Google has announced an upgrade to its Safe Browsing technology to provide Chrome users with real-time protection against phishing, malware, and other malicious sites.
This enhancement is set to revolutionize how users navigate the web, ensuring safety without compromising privacy.
For over 15 years, Google Safe Browsing has been a bulwark against online threats, safeguarding users across more than 5 billion devices worldwide.
However, the rapid evolution of online threats necessitates a more dynamic approach to protection.
Google’s latest update to Safe Browsing introduces real-time URL checks in Chrome’s Standard protection mode, a feature designed to adapt as swiftly as the threats it aims to counter.
Mitigating Vulnerability & 0-day Threats
Alert Fatigue that helps no one as security teams need to triage 100s of vulnerabilities.:
- The problem of vulnerability fatigue today
- Difference between CVSS-specific vulnerability vs risk-based vulnerability
- Evaluating vulnerabilities based on the business impact/risk
- Automation to reduce alert fatigue and enhance security posture significantly
AcuRisQ, that helps you to quantify risk accurately:
Traditionally, Chrome has protected users by comparing visited sites against a locally stored list of known unsafe sites, updated every 30 to 60 minutes.

However, this method struggles against the fleeting nature of modern malicious sites, which may exist for less than 10 minutes.
The introduction of real-time, privacy-preserving URL protection aims to close this window of vulnerability.
How Real-time Protection Works
The new system enhances security by checking URLs against a constantly updated list on the Safe Browsing server, capturing malicious sites as soon as they’re identified.
This process involves several privacy-preserving steps:
- URL Obfuscation: Chrome converts the URL into truncated, encrypted hash prefixes.
- Privacy-Preserving Checks: These encrypted hashes are sent to a privacy server, which anonymizes the data before forwarding it to the Safe Browsing server.
- Real-time Response: The Safe Browsing server matches these hashes against its database, alerting Chrome to any threats.
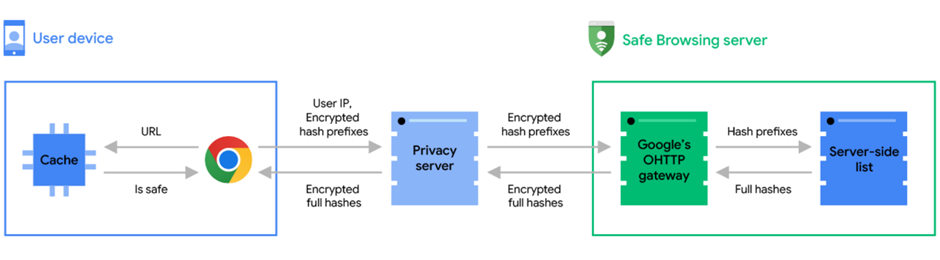
This method ensures that Google does not see the user’s IP address, and the privacy server, operated by Fastly, cannot decrypt the URL hashes, maintaining user privacy throughout the process.
Staying Speedy and Reliable
Despite the additional step of real-time checks, Google has implemented several measures to maintain a smooth browsing experience.
These include caching known-safe URLs and employing a fallback mechanism for slow or unsuccessful requests, ensuring that browsing remains fast and reliable.
For Chrome Users
With the latest Chrome update, users will automatically benefit from real-time phishing protection in Standard protection mode without needing to share their browsing history with Google.
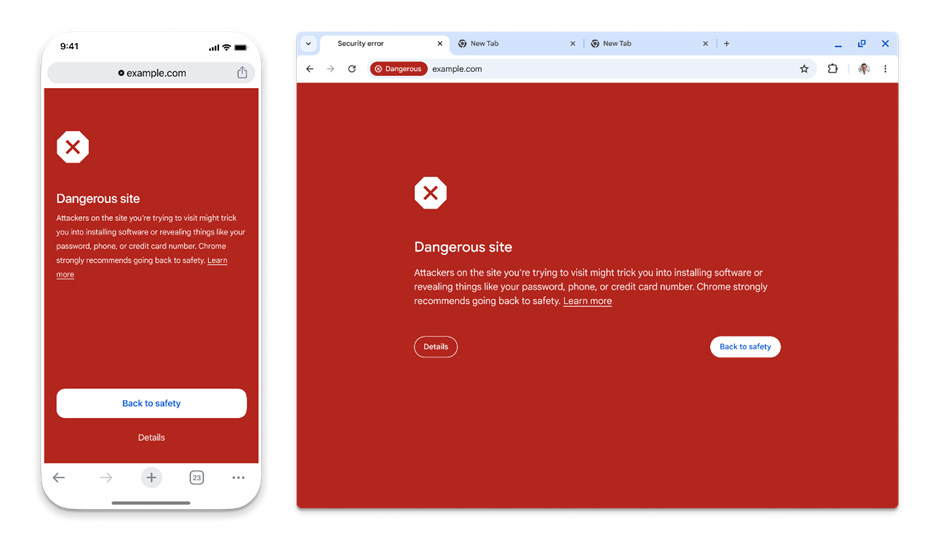
The real-time protection feature is enabled by default for Chrome users, including enterprise environments.
For the feature to function correctly, enterprises may need to configure their networks to allow traffic to the Fastly privacy server.
Additionally, Google plans to extend these protections to developers through the Safe Browsing API for non-commercial use, further expanding the ecosystem of secure web browsing.
Google’s introduction of real-time phishing protection in Chrome significantly advances online security.
By leveraging privacy-preserving technology, Google ensures users enjoy a safer browsing experience without sacrificing speed or privacy.
As the digital threat landscape continues to evolve, these enhancements to Safe Browsing demonstrate Google’s commitment to staying ahead of malicious actors and safeguarding the web for everyone.
With Perimeter81 malware protection, you can block malware, including Trojans, ransomware, spyware, rootkits, worms, and zero-day exploits. All are incredibly harmful and can wreak havoc on your network.
Stay updated on Cybersecurity news, Whitepapers, and Infographics. Follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter.
.webp?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)


.png
)
