A new recently patched remote code execution bug in PHP7 lets hackers hijack the websites running on some NGINX and php-fpm configurations. The vulnerability can be tracked as CVE-2019-11043.
The vulnerability resides in env_path_info in the file fpm_main.c of the FPM component. The FPM is the php-fpm module used for performance enhancement.
The manipulation of the file leads to memory corruption, chaining with other vulnerabilities allows attackers to remotely execute arbitrary code on web servers with vulnerable configurations.
PHP7 Vulnerability Detected
The vulnerability was found by security researcher Andrew Danau in a Realworld CTF program that took place between September 14th to 16th, 2019.
“When Andrew Danau sent %0a (newline) byte in the URL, the server response was peculiar. It returns more data than should be there. And, the amount of extra data was related to the number of bytes after %0a inside the URL”
```
location ~ [^/]\.php(/|$) {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+?\.php)(/.*)$;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
fastcgi_pass php:9000;
...
}
}
```
This sort of response could cause a memory corruption issue and may lead to information disclosure. Andrew, CTF players Emil and Omar decide to investigate further and exploit the issue.
“The reason for this issue is under the hood of the Nginx+fastcgi bundle, in particular, in a fastcgi_split_path directive and a regexp tricks with newlines. Because of %0a character, Nginx will set an empty value to this variable, and fastcgi+PHP will not expect this,” reads wallarm blog post.
Emil published a PoC exploit, which shows certain conditions need to be satisfied to exploit this vulnerability.
- Nginx + php-fpm to configured request forwarding to php-fpm
- The fastcgi_split_path_info directive must be there and contain a regexp starting with ^ and ending with $.
- The PATH_INFO variable to be assigned by fastcgi_param
- No checks in place such try_files $uri =404 or if (-f $uri) to determine the existence of the file.
- If the conditions satisfied the exploit works on PHP 7+ versions. The bug may also present in older versions.
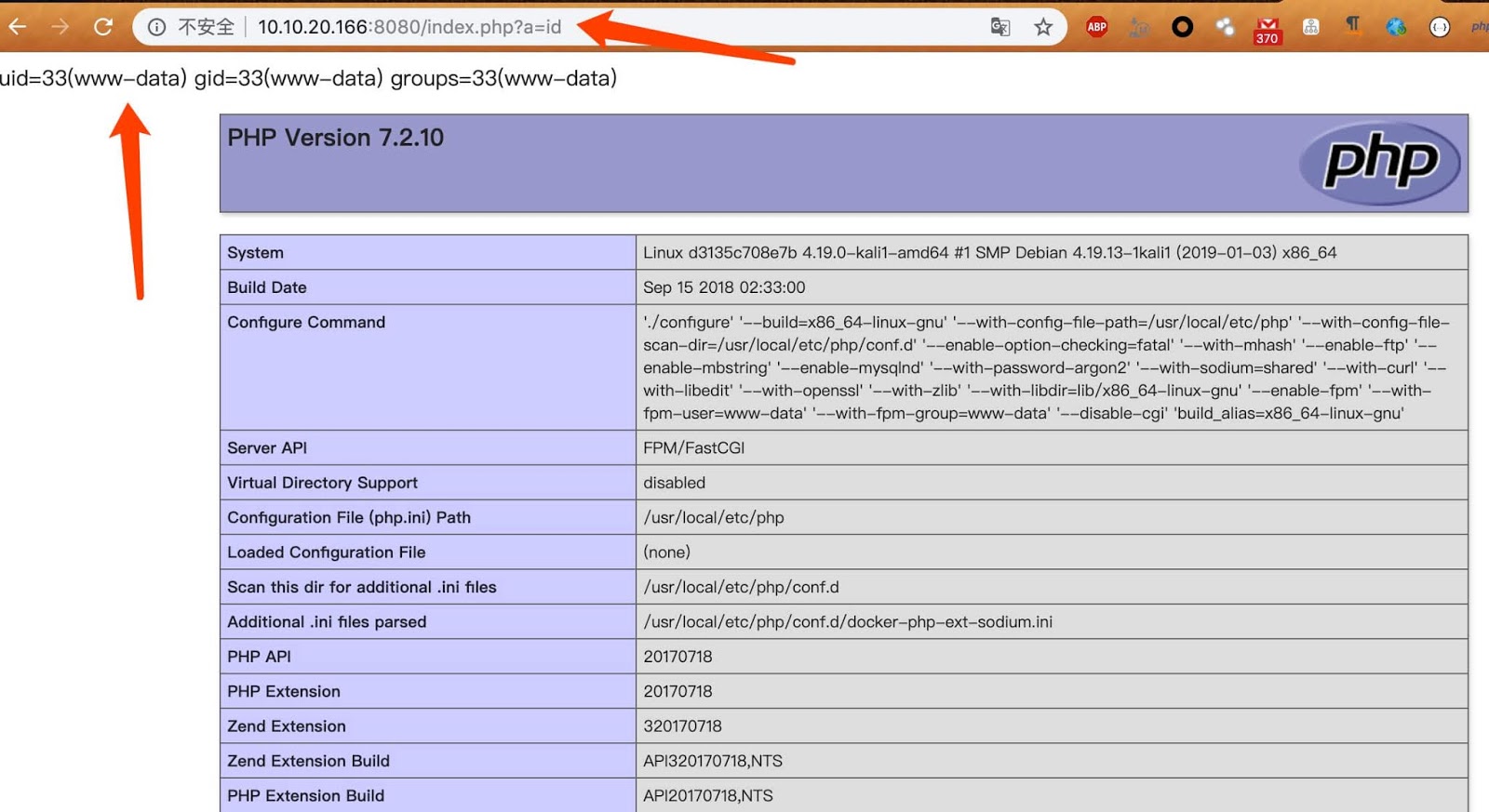
So if every condition satisfies attackers be able to execute payloads by appending ?a= to the script.
Mitigations
Following are the mitigations from Nextcloud
- If you are not using NGINX then this vulnerability will not affect you.
- Users are recommended to update with the latest versions 7.1.33,7.2.24 & 7.3.11.
- Recommended removal of $request_uri
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity and hacking news updates.



.png
)
