Researchers from Kaspersky seek out more IIS backdoors after the discovery of ‘Owowa’, a malicious IIS module deployed by attackers on Microsoft Exchange Outlook Web Access servers, stealing credentials and enabling remote command execution from OWA.
Also in 2021, Kaspersky noticed ‘ProxyLogon-type’ vulnerabilities within Microsoft Exchange servers, enabling threat actors to maintain persistent, update-resistant, and relatively stealthy access to the IT infrastructure of a targeted organization; be it to collect emails, update further malicious access, or clandestinely manage compromised servers that can be leveraged as malicious infrastructure.
Recently in 2022, the company discovered ‘SessionManager’. According to the report, SessionManager has been used against NGOs, government, military and industrial organizations in Africa, South America, Asia, Europe, Russia, and the Middle East, from at least March 2021.
“Because of the similar victims, and use of a common OwlProxy variant, we believe the malicious IIS module may have been leveraged by the GELSEMIUM threat actor, as part of espionage operations”, Kaspersky.
What is a SessionManager?
It is developed in C++, SessionManager is a malicious native-code IIS module loaded by some IIS applications, to process legitimate HTTP requests that are continuously sent to the server.
These malicious modules generally look forward to seemingly legitimate but specifically crafted HTTP requests from their operators, trigger actions based on the operators’ hidden instructions if any, then transparently pass the request to the server for it to be processed just like any other request.
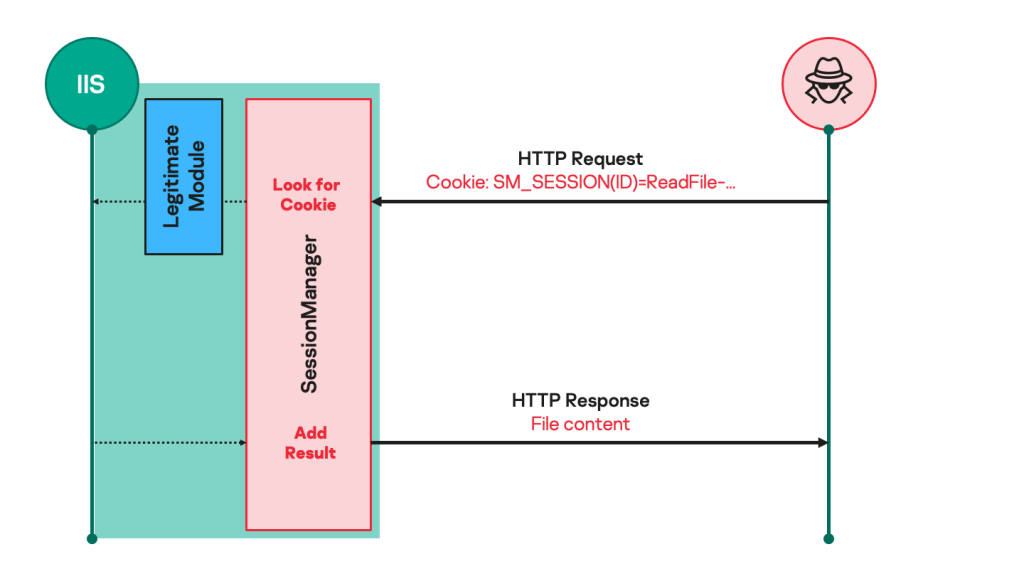
The capabilities of the SesssionManager include:
- Reading, writing to, and deleting arbitrary files on the compromised server.
- Executing arbitrary binaries from the compromised server, also known as “remote command execution”.
- Establishing connections to arbitrary network endpoints that can be reached by the compromised server, as well as reading and writing in such connections.
The report says; that though still investigating the attacks, Kaspersky found that most of the malware samples identified earlier were still deployed on 34 servers of 24 organizations (still running as late as June 2022).
Furthermore, months after the initial discovery, they were still not flagged as malicious by “a popular online file scanning service”. The tools that operators attempted to download and execute from SessionManager include a PowerSploit-based reflective loader for the Mimikatz DLL, Mimikatz SSP, ProcDump, and a legitimate memory dump tool from Avast.
To avoid detection by security products, researchers say SessionManager operators attempted additional malicious execution by running launcher scripts through the Windows services manager command line. From November 2021, operators tried to leverage custom PyInstaller-packed Python scripts to obfuscate command execution attempts.
Kaspersky security experts believe the SessionManager IIS backdoor was leveraged in these attacks by the Gelsemium threat actor as part of a worldwide espionage operation.
Since 2014, this hacking group has been active, when some of its malicious tools were spotted by G DATA’s SecurityLabs while investigating the “Operation TooHash” cyber-espionage campaign. In 2016, new Gelsemium indicators of compromise surfaced in a Verint Systems presentation during the HITCON conference.
According to Pierre Delcher, a Senior Security Researcher at Kaspersky, “The exploitation of exchange server vulnerabilities has been a favorite of cybercriminals looking to get into targeted infrastructure since Q1 2021.”
“The recently discovered SessionManager was poorly detected for a year and is still deployed in the wild. In the case of Exchange servers, we cannot stress it enough: the past year’s vulnerabilities have made them perfect targets, whatever the malicious intent, so they should be carefully audited and monitored for hidden implants if they were not already”, he added.
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity updates.



.png
)
