Cryptocurrency exchange Bybit suffered a sophisticated smart contract exploit on February 21, 2025, resulting in the theft of 401,346.76 ETH (approximately $1.2 billion at the time of the incident).
The attack vector leveraged advanced proxy contract manipulation through malicious delegatecall operations, marking one of the most technically complex exchange hacks in Web3 history.
Exploit Timeline and Key Components
The incident unfolded when attackers executed a precisely engineered transaction (0x46dee) targeting Bybit’s hot wallet proxy contract (0x1db92e2e).
Forensic analysis reveals the attack chain began with a seemingly routine interaction with the GnosisSafe contract (0x34cfac), a widely used multi-signature wallet implementation.
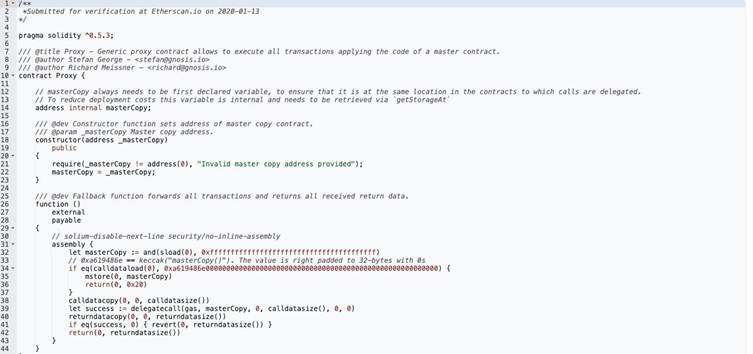
Central to the breach was the deployment of a malicious implementation contract at address 0x9622142, designed to hijack the proxy’s storage mechanism.
Security researchers highlight the attacker’s use of nested delegatecall operations to bypass traditional security checks:
{
“to”: “0x96221423681a6d52e184d440a8efcebb105c7242”,
“operation”: 1, // DelegateCall
“data”: “0xa9059cbb000000000000000000000000bdd077f651ebe7f7b3ce16fe5f2b025be29695160000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000”
}
This payload triggered a critical storage modification in the proxy contract’s slot0, effectively replacing the legitimate implementation address.
The malicious contract’s transfer function contained purpose-built logic to manipulate the proxy’s fundamental operations:
def transfer(address _to, uint256 _value) payable:
require calldata.size – 4 >= 64
require _to = _to
stor0 = _to # Overwrites proxy implementation pointer
Attack Execution and Fund Exfiltration
Following the successful contract hijacking, the perpetrators executed a 90 USDT test transaction before initiating the primary theft.
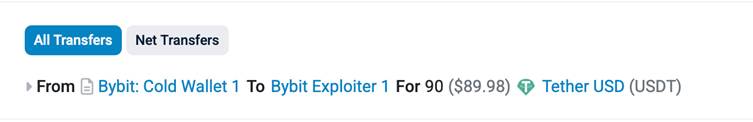
On-chain records show three coordinated transfers draining the wallet’s entire ETH balance through a series of batched transactions.
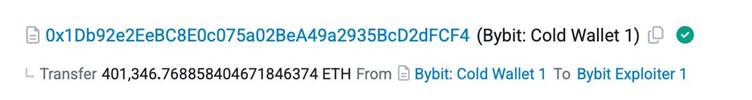
The final transfer, visible in block 18,432,107, moved 401,346.76 ETH to attacker-controlled addresses.
Security analysts note the exploit’s technical sophistication, particularly the abuse of proxy upgrade patterns combined with storage slot manipulation.
“This represents a paradigm shift in smart contract exploitation,” remarked Blockchain Intelligence Group lead researcher Dr. Elena Marquez.
“By combining delegatecall chaining with storage hijacking, the attackers essentially rewrote the wallet’s fundamental operating logic.”
Ongoing Investigations and Industry Response
As of March 6, 2025, Bybit’s security team continues working with chain analytics firms to trace fund movements across multiple blockchain networks.
Preliminary findings suggest the attackers utilized decentralized exchange aggregators and cross-chain bridges to obfuscate transaction trails.
The incident has prompted renewed calls for enhanced proxy contract safeguards, with the Ethereum Foundation announcing an emergency EIP (Ethereum Improvement Proposal) to modify delegatecall functionality in smart contract architectures.
Exchange operators are advised to implement real-time proxy storage monitoring systems and conduct immediate audits of all upgradeable contract implementations.
While Bybit has committed to covering user losses through insurance reserves, the exploit underscores the critical importance of robust smart contract governance mechanisms.
As the Web3 community awaits further technical disclosures, the incident serves as a stark reminder of the evolving challenges in decentralized system security.
Collect Threat Intelligence on the Latest Malware and Phishing Attacks with ANY.RUN TI Lookup -> Try for free



