In a stark revelation of the escalating cyber threat landscape, Flashpoint’s latest intelligence report highlights the alarming rise in compromised credentials and malware infections.
In 2024, threat actors managed to steal an unprecedented 3.2 billion login credentials, marking a 33% increase from the previous year.
This staggering figure underscores the growing reliance of cybercriminals on stolen data to fuel malicious activities such as ransomware attacks and data breaches.
The Rise of Infostealers
A significant portion of these stolen credentials approximately 2.1 billion were sourced from information-stealing malware, commonly referred to as infostealers.
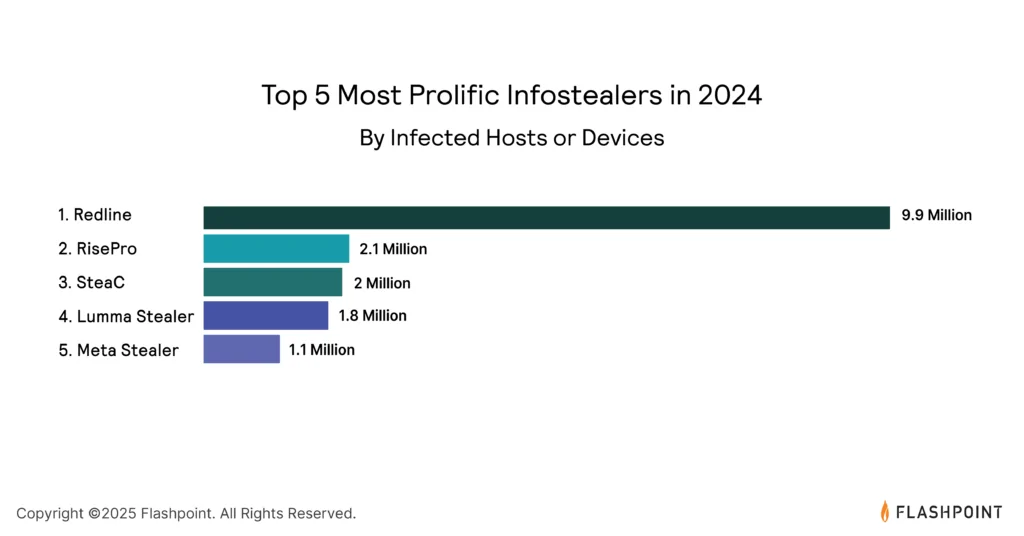
These malicious tools have become a primary vector for high-impact cyber threats, including ransomware and data breaches.
Their simplicity, effectiveness, and low operational costs have propelled infostealers to the forefront of cyber threats, infecting over 23 million devices worldwide.
This meteoric rise in infostealers highlights the need for organizations to enhance their security measures against these evolving threats.
The threat landscape is further complicated by the increasing number of vulnerabilities.
In 2024, Flashpoint identified 37,302 vulnerabilities, with over 39% having publicly available exploit code.
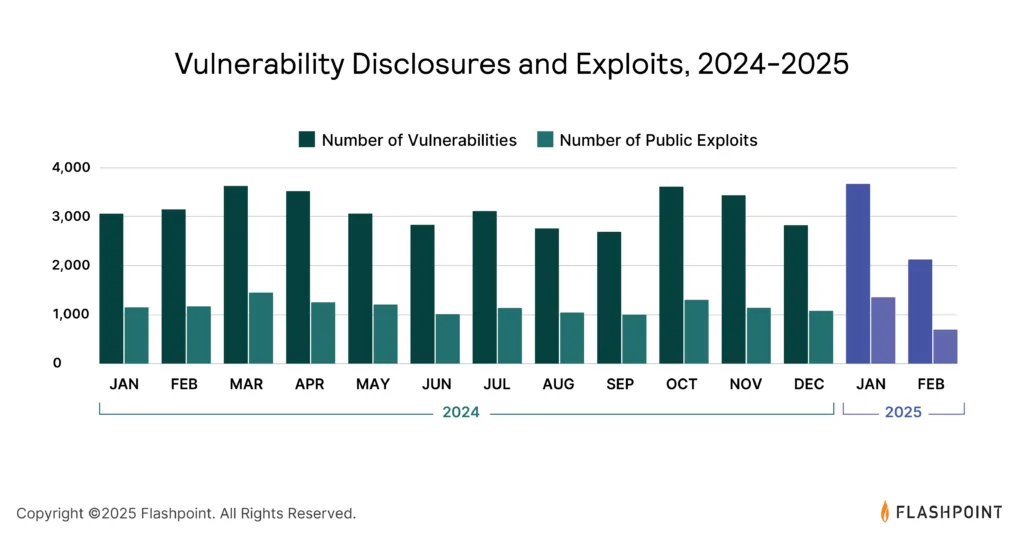
This allows threat actors to exploit these weaknesses, gaining unauthorized access to systems.
As the attack surface continues to expand, security teams must prioritize vulnerability management based on exploitability rather than severity alone.
Ransomware and Data Breaches on the Rise
The consequences of these compromised credentials and vulnerabilities are evident in the surge of ransomware attacks and data breaches.
Ransomware attacks increased by 10% across all sectors in 2024, following an 84% increase the previous year.
Notably, the five most prolific ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) groups were responsible for over 47% of reported attacks.
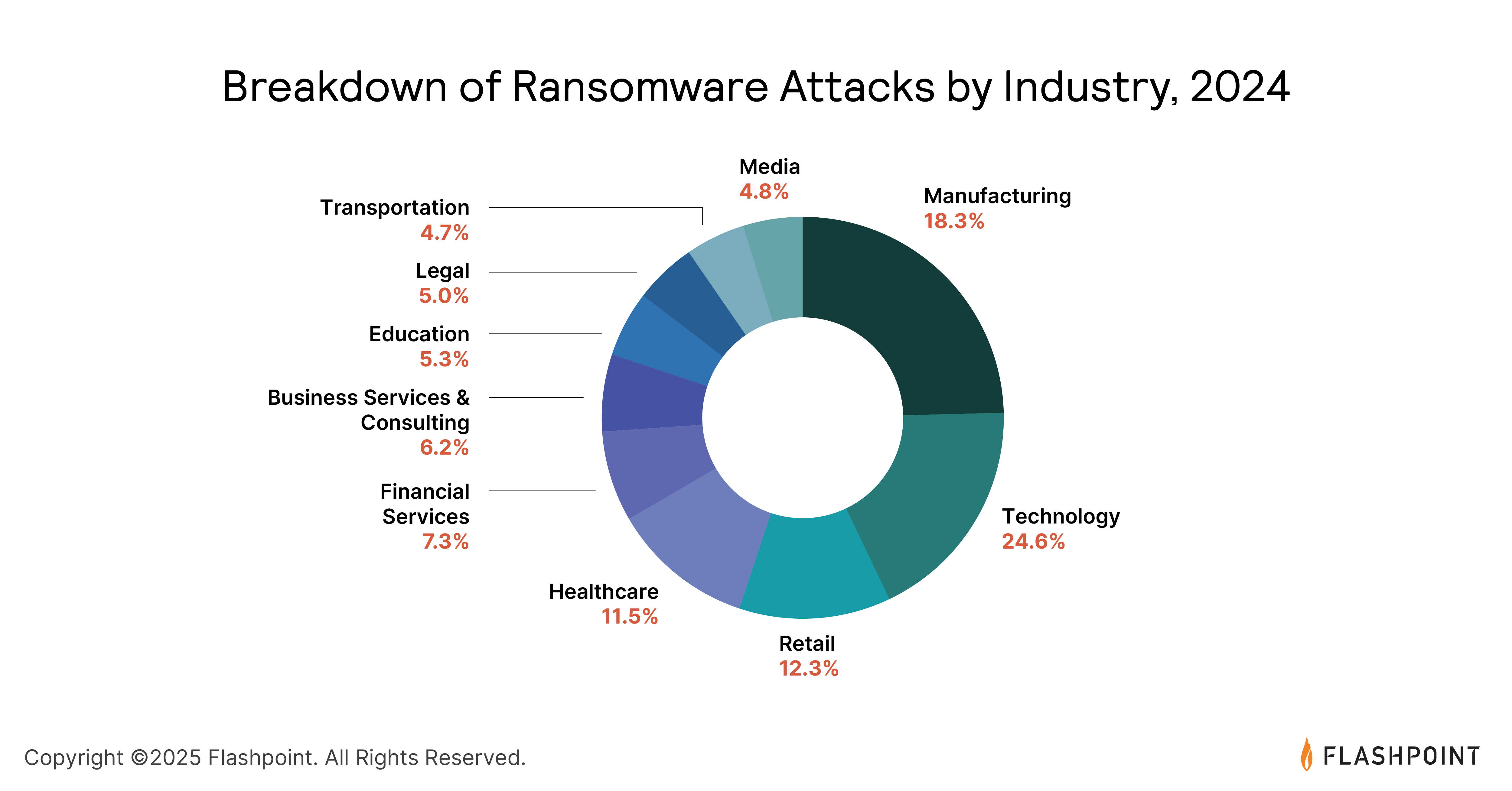
Additionally, data breaches saw a year-over-year increase of approximately 6%.
These trends emphasize the importance of maintaining robust defenses and incident response strategies to mitigate these threats.
As the cyber threat landscape evolves, organizations must adopt a proactive and holistic approach to security.
The Flashpoint 2025 Global Threat Intelligence Report provides critical insights into these emerging threats, equipping leaders and cybersecurity practitioners with the necessary intelligence to strengthen their security posture and safeguard critical assets.
With over 200 million credentials already compromised in 2025, the urgency for enhanced security measures has never been more pressing.
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams? – Analyse Malware Incidents & get live Access with ANY.RUN -> Start Now for Free.



.png
)
