CONSOLE campaign has been identified as a multi-stage attack with sinister objectives.
By using MSC files, threat actors bypass many traditional antivirus (AV) systems and deliver highly obfuscated backdoor payloads.
This strategy appears to be a shift from the abuse of LNK files, which have been a hallmark of phishing campaigns for years. Key aspects of this campaign include:
- Tax-Themed Phishing Lures: Emails trick users into opening benign tax-related documents.
- Advanced Obfuscation: From JavaScript to concealed DLLs, the attackers employ multiple obfuscation layers to hinder detection.
- DLL Sideloading: The use of legitimate Windows applications like Dism.exe to execute malicious code.
- Persistence Mechanisms: Scheduled tasks ensure the malware remains active even after the system reboots.
These techniques collectively demonstrate the lengths cybercriminals go to evade detection and establish persistent access.
2024 MITRE ATT&CK Evaluation Results Released for SMEs & MSPs -> Download Free Guide
How the Attack Works
Step 1: Phishing Lure
According to the Securonix report, the attack begins with a phishing email containing either a direct malicious attachment or a link. The attachment masquerades as a legitimate file, such as a tax document.
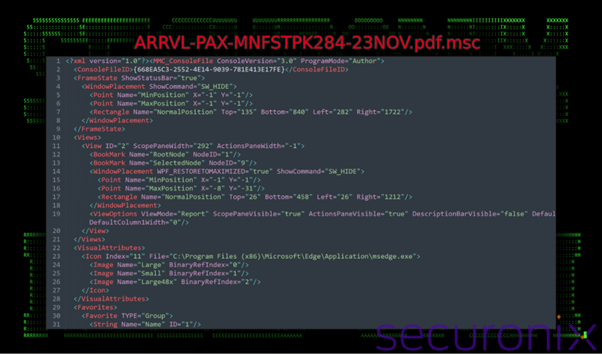
In this case, filenames like “Income-Tax-Deduction-and-Rebates202441712.pdf” are used.The deceptive .MSC file appears as a PDF, using a Windows feature where file extensions are hidden by default, further tricking users.

Step 2: Execution of the MSC File
Microsoft Common Console Document (.MSC) files are legitimate Windows tools used to configure administrative settings. However, in this campaign, attackers exploit their ability to execute embedded scripts or commands.
- When users double-click the .MSC file, malicious JavaScript or VBScript is executed under the guise of the legitimate mmc.exe process.
- The file also hides its activity by minimizing windows and employing advanced obfuscation.
Step 3: Payload Delivery
The .MSC file acts as both a loader and dropper. It initiates one of two delivery mechanisms:
- Embedded within the .MSC file itself.
- Downloaded from a remote server.
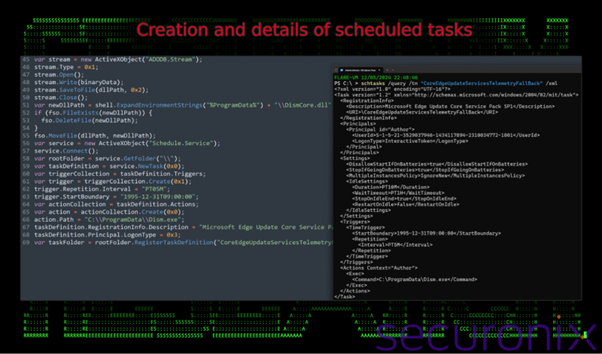
In both cases, it delivers a malicious payload in the form of a DLL file named DismCore.dll, which is sideloaded via the legitimate Dism.exe process.
Step 4: Persistence
Once the malware is active, it establishes persistence by creating scheduled tasks. For example, a task named “CoreEdgeUpdateServicesTelemetryFallBack” is created to execute the malicious Dism.exe every five minutes, ensuring the malware continues running.
Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in files (.MSC) are often used by IT administrators and aren’t typically perceived as malicious. Attackers exploit this trust factor. When opening an .MSC file:
- The legitimate mmc.exe process is triggered.
- The embedded malicious code runs inconspicuously under the guise of an administrative tool.
Additionally, because .MSC files can host scripts like JavaScript or VBScript, they offer a flexible yet powerful medium for executing malicious payloads.
Obfuscation Techniques
The FLUX#CONSOLE campaign employs cutting-edge obfuscation methods:
- JavaScript Layers: The initial script is obfuscated, often hiding malware execution commands. Multiple decryption steps are required to analyze its behavior.
- Base64 and Hex Encoding: Payloads are encoded to avoid static detection.
- DLL Obfuscation: Even the final DismCore.dll payload includes various junk code routines to confuse analysts.
These tactics make it challenging for traditional security tools to detect and block the malware.
Once inside the system, the backdoor:
- Communicates with a remote Command-and-Control (C2) server, sending encrypted requests and responses.
- Can exfiltrate sensitive data.
- Provides attackers with potential for lateral movement, enabling further compromise of corporate networks.
Although researchers disrupted the attack within 24 hours, the severity of the breach highlights the vulnerabilities in modern endpoint defenses.
The FLUX#CONSOLE campaign serves as a wake-up call for the cybersecurity community. By exploiting trusted tools like .MSC files and leveraging advanced obfuscation techniques, attackers continue to evade traditional defenses.
As such campaigns evolve, robust security solutions and proactive threat intelligence are essential to stay ahead of cybercriminals.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links, Malware & Phishing Attacks With ANY.RUN – Try for Free



.png
)
