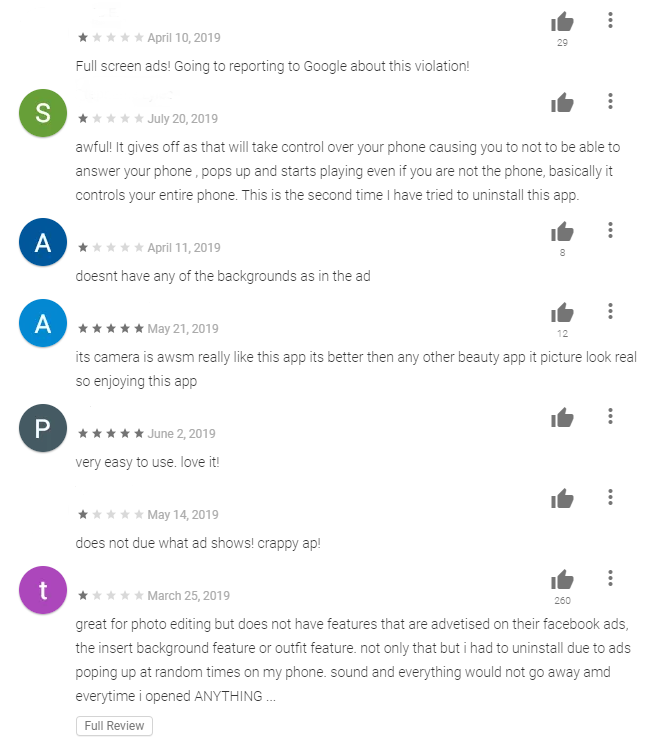
Researchers discovered a new type of strange malware that targeting android device, and use the victim’s mobiles to provide fake ratings in Google play store apps for malicious apps.
You may have seen reviews in Google Play apps that seem to be talking about something unrelated to the apps. this malware named as Trojan-Dropper.AndroidOS.Shopper.a. give it five stars, while dozens of users rate it as 1 start.
Cybercriminals used this trojan to boosting malicious, fake and adware apps and increasing the number of installations.
Also, the Trojan will perform various malicious activities such as display advertising messages on the infected device, create shortcuts to ad sites, and perform other actions.
Apart from reviewing with fake comments, the malware evades the user’s detection, the installation window is concealed by the app’s “invisible” window.
Shopper.a also enables the AccessibilityService to install the new apps from the 3rd party services.
According to the Kaspersky report, “With permission to use it, the malware has almost limitless possibilities for interacting with the system interface and apps. For instance, it can intercept data displayed on the screen, click buttons, and emulate user gestures.”
Shopper.a Infection Process
Once the malware enters the device via a malicious app, it decrypts and downloads the payload once the victim unlocked the device.
Soon after it collects the device information country, network type, vendor, smartphone model, email address, IMEI, IMSI and forward it to the c2 server that controlled by the attacker.
In response, the malware receives the set of commands to start to perform a variety of the following operation:
- Open links received from the remote server in an invisible window (whereby the malware verifies that the user is connected to a mobile network).
- After a certain number of screen unlocks, hide itself from the apps menu.
- Check the availability of AccessibilityService rights and, if not granted, periodically issue a phishing request to the user to provide them.
- Disable Google Play Protect.
- Create shortcuts to advertised sites in the apps menu.
- Download apps from the third-party “market” Apkpure[.]com and install them.
- Open advertised apps on Google Play and “click” to install them.
- Replace shortcuts to installed apps with shortcuts to advertised sites.
- Post fake reviews supposedly from the Google Play user.
- Show ads when the screen is unlocked.
Shopper.a mostly widespread in Russia with (28.46%), Brazil (18.70%) and third to India (14.23%).
IOCs
MD5
- 0a421b0857cfe4d0066246cb87d8768c
- 0b54b822683a70b9d4a3af08a2d506b2
- 0b682e9cae5b8623fc3e62048623dcdb
- 0ea057c5294a6cbfeffd2e91ae945981
- 0eb70afbb011916facf075f80cc07605
- 1a6d60b97fdeb29afc0bd16fcaa92d3a
- 1e82c197037ff0e21ccbc8c6161144c8
- 1e937712ca84a6364226a35e2fd9a550
- 1f13ba11ceba8ddb6e0faf61e6d8da23
- 2d234accdc400c892657b8568e217593
- 2d755050c896aed9701aa78a3668bf72
- 3a5ed5f6ecaa71f5c7b7447c1f451144
- 3ad3f270aef9f56d9117f711a3783a4a
- 3b1a2420c4afc019a19481a6f4282894
- 3c312fbb18e7822f87334a9366baf9fc
- 3cadeea4dedaf7d7db8b84d52cd6caea
- 03ccb6adbe12daef1b40f7a6d7d26dbc
- 3dc6538239e90e51233789c5876ccb71
- 3fe0e78d451bb8389f1d8cb5009c3452
- 4a3099f300741123e3c18b3a6d587ed8
- 4e44fb07073ea46390ea94ce26d7d737
- 5bbc06fc3058b76ee09d3cce608ebdda
- 5c316045836c4b4110552cc80af2fe75
- 5e313e5e4e37e87633ea342a24c27534
- 6ec7e5334f8b11499c150ba28f06e78c
- 7a0d40f3598a91fc1206b3b2bdd49c2c
- 7c68eb0bd93d8cf27539d2ff7da5bb15



.png
)
