Google has taken a significant step in enhancing internet safety by integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into its “Safe Browsing” feature in Google Chrome.
This innovative update, which has successfully rolled out to the Stable version of Chrome, leverages AI technology to provide more robust protection against malicious websites and harmful downloads.
The update is part of Chrome’s “Enhanced Protection” mode, a security feature designed to protect users in real time.
Previously reliant on traditional methods to detect online threats, the feature now uses AI to improve its ability to identify and block malware, phishing attempts, and other digital attacks that could compromise user safety.
AI-Powered Safe Browsing
The AI-powered addition to “Safe Browsing” is now available to users worldwide. The description of this feature in Chrome for Android explicitly highlights its AI foundation.
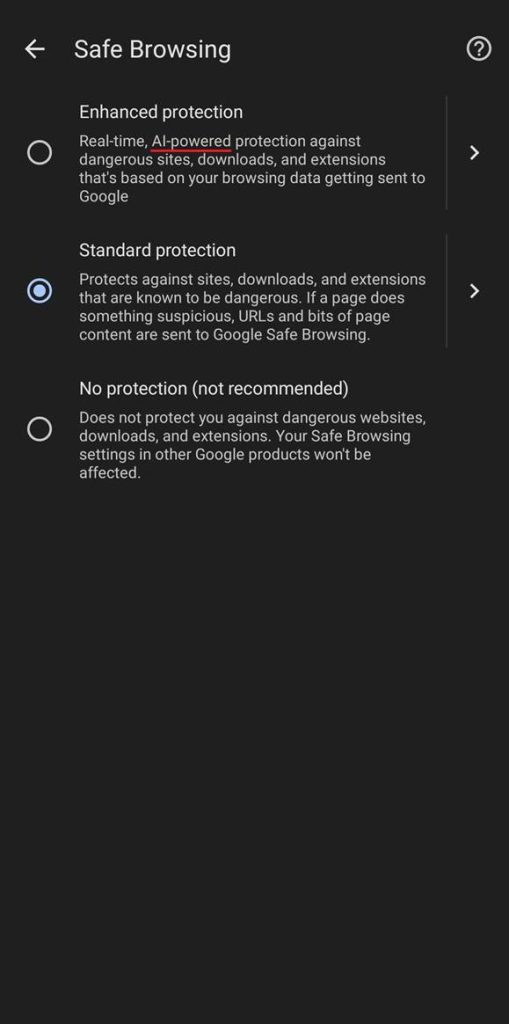
The technology is engineered to analyze websites and file downloads with heightened precision, significantly reducing false positives while ensuring potentially harmful content is flagged to users before they encounter it.
A significant benefit of this AI upgrade is its adaptability. By continuously learning from the ever-evolving tactics used by cybercriminals, Google’s AI system can stay ahead of potential threats, offering proactive security rather than reactive responses.
This marks a substantial improvement in the speed and accuracy of detecting harmful content.
With this update, users under “Enhanced Protection” will get real-time alerts and enhanced safeguards not only against known threats but also against subtle or emerging ones.
The change comes at a time of growing concern over increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, which target unsuspecting internet users through phishing campaigns, fake downloads, and more.
Google has positioned this development as part of its ongoing commitment to making the internet safer.
By incorporating AI into its security framework, Chrome users can surf the internet with greater confidence, knowing that their browser is actively working to protect them from harm.
This smart integration of AI into one of the world’s most widely used browsers underscores Google’s vision of a safer digital ecosystem.
As cyber threats become more complex, Google’s move to embrace AI in its browser security highlights a proactive approach that could set the benchmark for online safety in the future.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links & Phishing Attacks With Threat Intelligence Lookup - Try for Free



.png
)
