In a groundbreaking Check Point Research (CPR) analysis, vulnerabilities have been uncovered in several popular dating applications, cumulatively boasting over 10 million downloads.
This investigation focused on the inherent risks associated with the use of geolocation data—a feature that, while designed to connect users with potential matches in their vicinity, may compromise their privacy.
Among the scrutinized apps, “Hornet,” a widely used gay dating platform, was found to have significant security flaws that could reveal the exact locations of its users.
CPR’s research highlighted a technique to pinpoint user coordinates using distance information.
Despite Hornet’s efforts to safeguard user privacy by disabling the display of distances, CPR developed a method that achieved location accuracy within 10 meters in controlled experiments.
Following the discovery, Hornet’s developers have taken steps to mitigate these risks, reducing location accuracy to 50 meters.
However, the initial vulnerability posed a substantial privacy risk to its users.
Understanding Geolocation & Possible Dangers
Geolocation technology can pinpoint the real-world geographic location of a device with varying degrees of accuracy.
AI-Powered Protection for Business Email Security
Trustifi’s Advanced threat protection prevents the widest spectrum of sophisticated attacks before they reach a user’s mailbox. Try Trustifi Free Threat Scan with Sophisticated AI-Powered Email Protection .
While this technology offers numerous benefits, it also presents several privacy and security risks, such as unauthorized data access, unintended sharing with third parties, and potential exploitation by malicious actors.
Methodology for Determining Distance
CPR’s methodology involved sorting users by ascending the distance order and using two known distances to estimate the target user’s location.

Additionally, by registering an additional account with controllable coordinates, researchers could refine their search and narrow the distance between the target and the auxiliary account, achieving remarkable precision.
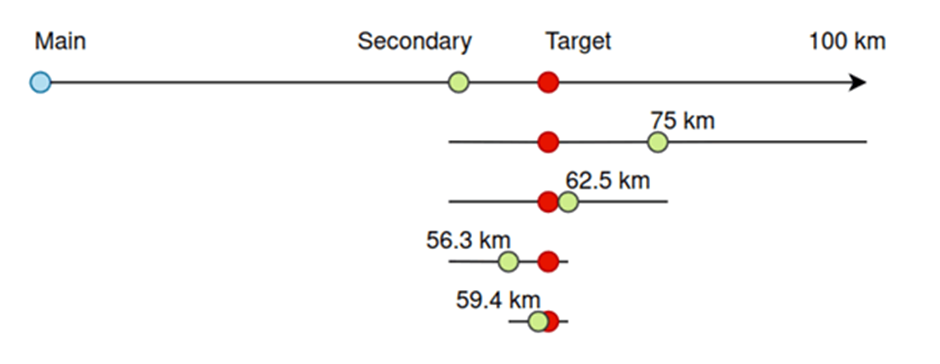
Trilateration Methodology
The research utilized a two-step trilateration process, initially identifying two possible candidate locations before selecting the correct solution with information from a third reference point.
This method allowed for an astonishingly high accuracy in determining user locations.
The vulnerabilities discovered in the Hornet dating app underscore the significant privacy risks of exposing user geolocation.
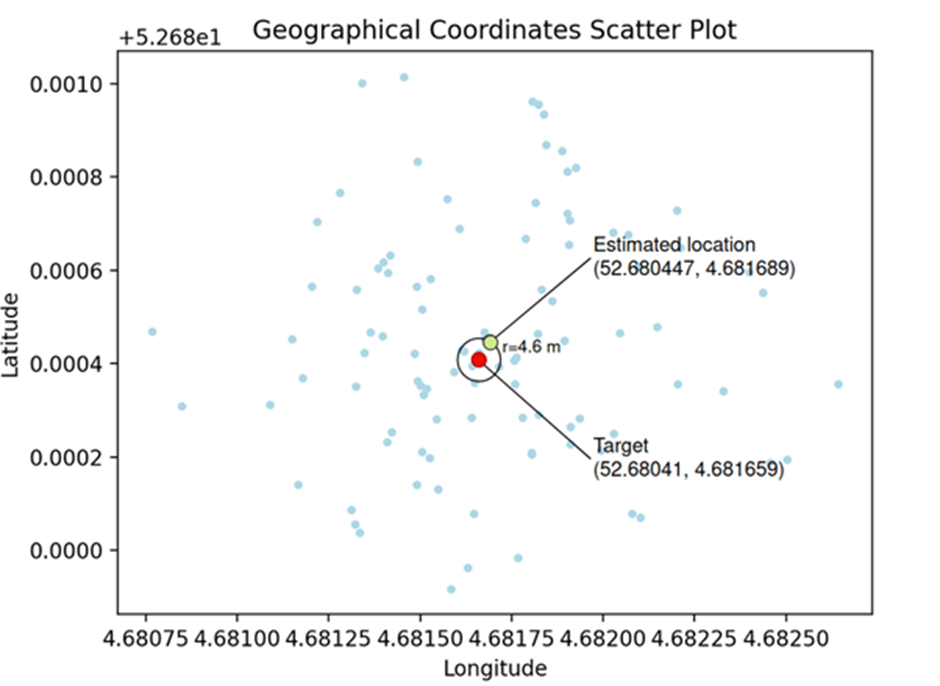
Despite improvements made by Hornet’s developers, the potential for location determination remains.
CPR advises users to exercise caution with app permissions and to disable location services to protect their privacy.
This proactive approach can prevent apps from tracking movements and sharing personal data with external entities, ensuring a safer online dating experience.
Stay updated on Cybersecurity news, Whitepapers, and Infographics. Follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter.


