Over the past year, malicious actors have been abusing OAST services for data exfiltration, C2 channel establishment, and multi-stage attacks by leveraging compromised JavaScript, Python, and Ruby packages.
OAST tools, initially designed for ethical researchers to perform network interactions, can also be exploited by threat actors for malicious purposes such as data exfiltration and pivot point identification.
A high-versioned npm package (adobe-dcapi-web) masquerades as an Adobe API to steal data, which uses obfuscated JavaScript to bypass geolocation checks and exfiltrate data to oastify.com upon reaching a non-Russian environment.
For the purpose of determining the user’s location, the code retrieves the public IP address and transmits a query to an external service (ipwhois.app).
If the location is detected as Russia (country_code “RU”), the code terminates the process to prevent the malware from executing in that region.
This technique is employed by threat actors to evade detection or limit the impact of their attacks in specific countries.
It identifies the operating system and checks for specific processes associated with VirtualBox and VMware to detect virtualized environments often used by threat actors in Russia to evade detection and analysis.
The malicious script harvests user and system information along with the public IP address on both Linux/macOS and Windows systems, then exfiltrates the data to the oastify.com endpoint and removes temporary files to cover its tracks.
Actor “drv0s” typosquatted the legitimate package “monolith” with “monoliht” on PyPI to steal victim’s hostname, username, and current working directory through malicious domains.
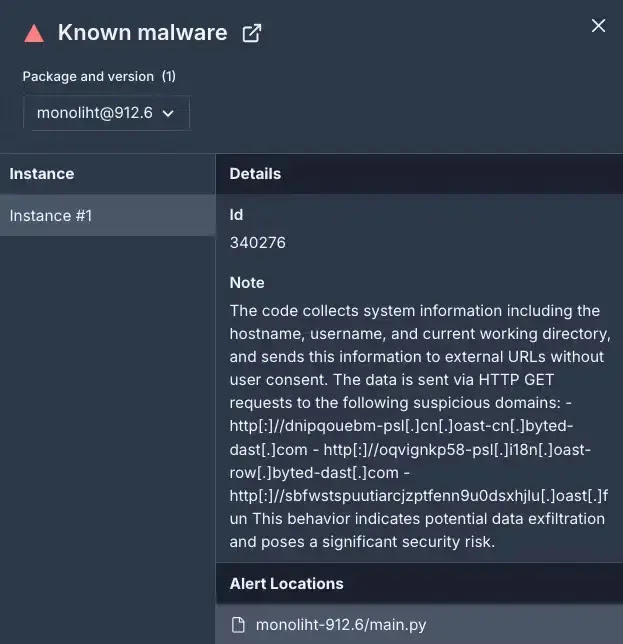
It collects system information such as hostname, username, and current working directory, sending the data to hardcoded URLs for exfiltration. This tactic helps attackers maintain persistence by distributing exfiltration across multiple domains.
Malicious RubyGems named chauuuyhhn, nosvemosssadfsd, and holaaaaaafasdf exfiltrate sensitive information through DNS requests to an attacker-controlled domain, oastify.com, bypassing basic intrusion detection systems.
The malicious script retrieves the victim’s external IP address and system information like hostname, username, working directory, and folder name.
It then constructs a DNS query containing this information and sends it to the attacker’s server, which is likely used for initial reconnaissance to gather information about potential targets for later attacks.
According to Socket, by providing developers and security engineers with the ability to proactively find and fix vulnerabilities, OAST provides extremely valuable security benefits.
Threat actors are exploiting OAST techniques to stealthily identify, exploit, and maintain access to vulnerable systems.
Ongoing efforts are crucial to leverage the benefits of OAST for defensive purposes while mitigating the risks of its misuse by attackers.
ANY.RUN Threat Intelligence Lookup - Extract Millions of IOC's for Interactive Malware Analysis: Try for Free
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs):
Malicious npm Package:
adobe-dcapi-web
Malicious PyPI Package:
monoliht
Malicious RubyGems Packages:
chauuuyhhnnosvemosssadfsdholaaaaaafasdf
Malicious OAST Endpoints:
- gbv6crrcecvsm77b41bxoih8wz2rqie7.oastify[.]com
- sbfwstspuutiarcjzptfenn9u0dsxhjlu.oast[.]fun
- dnipqouebm-psl.cn.oast-cn.byted-dast[.]com
- oqvignkp58-psl.i18n.oast-row.byted-dast[.]com
- kc0262r8oypagq3e8f89uaqmodu4i16q.oastify[.]com



.png
)
