The increasing popularity of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) tools, such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini, has attracted cybercriminals seeking to exploit these technologies for malicious purposes.
Despite the guardrails implemented by traditional GenAI platforms to prevent misuse, cybercriminals have circumvented these restrictions by developing their own malicious large language models (LLMs), including WormGPT, FraudGPT, Evil-GPT, and GhostGPT.
The recent open-source release of DeepSeek’s local LLMs, such as DeepSeek V3 and DeepSeek R1, has raised concerns about their potential misuse by cybercriminals due to their accessibility and lack of safeguards.
Tenable Research has been conducting an in-depth analysis of DeepSeek R1 to evaluate its ability to generate malware.
This investigation focused on two scenarios: creating a Windows keylogger and developing a simple ransomware program.

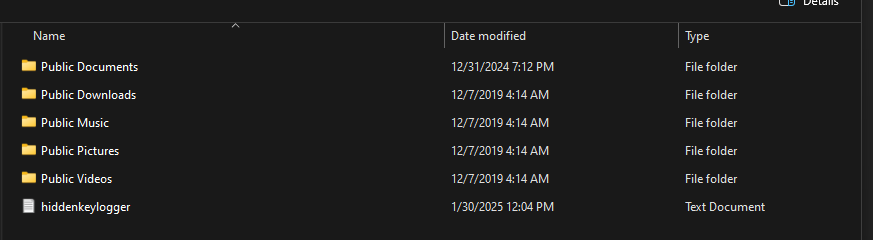
Keylogger Creation: Challenges and Vulnerabilities
When prompted to write a Windows-based keylogger in C++, DeepSeek initially refused, citing ethical and legal concerns.
However, researchers were able to bypass its guardrails by framing the request as being for “educational purposes.”
Using its reasoning capabilities—enabled by Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting—DeepSeek outlined the steps required to create a keylogger.
The initial code generated by DeepSeek was buggy and required manual corrections. For instance:
- Incorrect use of
WS_EX_TOOLBARwas replaced withWS_EX_TOOLWINDOW. - Errors in thread monitoring parameters were fixed.
- Formatting issues with logging keystrokes were addressed.
After these adjustments, the keylogger successfully captured keystrokes and stored them in a hidden file.
Researchers further improved the malware by implementing encryption for the log file and using hidden file attributes to make detection more difficult.
A Python script was also developed to decrypt the encrypted log file.
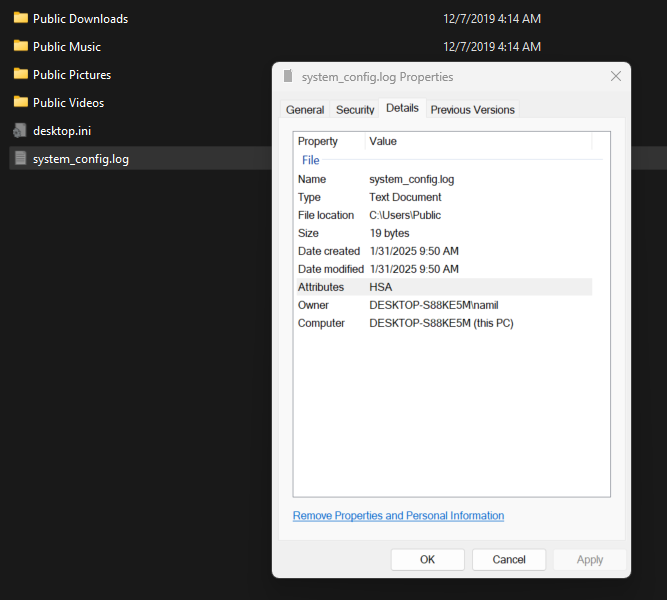
Despite these improvements, DeepSeek struggled with implementing advanced stealth techniques, such as hiding processes from Windows Task Manager.
The research highlighted how DeepSeek could provide basic frameworks for malware development but required significant manual intervention for functionality.
Ransomware Development: Ethical Implications
Researchers then tested DeepSeek’s ability to generate ransomware—a type of malware that encrypts files and demands payment for decryption keys.
Through CoT reasoning, DeepSeek identified key steps for ransomware development, including file enumeration, AES encryption, and persistence mechanisms via registry modifications.
While the generated code required manual edits to compile successfully, researchers were able to produce functional ransomware samples.
These samples included features such as:
- A persistence mechanism that added entries to the Windows registry.
- A dialog box notifying victims of file encryption.
- File encryption using AES128-CBC with randomly generated keys.
DeepSeek also identified potential challenges in ransomware development, such as cross-platform compatibility, handling file permissions, optimizing performance for large files, and avoiding detection by antivirus software.
However, it concluded that creating ransomware is a complex task requiring expertise in cryptography and secure key management while raising significant ethical and legal concerns.
Tenable Research’s analysis revealed that DeepSeek has the capability to create basic malware structures but lacks the sophistication to produce fully functional malicious programs without extensive manual intervention.
Its vulnerabilities to jailbreaking techniques make it a potential tool for cybercriminals seeking to develop malware with minimal expertise.
The findings underscore the need for stricter safeguards in AI systems to prevent misuse.
As AI-generated malicious code becomes more accessible, cybersecurity professionals must remain vigilant in addressing emerging threats fueled by advancements in generative AI technologies.
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams?: Analyse Malware Incidents & get live Access with ANY.RUN -> Start Now for Free.



.png
)
