A recent phishing campaign uncovered by the Cofense Phishing Defense Center (PDC) has been exploiting fake Meta emails to deceive users into surrendering their Meta Business account credentials.
The attackers initiate the phishing attempt by sending fraudulent emails disguised as official Instagram notifications, alerting users that their advertising accounts have been temporarily suspended due to alleged violations of advertising policies, including references to EU GDPR regulations.

Sophisticated Phishing Campaign Targets Meta Business Users
According to Cofense Report, these deceptive emails feature subject lines such as “Critical Advertising Restrictions on Your Account,” creating urgency and prompting immediate action.
Users are instructed to click a button labeled “Check more Details,” leading them to a convincingly crafted fake webpage.
Although visually similar to legitimate Meta pages, careful examination reveals discrepancies in the URL, which directs victims to malicious domains like “businesshelp-manager[.]com” instead of authentic Meta domains.

Attackers Employ Fake Chat Support and Malicious Two-Factor Authentication
The phishing attack further escalates through sophisticated social engineering tactics involving fake chat support services.
Victims who follow the email link are prompted to enter personal information and engage with a seemingly authentic chatbot designed to mimic Meta’s customer support.
During these interactions, attackers request sensitive details such as screenshots of business account settings and personal information pages, ostensibly for verification purposes.
Additionally, the attackers attempt to gain persistent access by guiding victims through a fraudulent “System Check” procedure.
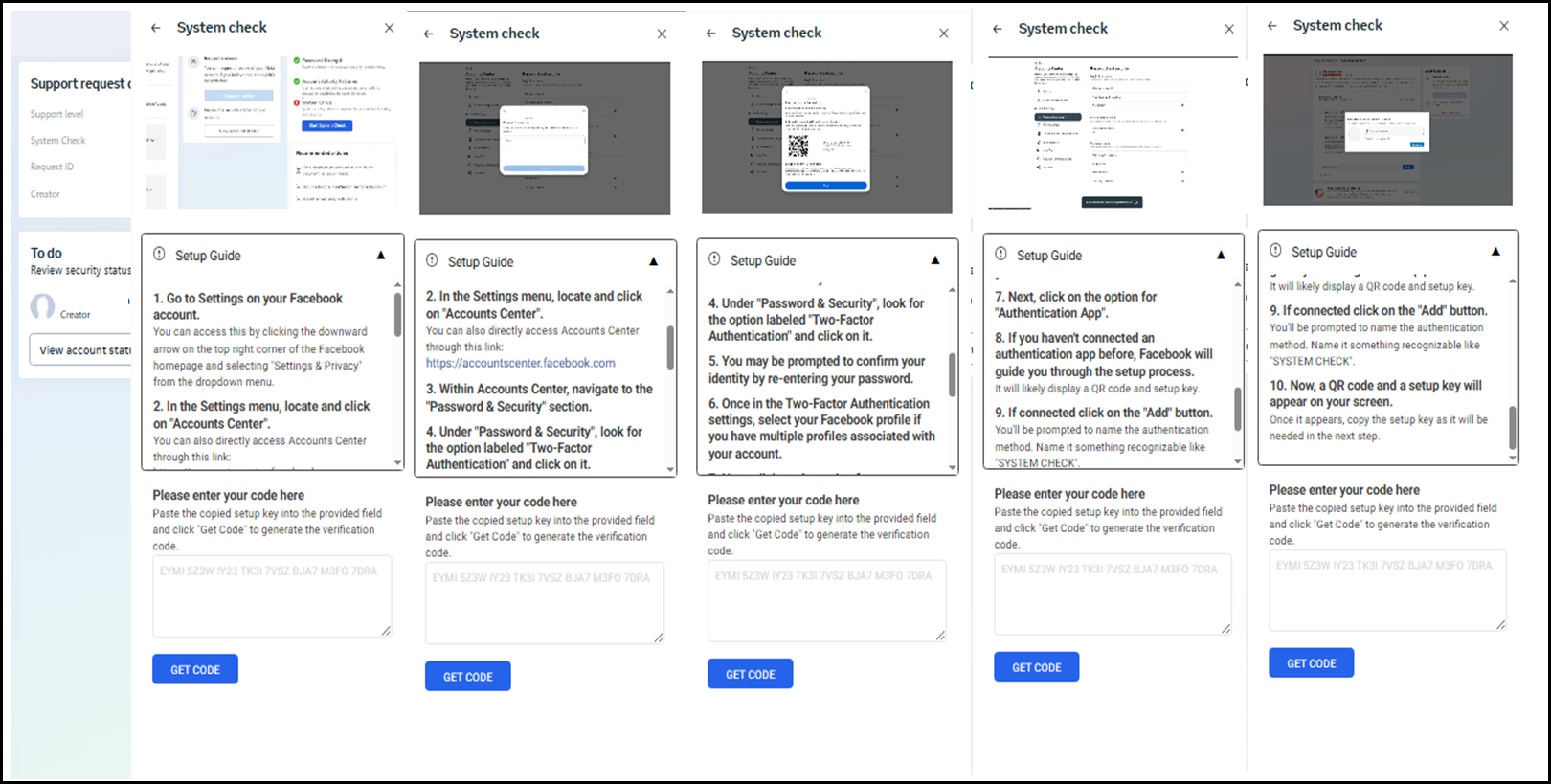
This method deceitfully instructs users on setting up Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) using an authenticator app controlled by the hackers themselves.
The malicious app, deceptively named “SYSTEM CHECK,” allows attackers to register their devices as trusted login methods, effectively hijacking the victim’s account.
In cases where victims do not engage with the chatbot support, attackers provide detailed step-by-step instructions disguised as self-help guides for resolving account suspension issues.
These instructions similarly lead users into unknowingly configuring malicious 2FA setups, granting attackers alternate avenues for account takeover.
This phishing campaign demonstrates a high degree of sophistication and meticulous attention to detail, leveraging realistic email templates, convincing landing pages, and interactive chatbot experiences.
Such tactics significantly increase the likelihood of successful credential theft and unauthorized account access.
Security experts urge businesses and individual users relying on social media platforms for advertising purposes to exercise heightened vigilance.
Users should meticulously verify sender addresses, carefully inspect URLs before interacting with links or buttons, and remain skeptical of unsolicited communications requesting sensitive information or immediate actions.
Prompt reporting of suspicious activities is essential in mitigating potential damage from evolving cyber threats targeting social media credentials.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links & Phishing Attacks With Threat Intelligence Lookup – Try for Free



.png
)
