In a significant cybersecurity development, researchers have uncovered critical vulnerabilities in F5’s Next Central Manager, which could potentially allow attackers to gain full administrative control over the device.
This alarming security flaw also creates hidden rogue accounts on any managed assets, posing a severe threat to organizations’ network infrastructures.
F5, a leading networking and cybersecurity solutions provider, has acknowledged the vulnerabilities and promptly issued fixes.
The vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2024-21793 and CVE-2024-26026, have been addressed in software version 20.2.0, now available to F5 customers.
Despite the swift response, discovering these vulnerabilities underscores the ongoing challenges in securing critical network infrastructure against sophisticated cyber threats.
Is Your Network Under Attack? - Read CISO’s Guide to Avoiding the Next Breach - Download Free Guide
The vulnerabilities were discovered as part of ongoing research into the security of networking and application infrastructure, which has become a prime target for attackers in recent years.
F5’s Next Central Manager, described as the centralized point of control for managing the BIG-IP Next fleet, was found to be susceptible to unauthenticated OData and SQL injection attacks.
These attacks could lead to the leakage of sensitive information, such as administrative password hashes, and the creation of unauthorized accounts that are that are invisible from the Central Manager.
Technical Analysis and Proof of Concept
The research team provided detailed technical analysis and proof-of-concept for both vulnerabilities.
The OData injection vulnerability, CVE-2024-21793, allows attackers to inject malicious code into an OData query filter parameter, potentially leaking sensitive information.
The SQL injection vulnerability, CVE-2024-26026, enables attackers to execute malicious SQL statements, bypassing authentication mechanisms to gain administrative access.
Additionally, the researchers uncovered other security issues, including an undocumented API allowing Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) and inadequate bcrypt hashing cost for admin password hashes.
These vulnerabilities further compound the security risks associated with the Next Central Manager.
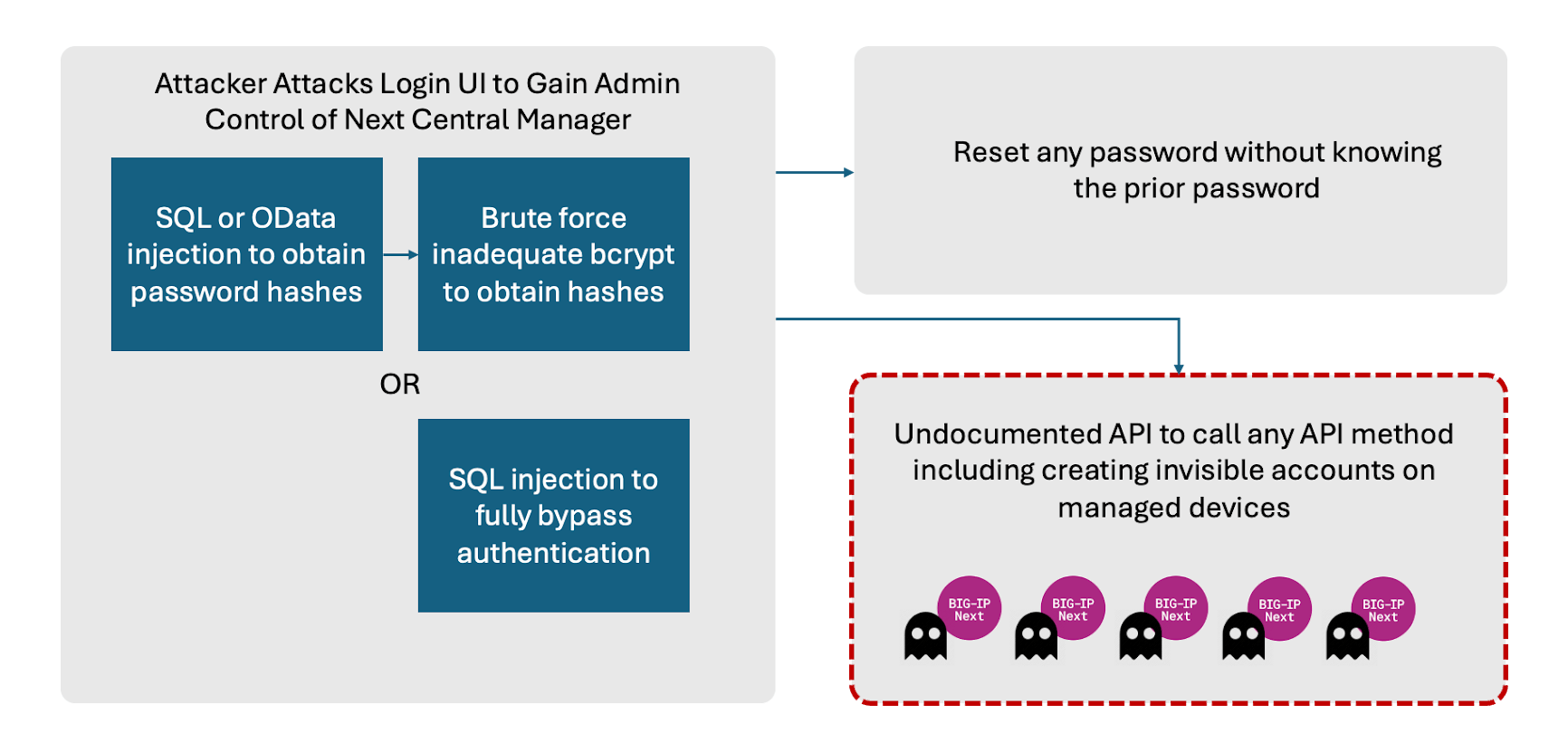
“These weaknesses can be used in a variety of potential attack paths. At a high level attackers can remotely exploit the UI to gain administrative control of the Central Manager. Change passwords for accounts on the Central Manager. But most importantly, attackers could create hidden accounts on any downstream device controlled by the Central Manager.” Eclypsium says.
Recommendations and Mitigation
F5 has recommended that organizations using the Next Central Manager upgrade to the latest version immediately to mitigate the risks posed by these vulnerabilities.
In the meantime, restricting access to the Central Manager to trusted users over a secure network is advised to reduce the likelihood of exploitation.
The discovery of these vulnerabilities serves as a reminder of the importance of vigilance and proactive security measures in protecting critical network infrastructure.
As attackers continue to target these systems, organizations must stay ahead by ensuring their security solutions are up-to-date and by adopting comprehensive cybersecurity strategies.
While F5’s prompt response to these vulnerabilities is commendable, the incident underscores the need for continuous monitoring, rapid response, and robust security measures to safeguard against evolving cyber threats.
Are you from SOC and DFIR Teams? – Analyse malware Incidents & get live Access with ANY.RUN -> Start Now for Free.



.png
)
