Security researchers have disclosed critical details about CVE-2025-20029, a command injection vulnerability in F5’s BIG-IP Traffic Management Shell (TMSH) command-line interface.
The flaw enables authenticated attackers with low privileges to bypass security restrictions, execute arbitrary commands, and gain root-level access to vulnerable systems.
A proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit demonstrating remote code execution was released on February 24, 2025, raising the urgency for organizations to patch affected devices.
CVE-2025-20029 Overview
The vulnerability resides in the TMSH parser’s handling of user-supplied inputs.
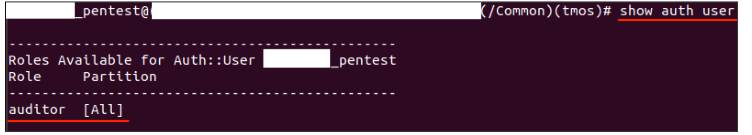
Attackers with valid credentials—even for accounts assigned non-administrative roles like auditor—can craft malicious commands that escape the CLI’s security sandbox.
This allows the injection of operating system commands directly into the underlying Linux environment.
Affected versions include F5 BIG-IP v16.1.4.1 and earlier. Successful exploitation grants full control over the device, enabling data theft, network traffic interception, or lateral movement into connected systems.
PoC Exploit Methodology
Github published PoC exploits that the save sys config TMSH command, which runs with root privileges by default.
Attackers inject a payload using shell metacharacters to split the original command into two parts:
- A legitimate save operation to the Common configuration partition.
- An arbitrary command executed via bash:
save sys config partitions { Common "\}; " bash -c id " ; \#" }This payload leverages TMSH’s syntax parsing weaknesses.
The \}; sequence terminates the save command prematurely, while the subsequent bash -c id executes a system call to print the current user’s ID—confirming execution as root.
- Requires access to the TMSH interface (via SSH or iControl REST API).
- Injected commands must use binaries whitelisted by F5 (e.g., bash, tcpdump).
- Target partition names (e.g., “Common”) must be valid to avoid command failure.
F5 released patches in Q1 2025. Administrators should:
- Immediately upgrade to BIG-IP v16.1.4.2 or later.
- Restrict TMSH access to essential users and audit role assignments.
- Monitor logs for unusual save commands or partition modifications.
Unpatched systems remain vulnerable to attackers leveraging compromised credentials.
F5 advises implementing network segmentation and multi-factor authentication for BIG-IP management interfaces.
The public release of this PoC underscores the risk of delayed patching for network infrastructure.
Organizations using F5 BIG-IP for load balancing, firewall, or application delivery services should treat CVE-2025-20029 as a critical priority.
Free Webinar: Better SOC with Interactive Malware Sandbox for Incident Response, and Threat Hunting - Register Here



.png
)
