The oil and gas sector faces a significant cybersecurity threat with the emergence of a new and sophisticated Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) infostealer known as Rhadamanthys Stealer.
This advanced phishing campaign has successfully reached its intended targets within the industry, raising concerns about the potential impact on critical infrastructure and sensitive data.
You can analyze such malware files, networks, modules, and registry activity with the ANY.RUN malware sandbox, and the Threat Intelligence Lookup that will let you interact with the OS directly from the browser.
Rhadamanthys Stealer
Rhadamanthys Stealer is a C++ information stealer that first appeared in August 2022. It is designed to target email, FTP, and online banking service account credentials.
The malware has evolved rapidly, with recent versions adding new stealing capabilities and enhanced evasion techniques.
The stealer can modify clipboard data to divert cryptocurrency payments to attackers and recover deleted Google Account cookies.
How do Hackers Bypass 2FA?
Live attack simulation Webinar demonstrates various ways in which account takeover can happen and practices to protect your websites and APIs against ATO attacks .
The deployment of Rhadamanthys Stealer came shortly after law enforcement took down the LockBit ransomware group, one of the most active Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) operations.
This timing suggests a possible connection or opportunistic pivot by cybercriminals in response to the crackdown on LockBit.
In early 2023, various vendors specializing in threat intelligence and anti-virus software identified the emergence of the MaaS Rhadamanthys Stealer. Presently, there has been a resurgence of this malware in the MaaS model.
Phishing Campaign Details
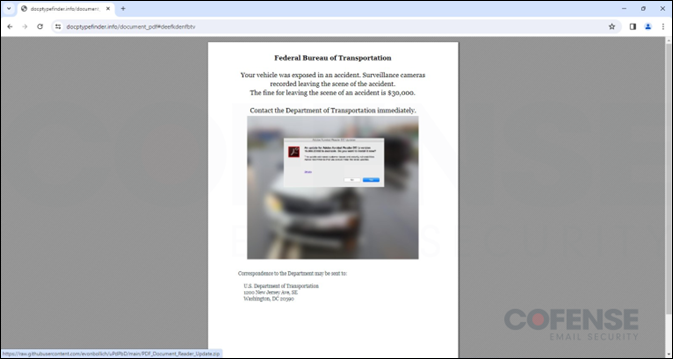
The campaign begins with a phishing email that employs various tactics to bypass secure email gateways and deliver the malware.
These emails contain a clickable PDF file hosted on a recently registered domain, which, when accessed, initiates the malware infection process, said Cofense researchers.

The phishing emails are part of a more significant trend of infostealer incidents that have escalated in early 2023, with incidents involving stealers more than doubling compared to the previous year.
The Rhadamanthys Stealer is distributed via the MaaS model and has been gaining popularity on the dark web.
Impact on the Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry is a critical sector increasingly reliant on digital technologies, making it a lucrative target for cybercriminals.
The successful infiltration of Rhadamanthys Stealer into this sector could lead to the theft of sensitive information, financial loss, and potential disruption of operations.
Sophisticated malware campaigns pose a significant threat to the industry. Organizations must remain vigilant and adopt robust cybersecurity measures to mitigate the risks, according to the Cofense report.
This includes implementing advanced threat detection and prevention systems, regularly updating software and security patches, and conducting employee awareness and training programs to prevent social engineering attacks.
Additionally, organizations should monitor their network traffic, implement access controls, and perform regular vulnerability assessments to identify and address any potential security gaps.
The emergence of Rhadamanthys Stealer as a new threat to the oil and gas industry underscores the need for continuous monitoring and improvement of cybersecurity defenses.
Companies in the sector should be aware of the methods used by cybercriminals, such as phishing campaigns, and ensure that employees are trained to recognize and respond to such threats.
You can block malware, including Trojans, ransomware, spyware, rootkits, worms, and zero-day exploits, with Perimeter81 malware protection. All are extremely harmful, can wreak havoc, and damage your network.
Stay updated on Cybersecurity news, Whitepapers, and Infographics. Follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter.



.png
)
