A breakthrough framework named SCAVY has been introduced to proactively detect memory corruption targets that could potentially lead to privilege escalation in the Linux kernel.
Presented at the prestigious USENIX Security Symposium in August 2024, the framework aims to address long-standing gaps in understanding how memory corruption can be exploited to compromise system integrity.
SCAVY’s developers have hailed it as a new tool in the fight against Linux kernel vulnerabilities, urging researchers to take proactive measures.
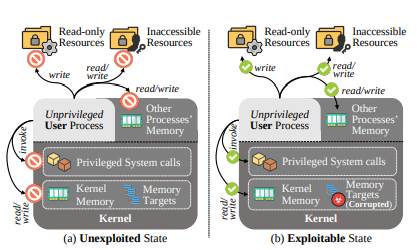
Privilege escalation attacks typically exploit memory corruption vulnerabilities in the Linux kernel. By targeting specific memory locations, attackers can elevate their permissions, enabling unauthorized access to resources such as files or processes.
Historically, defenders have focused on identifying known vulnerabilities, but only a small subset of kernel memory structures—those with function pointers—have been systematically explored.
Approximately 90% of Linux kernel structures remain overlooked, leaving a substantial attack surface unprotected.
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams? - Analyse Malware Files & Links with ANY.RUN Sandox -> Try for Free
Enter SCAVY: A Game-Changer
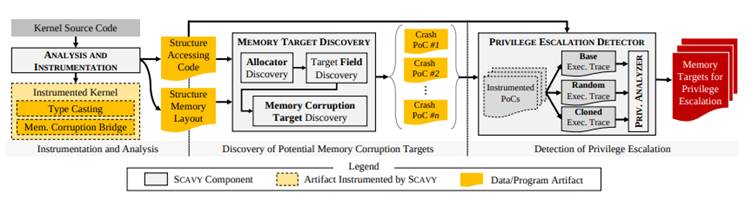
SCAVY (short for “Scavenger”) is a cutting-edge automated framework designed to identify kernel memory corruption targets beyond the traditionally prioritized function pointers.
Unlike previous tools that focus narrowly on specific vulnerabilities, SCAVY adopts a broader, vulnerability-agnostic approach. The tool systematically explores kernel memory structures to detect areas that, if corrupted, could escalate privileges.
SCAVY combines advanced fuzzing techniques with differential analysis to evaluate how memory corruption changes access to sensitive resources. By comparing system behavior with and without corruption, SCAVY pinpoints exploitable fields in kernel structures.
Key Innovations of SCAVY:
- Broader Scope: SCAVY examines all memory fields in Linux kernel structures, including the 88.7% previously unexplored.
- Automated Target Discovery: The framework autonomously identifies memory corruption targets through efficient fuzzing and execution-state reasoning.
- Defense-Bypassing Capabilities: SCAVY can uncover privilege escalation vectors that evade existing defenses such as Control Flow Integrity (CFI) and Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR).
Through its comprehensive analysis, SCAVY discovered 955 proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits, highlighting 17 previously unknown memory corruption targets spread across 12 kernel structures.
SCAVY also demonstrated its potential by developing six exploits for five known CVE vulnerabilities. These exploits showcased how new memory targets could make once-dismissed vulnerabilities exploitable.
A Real-World Case Study:
One notable target identified by SCAVY is the vm_area_struct::vm_file field. In practice, modifying this field enabled attackers to manipulate temporary files and gain unauthorized access to privileged files like /etc/passwd.
The researchers implemented a PoC using the CVE-2022-27666 vulnerability to exploit this memory target without triggering traditional kernel defenses, such as Supervisor Mode Access Prevention (SMAP).
SCAVY not only enhances attackers’ capabilities but also provides defenders with unprecedented opportunities to proactively address vulnerabilities.
By identifying broader categories of memory corruption targets, the framework equips developers with insights to secure kernel structures more effectively.
For example, targeted protections such as slab cache randomization or write-once memory policies could be deployed for fields identified by SCAVY, reducing system overhead compared to broader defenses.
The findings highlight the urgent need for kernel developers and security researchers to re-evaluate the definition of privilege escalation targets within the Linux kernel ecosystem.
The research team behind SCAVY has made the framework’s source code open for future studies, providing the broader community with a powerful new tool. Details, documentation, and the PoC exploits are available via the SCAVY GitHub repository.
While SCAVY introduces a robust methodology for identifying single-field memory corruption targets, the researchers acknowledge the need for further work.
Automating multi-field target analysis and integrating SCAVY into larger exploit-generation pipelines could unlock even greater potential for both attack simulation and defense mechanism design.
SCAVY marks a revolution in addressing security concerns in the Linux kernel, bridging critical gaps in automated target discovery for privilege escalation.
By broadening the attack surface and introducing efficient strategies to counter these exploits, SCAVY is poised to become an essential asset in securing Linux systems worldwide.
Integrating Application Security into Your CI/CD Workflows Using Jenkins & Jira -> Free Webinar



