Researchers uncovered an information-stealing malware called Raccoon that delivered by the Fallout and RIG Exploit Kits to steal sensitive data from compromised victims’ devices.
Raccoon malware reportedly hacked more than 100,000 computers around the world since April 2019, and the malware believed to be delivered from a team of Russian hackers.
Malware doesn’t use any stealthy infection technique, and it steals the various sensor data such as important data, including credit card information, cryptocurrency wallets, browser data, and email credentials
Malware authors selling the Raccoon malware as a malware-as-a-service model in underground forums, and become one of the top 10 most-referenced malware on the market in 2019.
Also, the actors providing support for the buyer and handling the malware is a quick-and-easy way to make money stealing sensitive data without a huge personal investment.
The raccoon is written in C++ and is developed to compromise both 32 and 64-bit operating systems, and it is mainly used the exploit kits to deliver into victims’ machines.
Researchers from cybereason found a strong indication of this malware that infected hundreds of thousands of endpoints globally across organizations and individuals in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Some indication refers that the malware attribute to the well-known member, glad0ff. Alexuiop1337 – authors of predator stealer and the further analyse found Raccoon stealers database in February of 2019 that was created by glad0ff, and the person or team activity advertising this malware in an underground forum.
In an underground forum where this malware being advertised, many individuals write reviews for Raccoon, and the malware authors also have written a detailed write up about the Raccoon in a blog post.
Raccoon Malware Infection Process
Threat actors choose defect medium including exploit kits, phishing attacks, and bundled malware to deliver the Raccoon malware.
Exploit kits are developed to trigger the vulnerabilities in the target system while the victims browsing online and visiting malicious sites from where the exploit code will be delivered into the victim’s devices without any sort of user interaction.
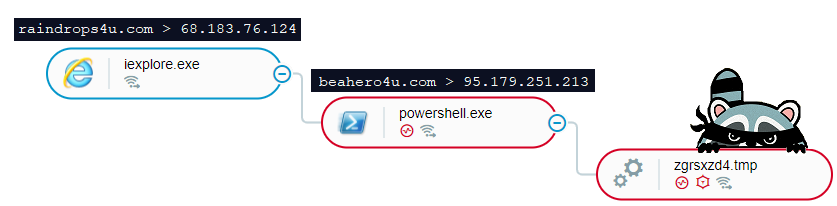
The attacker initially leverages the Fallout exploit kit that helps to spawn the malicious PowerShell script from IE and connect to the remote server to download the main payload.
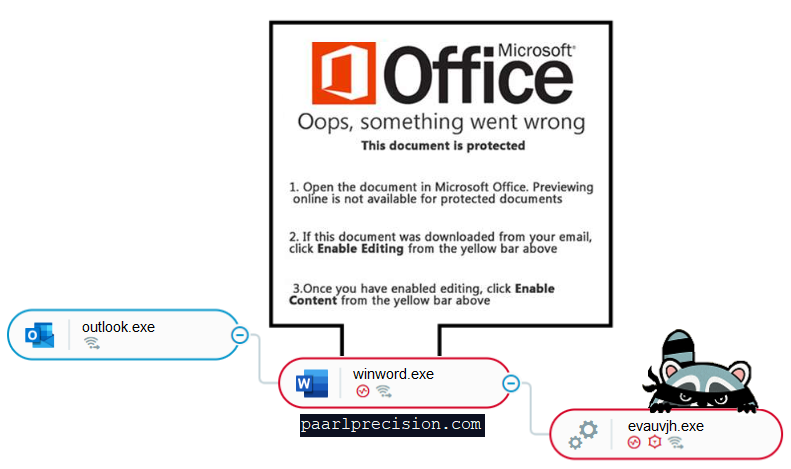
In another scenario, Attackers using phishing and social engineering techniques to trick users into executing malicious content that delivered via email with an attached malicious word or PDF document.
“attackers use an email with an attached Word document. Upon opening the Word document and enabling macros, the macro code creates a connection to a malicious domain and downloads the main payload of the info stealer.”
Once the loader successfully executed in the targeted machine, Raccoon unpacks itself and connect to the c2 server to verify the Raccoon’s Bot ID, it downloads a compressed zip file with multiple different DLLs.
Later it checks the infected device local setting to confirm the language whether it matches the following language: Russian, Ukrainian, Belarussian, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Armenian, Tajik, and Uzbek. if it doesn’t match then the malware aborts itself.
Finally, its perform various stealing operation such as screen capture of the target machine, collects system information such as username, IP address, language settings, OS version, information on installed apps, and CPU and memory information, stealing the browser information, extract the outlook account information, stealing the cryptocurrency wallets.
“As malware authors choose to develop MaaS, they must partake in many of the same activities as a legitimate SaaS business: marketing efforts, relying on positive reviews, responsive customer support, and regularly improving features in their product. We only expect this trend to continue into 2020 and push the evolution of MaaS forward.”cybereason concluded.
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity and hacking news updates.



.png
)
