TrickBot is one of the top modular banking malware that primarily targets financial information of users’ and also it acts as a dropper for other malware.
The malware was first spotted in 2016 and it was mostly distributed via malvertising campaign, it evolves from a small banking trojan to an Access-as-a-Service model.
Trickbot New Malware Campaign
Unit 42 security researchers observed a new distribution campaign that delivered through phishing emails that has the subject lines as payroll or annual bonuses.
The campaign includes embedded links points to the legitimate Google Docs document which contains links to download the malicious file from Google drive. For further obfuscation email delivered through SendGrid.
According to Unit 42 research, “the email appeared to be originated from individuals at .edu email addresses and then attackers used SendGrid’s EDS to distribute the malware.”
The email contains the attractive text and links, once the user clicks on the link it gets redirected to the Google Doc document that contains the link of the file that hosted on the Google drive.

From the Google drive, two executable downloaders appear as word document gets downloaded to the victim’s computer. Both the downloaders are signed with a digital certificate.
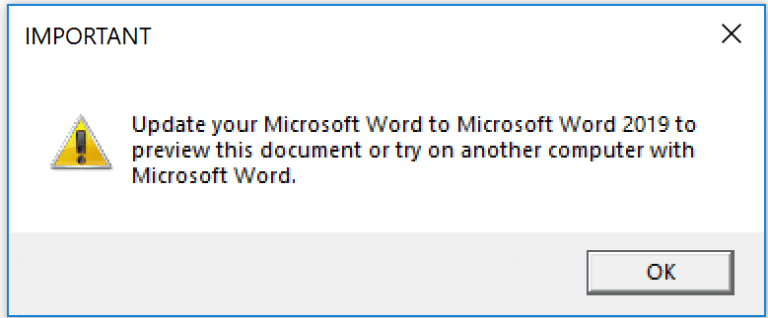
Upon opening the document it shows a fake pop-up that asks users to use Microsoft word 2019 and gives to option to close or to click ok. Regardless of the user response, the pop-up get’s closed and the downloaders proceed further downloading the Trickbot payload.
Recent versions of the Trickbot includes a spamming component called TrickBooster that send spam emails from the Trickbot infected computer. It is also capable of leveraging Server Message Block (SMB) vulnerability for propagating to other systems on the same network.
This campaign legitimate services such as SendGrid and GSuite to obfuscate malicious activity. Researchers recommend organizations preventing download or execution of the unknown executable on the endpoint.
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity and hacking news updates.



.png
)
