Microsoft continues its analysis and work with partners and customers to gather more information about the threat actor behind Solarwinds supply chain act that compromised SolarWinds and impacted multiple other organizations.
More than 18000 customers, including US government agencies, were believed to be affected by this massive attack. As a result, Microsoft has identified three new pieces of malware being used in late-stage activity by NOBELIUM – the actor behind the SolarWinds attacks, SUNBURST, and TEARDROP, which are:
- GoldMax
- Sibot
- GoldFinder
GoldMax
This GoldMax malware was identified to be sticking on networks as a scheduled task impersonating systems management software.
The scheduled task was named after the software that existed in the environment. It pointed to a subfolder in ProgramData named after that software, with a similar executable name. The executable, however, was the GoldMax implant.
The malware writes an encrypted configuration file to disk, while the configuration data is encrypted using the AES-256 encryption algorithm, CFB encryption mode, and the following cipher key: “4naehrkz5alao2jd035zjh3j1v1dvyyc” (key varies in different versions of GoldMax).
The AES encrypted configuration data is Base64-encoded using the custom Base64 alphabet “ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789-_” before it is stored in the configuration file on the file system.
When run, GoldMax decodes (Base64) and decrypts (AES-256) the configuration data to reveal a custom data structure comprised of the following dynamically generated and hardcoded values (delimited by ‘|’)

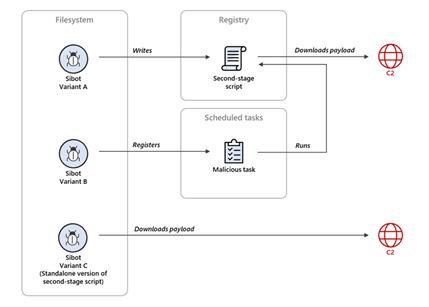
Sibot
Sibot is a two-way purpose malware implemented in VBScript. It is designed to achieve persistence on the infected machine. It downloads and executes a payload from a remote C2 server.
The VBScript file is given a name that impersonates legitimate Windows tasks and is stored either in the registry of the compromised system or in an obfuscated format on disk. The VBScript is then run via a scheduled task.
There are three variants of Sibot:
- Variant A only installs the second-stage script in the default registry value under the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\sibot.
- Variant B registers a scheduled task named Sibot and programmed to run daily. This task, C:\Windows\System32\Tasks\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\sibot, runs the following command-line daily:
- Variant C is a standalone version of the second-stage script. The second-stage script from Variant A is designed to be executed from the registry, this variant is designed to run from a file.
GoldFinder
GoldFinder is a custom HTTP tracer tool which logs the route or hops that a packet takes to reach a hardcoded C2 server.
When launched, the malware sends an HTTP request for a hardcoded IP address and logs the HTTP response to a plaintext log file.
GoldFinder uses the following hardcoded labels to store the request and response information in the log file:
- Target: The C2 URL
- StatusCode: HTTP response/status code
- Headers: HTTP response headers and their values
- Data: Data from the HTTP response received from the C2
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity, and hacking news updates.
Also Read
SolarWinds Hack – Multiple Similarities Found Between Sunburst Backdoor and Turla’s Backdoor
DOJ Says SolarWinds Hackers Accessed 3% of it’s Office 365 Mailboxes
New Malware Discovered in SolarWinds Attack that Used 7-Zip Code to Hide



.png
)
