In a significant cybersecurity revelation, researchers have uncovered a large-scale campaign exploiting a Windows policy loophole to deploy malware while evading detection.
The attack hinges on the abuse of a legacy driver, Truesight.sys (version 2.0.2), which contains vulnerabilities that allow attackers to bypass modern security measures.
This driver, part of Adlice’s RogueKiller Antirootkit suite, has been exploited in over 2,500 distinct variants, each digitally signed to avoid detection mechanisms.
The campaign, active since mid-2024, leverages the exception in Microsoft’s driver signing policy that permits older drivers signed before July 29, 2015, to load on the latest Windows versions.
By exploiting this loophole, attackers bypassed Microsoft’s Vulnerable Driver Blocklist and other detection systems like LOLDrivers.
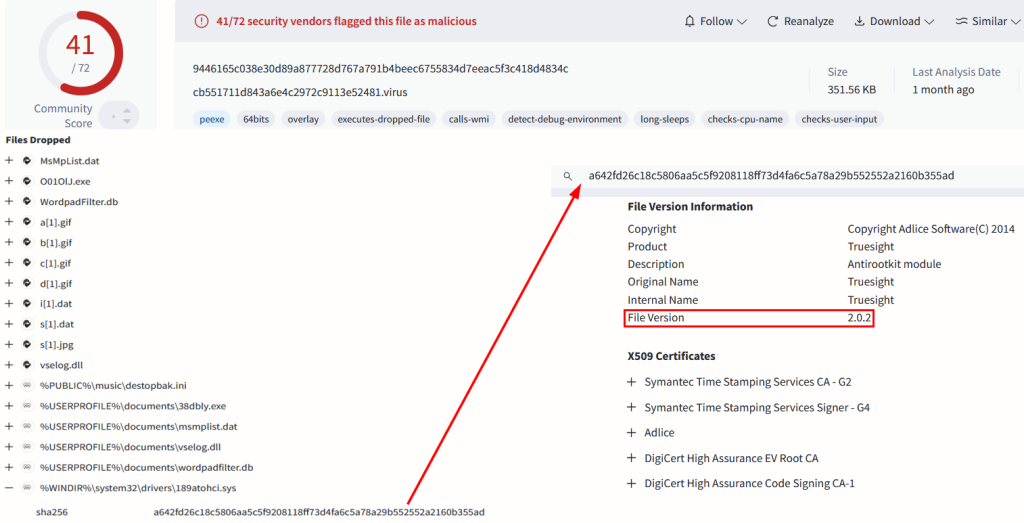
The Truesight driver version 2.0.2 was specifically chosen as it retains exploitable code while evading blocklist attributes applied to newer driver versions.
To further obfuscate their activities, attackers modified specific parts of the Portable Executable (PE) file structure of the driver, altering checksum fields and padding bytes without invalidating its digital signature.
This technique enabled the generation of thousands of unique file hashes for the same driver, effectively neutralizing hash-based detection systems.

Multi-Stage Infection Chain and Advanced Techniques
Initial-stage malware samples masquerade as legitimate applications and are distributed via phishing campaigns involving deceptive websites and messaging app channels.
These samples act as downloaders for subsequent payloads, including the EDR/AV killer module designed to disable endpoint security solutions by exploiting the Truesight.sys vulnerability.
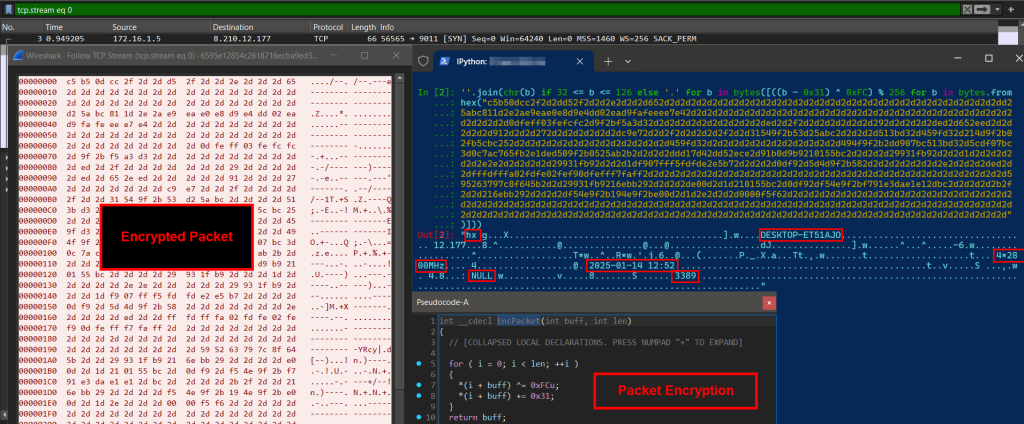
The EDR/AV killer module communicates with the vulnerable driver using a custom IOCTL code (0x22E044) to terminate processes associated with security tools running as protected processes (PP/PPL).
According to the Check Point Research, this enables attackers to disable critical defenses before deploying final-stage payloads such as Gh0st RAT a powerful remote access trojan capable of data theft and system control.

The campaign’s infrastructure is hosted primarily in public cloud regions in China, with approximately 75% of victims located in China and others spread across Asia.
The attackers’ use of advanced techniques such as DLL side-loading, encrypted payloads disguised as image files (e.g., PNG or JPG), and commercial protectors like VMProtect underscores their sophistication and intent to evade detection for extended periods.
Microsoft Responds with Updated Blocklist
Following reports from researchers, Microsoft updated its Vulnerable Driver Blocklist on December 17, 2024, to include all variants of the exploited Truesight driver.
However, organizations are advised to manually apply these updates as they are not auto-deployed frequently.
This campaign highlights critical gaps in traditional detection methods like hash-based systems and emphasizes the need for proactive hunting rules targeting unknown vulnerabilities.
It also underscores the importance of robust security mechanisms like Microsoft’s blocklist that rely on multi-attribute detection rather than simple hash matching.
The discovery serves as a stark reminder for defenders to stay vigilant against evolving threats that exploit overlooked vulnerabilities in legacy systems while leveraging sophisticated evasion techniques.
Free Webinar: Better SOC with Interactive Malware Sandbox for Incident Response, and Threat Hunting - Register Here



.png
)
