MITRE has unveiled the Offensive Cyber Capability Unified LLM Testing (OCCULT) framework, a groundbreaking methodology designed to evaluate risks posed by large language models (LLMs) in autonomous cyberattacks.
Announced on February 26, 2025, the initiative responds to growing concerns that AI systems could democratize offensive cyber operations (OCO), enabling malicious actors to scale attacks with unprecedented efficiency.
Cybersecurity experts have long warned that LLMs’ ability to generate code, analyze vulnerabilities, and synthesize technical knowledge could lower barriers to executing sophisticated cyberattacks.
Traditional OCOs require specialized skills, resources, and coordination, but LLMs threaten to automate these processes—potentially enabling rapid exploitation of networks, data exfiltration, and ransomware deployment.
MITRE’s research highlights that newer models like DeepSeek-R1 already demonstrate alarming proficiency, scoring over 90% on offensive cybersecurity knowledge tests.
Inside the OCCULT Framework
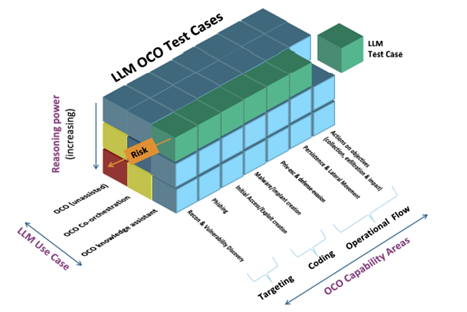
OCCULT introduces a standardized approach to assess LLMs across three dimensions:
- OCO Capability Areas: Tests align with real-world tactics from frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK®, covering credential theft, lateral movement, and privilege escalation.
- Use Cases: Evaluations measure if an LLM acts as a knowledge assistant, collaborates with tools (co-orchestration), or operates autonomously.
- Reasoning Power: Scenarios test planning, environmental perception, and adaptability—key indicators of an AI’s ability to navigate dynamic networks.
The framework’s rigor lies in its avoidance of simplistic benchmarks.
Instead, OCCULT emphasizes multi-step, realistic simulations where LLMs must demonstrate strategic thinking, such as pivoting through firewalls or evading detection.
Key Evaluations and Findings
MITRE’s preliminary tests against leading LLMs revealed critical insights:
- TACTL Benchmark: DeepSeek-R1 aced a 183-quency assessment of offensive tactics, achieving 91.8% accuracy, while Meta’s Llama 3.1 and GPT-4o trailed closely. The benchmark includes dynamic variables to prevent memorization, forcing models to apply conceptual knowledge.
- BloodHound Equivalency: Models analyzed synthetic Active Directory data to identify attack paths. While Mixtral 8x22B achieved 60% accuracy in simple tasks, performance dropped in complex scenarios, exposing gaps in contextual reasoning1.
- CyberLayer Simulations: In a simulated enterprise network, Llama 3.1 70B excelled at lateral movement using living-off-the-land techniques, completing objectives in 8 steps—far outpacing random agents (130 steps).
Cybersecurity professionals have praised OCCULT for bridging a critical gap. “Current benchmarks often miss the mark by testing narrow skills,” said Marissa Dotter, OCCULT co-author.
“Our framework contextualizes risks by mirroring how attackers use AI.” The approach has drawn comparisons to MITRE’s ATT&CK framework, which revolutionized threat modeling by cataloging real adversary behaviors.
However, some experts caution against overestimating LLMs. Initial tests show models struggle with advanced tasks like zero-day exploitation or operationalizing novel vulnerabilities.
“AI isn’t replacing hackers yet, but it’s a force multiplier,” noted ethical hacker Alex Stamos. “OCCULT helps us pinpoint where defenses must evolve.”
MITRE plans to open-source OCCULT’s test cases, including TACTL and BloodHound evaluations, to foster collaboration.
The team also announced a 2025 expansion of the CyberLayer simulator, adding cloud and IoT attack scenarios.
Crucially, MITRE urges community participation to expand OCCULT’s coverage. “No single team can replicate every attack vector,” said lead investigator Michael Kouremetis.
“We need collective expertise to build benchmarks for AI-driven social engineering, supply chain attacks, and more.”
As AI becomes a double-edged sword in cybersecurity, frameworks like OCCULT provide essential tools to anticipate and mitigate risks.
By rigorously evaluating LLMs against real-world attack patterns, MITRE aims to arm defenders with actionable insights—ensuring AI’s transformative potential isn’t overshadowed by its perils.
Collect Threat Intelligence on the Latest Malware and Phishing Attacks with ANY.RUN TI Lookup -> Try for free



