Cybersecurity researchers from SafeBreach Labs have revealed new vulnerabilities in Google’s Quick Share file-transfer utility for Windows, including a critical flaw that allows attackers to execute code on targeted devices.
The findings, disclosed this week, highlight risks in the widely used tool—even after Google patched earlier issues reported in 2024.
The QuickShell Exploit Chain
Initially presented at DEF CON 32 (2024), the “QuickShell” research exposed 10 vulnerabilities in Quick Share, a cross-platform tool for transferring files between Android, Windows, and ChromeOS devices.
The utility employs Bluetooth, Wi-Fi Direct, and other protocols to enable peer-to-peer sharing.
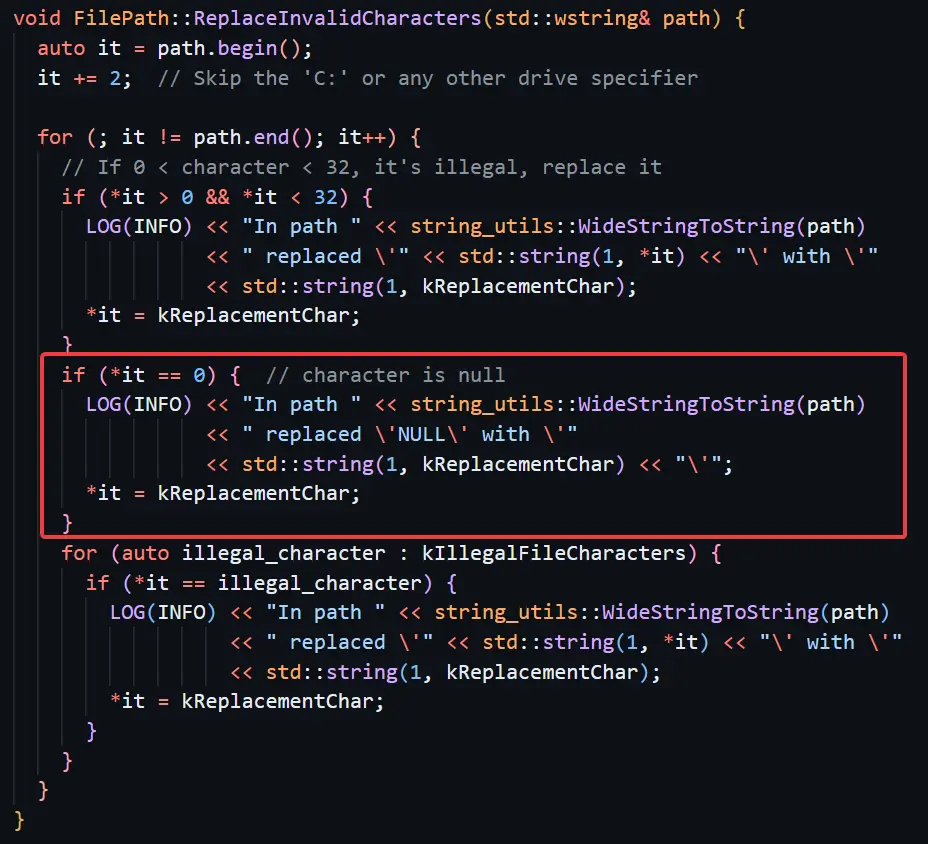
Researchers Shir Tamari and Shmuel Cohen discovered that attackers could chain these flaws to achieve remote code execution (RCE) on Windows systems, enabling full device takeover.
Key weaknesses included:
- Unauthorized file writes (CVE-2024-38272)
- Directory traversal exploits
- Multiple denial-of-service (DoS) vulnerabilities
Google addressed these flaws in early 2024, but follow-up tests revealed gaps in the fixes.
Patch Bypass: New Attack Vector Emerges
In August 2024, SafeBreach researchers revisited the patched vulnerabilities and identified two critical oversights:
- Incomplete DoS Fix
A vulnerability causing crashes via invalid UTF-8 filenames (e.g., \x00FileName) was only partially resolved. Google blocked filenames starting with null terminators, but researchers bypassed this by using other invalid UTF-8 sequences (e.g., \xc5\xffFileName), crashing the application. - Unauthorized File Write Bypass
The original exploit (CVE-2024-38272) allowed sending files without user consent. Google’s fix auto-deleted “unknown” files post-transfer. However, researchers found that sending two files with identical payload IDs tricked Quick Share into deleting only one, leaving the second malicious file in the user’s Downloads folder.
Google addressed the new flaws in late 2024, assigning CVE-2024-10668 to the file-write bypass. Patches have been rolled out via automatic updates.
“This case underscores the challenges of securing complex, protocol-diverse applications,” said Tamari. “While Google responded swiftly, layered defenses and rigorous patch verification are essential.”
Implications for Users
Quick Ship pre-installs on newer Windows PCs amplify risks. Users are urged to:
- Ensure Quick Share is updated to the latest version.
- Disable the tool if unused.
- Avoid accepting files from untrusted devices.
The findings highlight broader lessons for multi-protocol software—particularly tools bridging mobile and desktop ecosystems. As Tamari noted, “Attackers will always seek gaps in logic. Defenders must think like them.”
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, & X to Get Instant Updates!



.png
)
