Security researchers at Zscaler ThreatLabz have identified a new sophisticated malware family called CoffeeLoader, which emerged around September 2024.
This advanced loader employs numerous techniques to bypass security solutions and evade detection while delivering second-stage payloads, particularly the Rhadamanthys stealer.
CoffeeLoader utilizes a specialized packer named Armoury that leverages the GPU to execute code, hindering analysis in virtual environments.
The malware implements call stack spoofing, sleep obfuscation, and Windows fibers to defeat endpoint security software.
Additionally, it uses a domain generation algorithm (DGA) as a backup communication channel and certificate pinning to prevent TLS man-in-the-middle attacks.
Rhadamanthys Stealer: A Potent Threat
The primary payload delivered by CoffeeLoader is the Rhadamanthys stealer, a C++ information-stealing malware that has been active since late 2022.

Rhadamanthys targets a wide range of sensitive data, including credentials from web browsers, VPN clients, email clients, chat applications, and cryptocurrency wallets.
Recent updates to Rhadamanthys have introduced AI-powered capabilities, such as optical character recognition (OCR) for extracting cryptocurrency wallet seed phrases from images.
According to the Report, this feature, known as “Seed Phrase Image Recognition,” significantly enhances the malware’s threat to cryptocurrency users.
Infection Chain and Distribution
CoffeeLoader has been observed being distributed via SmokeLoader, with both malware families sharing behavioral similarities.
Rhadamanthys, on the other hand, is primarily spread through malicious Google advertisements that mimic legitimate software platforms like AnyDesk, Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Notepad++.
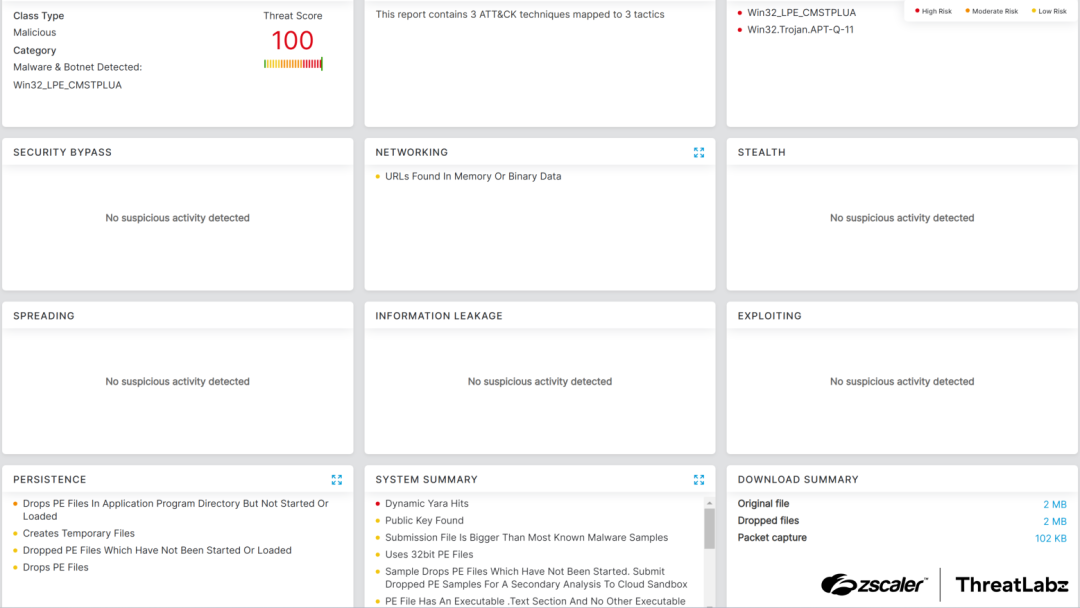
The infection chain typically consists of three components: the Dropper, the Rhadamanthys Loader (second shellcode), and the Rhadamanthys Stealer (Nsis module).
This layered approach allows the malware to maintain stealth and efficacy throughout the infection process.
As cybercriminals continue to evolve their tactics, the combination of CoffeeLoader’s advanced evasion techniques and Rhadamanthys’ powerful stealing capabilities presents a significant threat to organizations and individuals alike.
Security professionals must remain vigilant and implement robust defense mechanisms to protect against these sophisticated malware families.
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams? – Analyse Malware, Phishing Incidents & get live Access with ANY.RUN -> Start Now for Free.



.png
)
